🩸 Tissues & Blood
CN-1102: Body Tissues & Blood
- 4 Types of Tissues (Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve)
- Blood Composition (Plasma, RBC, WBC, Platelets)
- Functions of Blood Cells & Clinical Significance

"E C M N Every Classroom Must be Neat"
Epithelial · Connective · Muscle · Nerve
🔴 EPITHELIAL TISSUE
Function: Covering, lining, glandular secretion
Types:
- Simple (single layer)
- Stratified (multiple layers)
- Glandular (forms glands)
Location: Skin, mucous membranes, inner organ linings
🟢 CONNECTIVE TISSUE
Function: Support, bind, protect, transport
Subtypes:
- Proper (areolar, adipose, dense)
- Supporting (cartilage, bone)
- Fluid (blood, lymph)
Location: Everywhere! Most abundant tissue
🔵 MUSCLE TISSUE
Function: Movement, contraction
Types:
- Skeletal (voluntary, striated)
- Cardiac (involuntary, heart)
- Smooth (involuntary, organs)
Location: Muscles, heart, blood vessels, intestines
🟡 NERVE TISSUE
Function: Communication, control, coordination
Cells:
- Neurons (conduct impulses)
- Neuroglia (support cells)
Location: Brain, spinal cord, nerves
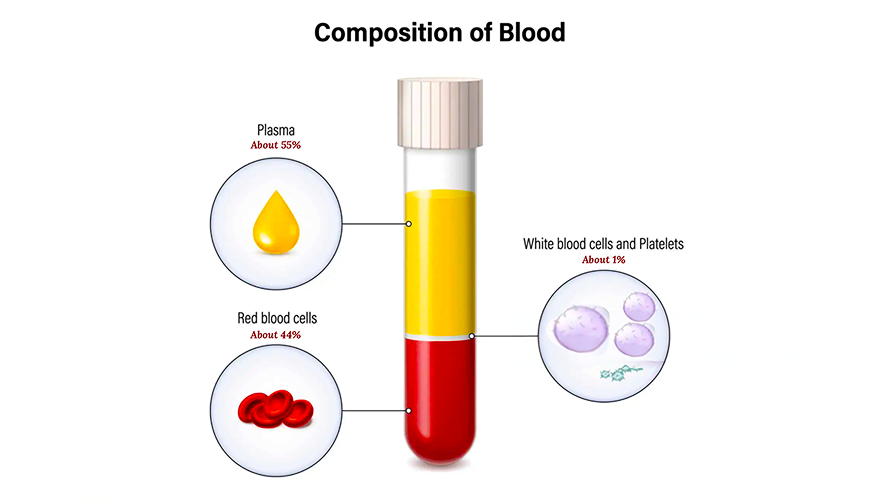
🧪 TOTAL BLOOD VOLUME = 4-6 LITRES (8% of body weight)
"55 & 45"
Plasma = 55% | Formed Elements = 45%
💧 PLASMA (55%)
91% Water
9% Solutes:
- Proteins (albumin, globulin, fibrinogen)
- Electrolytes (Na+, K+, Cl-)
- Nutrients (glucose, amino acids)
- Waste (urea, creatinine)
- Hormones
🩸 FORMED ELEMENTS (45%)
Three main components:
- Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Platelets (Thrombocytes)
🔴 NORMAL VALUES & FUNCTION
Structure:
- Biconcave disc shape (increases surface area)
- No nucleus (cannot divide)
- Contains hemoglobin (Hb)
- Lifespan: 120 days
Functions:
- Transport O₂ from lungs to tissues
- Transport CO₂ from tissues to lungs (70%)
- Buffer system (maintain pH)
"Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas"
Neutrophils > Lymphocytes > Monocytes > Eosinophils > Basophils
(Order of abundance in blood)
⚪ NORMAL TOTAL WBC COUNT = 4,000 - 11,000/μL
1. NEUTROPHILS (50-70%)
Type: Granulocyte
Function: Phagocytosis of bacteria
Key Feature: Multi-lobed nucleus (3-5 lobes)
Clinical: ↑ in bacterial infections
2. LYMPHOCYTES (25-35%)
Type: Agranulocyte
Functions:
- T-cells: Cell-mediated immunity
- B-cells: Produce antibodies
Clinical: ↑ in viral infections
3. MONOCYTES (3-8%)
Type: Agranulocyte
Function: Phagocytosis & antigen presentation
Key Feature: Largest WBC, kidney-shaped nucleus
Clinical: ↑ in chronic infections
4. EOSINOPHILS (1-4%)
Type: Granulocyte
Function: Allergic reactions & parasite destruction
Key Feature: Red-orange granules
Clinical: ↑ in allergies, asthma, worm infestations
5. BASOPHILS (0.5-1%)
Type: Granulocyte
Function: Release histamine in allergic reactions
Key Feature: Least common, dark granules
Clinical: ↑ in hypersensitivity reactions
🔹 NORMAL COUNT = 150,000 - 450,000/μL
< 50,000 = Dangerous bleeding risk
> 1,000,000 = High clot risk
Functions:
- Clot formation: Form plug to stop bleeding
- Vascular spasm: Vasoconstriction
- Coagulation: Release clotting factors
"T R A N S P O R T"
T - Transport (O₂, CO₂, nutrients, hormones)
R - Regulation (pH, temperature, fluid balance)
A - Protection (clotting, WBCs fight infection)
N - Nutrient distribution
S - Security (immune defense)
P - pH balance
O - Osmotic pressure control
R - Remove waste
T - Temperature regulation
1. The four basic types of body tissues are __________, __________, __________, and __________.
2. Normal hemoglobin value for adult females is _______ g/dL, and for males is _______ g/dL.
3. Which WBC is MOST abundant in blood and fights bacterial infections?
B) Eosinophils
C) Neutrophils ⭐CORRECT
D) Monocytes
4. Which of the following is NOT a function of blood?
B) Hormone production ⭐CORRECT ANSWER
C) Temperature regulation
D) Clot formation
5. Explain the difference between RBCs and WBCs in terms of structure, function, and normal count.
6. A 28-year-old woman comes to your clinic in rural Uganda with complaints of fatigue, dizziness, and pale conjunctiva. You suspect anemia.
b) What physical signs would you check? (2 marks)
c) Explain the role of hemoglobin in her condition (3 marks)
d) Name two common causes of anemia in Uganda (2 marks)
7. Match the WBC type with its function:
B. Lymphocytes 2. Phagocytize bacteria
C. Eosinophils 3. Immune response
D. Monocytes 4. Chronic infection defense
E. Basophils 5. Histamine release
