Table of Contents
ToggleMANAGING BUSINESS RISKS
Risk refers to the probability that an event will occur.
It can also be understood as an uncertain event or set of events that, should it occur, may affect the achievement of the business.
Risk Management refers to the systematic application of procedures to the tasks of identifying, assessing, and controlling risks through the implementation of planned risk responses.
Business Risk Management is a subset of risk management that focuses on the risks of businesses’ operations, systems, and processes.
It consists of a combination of:
- The probability of a perceived threat or opportunity occurring
- The magnitude of its impact on the objectives of the business
Threat refers to an uncertain event that could have a negative impact on the objectives of the business.
Opportunity refers to an uncertain event that could have a positive impact on the objectives of the business.

Types of Risks:
a) Systematic Risks:
- Also known as external risks, these influence a number of assets and are often called market risks.
- They affect nearly every business, including interest rates, inflation, and environmental regulations.
- They are not under the direct control of management.
b) Unsystematic Risks:
- These affect a small number of assets and are sometimes called unique or specific risks.
- Examples include staff strikes, location factors, unavailability of raw materials, poor service delivery, and poor controls.
- They are within the direct control of management.
c) Low Risks:
- These are minimal risks that do not yield significant benefits or cause substantial damage.
- Such risks tend to discourage entrepreneurs from investing resources due to their low return on investment.
d) Moderate (Calculated) Risks:
- These risks can be forecasted, calculated, and managed by entrepreneurs.
- They are not always desirable but offer a potentially higher benefit with a manageable loss propensity.
- Examples include fire, theft, and burglary.
e) High Risks:
- These risks have a high chance of occurrence, and if they occur, one has little or no control over them.
- Examples include smuggling and dodging government taxes.
Forms of Risks
Financial Risks:
- These risks may result in financial loss or gain.
- Most businesses take risks with their financial assets regularly.
- Choosing the wrong supplier or distributor can lead to problems if supplies don’t arrive on time or the distributor goes out of business.
- Relationships with customers can also be risky, especially if a company relies on customers carelessly.
Employee Risk
- While these may include physical risks, business risk management should consider preventing theft, fraud, and other crimes by employees.
- Another risk caused by employees is human error, where even a tiny mistake in data entry or the manufacturing process can have significant consequences.
- Risk management should include a quality control process for data input and production to minimize the impact of employee error.

Risk Management
Risk management refers to the identification, analysis, assessment, control, and avoidance, minimization, or elimination of unacceptable risks.
An organization may use risk assumptions, risk avoidance, risk retention, risk transfer, or any other strategy or combination of strategies to manage future events effectively.
Techniques or Methods of Managing Risks in Business:
- Risk Transfer/Sharing: An entrepreneur shifts the risk to another party to suffer the loss if it happens. For example, insurance companies suffer losses whenever they occur.
- Risk Avoidance: An entrepreneur takes measures to prevent the risk from occurring. For example, establishing quality assurance measures to avoid producing poor-quality products, paying taxes promptly, etc.
- Risk Reduction/Mitigation: The entrepreneur accepts that a risk or loss may happen but devises means to minimize its impact. For example, installing strong steel bars across a taxi or vehicle to reduce the impact of an accident.
- Risk Retention: Involves accepting the risk and budgeting for it when it occurs. This method is appropriate for small possible losses, especially when the cost of insuring the asset is greater than the possible loss.
- Risk Exploitation: This works for risks that have benefits for the business. The entrepreneur is encouraged to use the chance to make more profits, sales, among others.
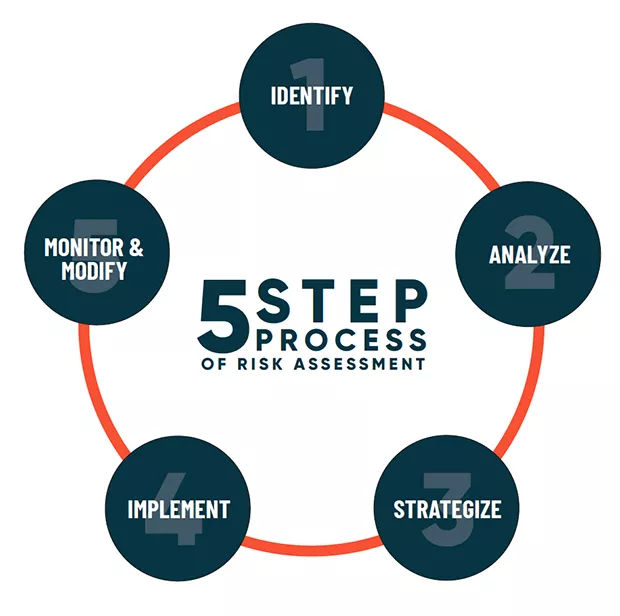
The Risk Management Process
Risk managers follow a five-step approach;
- Identify the risks: This involves identifying all potential risks that could impact the business, considering all aspects of the organization.
- Assess the risks: This step involves evaluating the likelihood of each risk occurring and the potential impact it could have on the business.
- Develop risk responses: Once the risks have been assessed, the risk manager develops strategies to address each risk. These strategies may include risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, or risk acceptance.
- Implement the risk responses: The risk manager then puts the chosen risk responses into action, ensuring that appropriate measures are taken to manage each risk effectively.
- Monitor the risks: Finally, the risk manager continuously monitors the risks and the effectiveness of the risk responses. This involves tracking key risk indicators and making adjustments to the risk management plan as needed.
Importance of Business Risk Management:
1. Business sustainability: Risk management helps businesses prepare for and respond to emergencies, ensuring that they can continue operating even in the face of unexpected events.
2. Confidence among entrepreneurs: Effective risk management instills confidence among entrepreneurs, particularly in areas such as goods in transit, transportation, freight, and shipping.
3. Cultivates faithfulness: Risk management fosters trust and loyalty among traders, as they are united by a common goal of managing risks effectively.
4. Employment opportunities: Risk management creates employment opportunities for professionals such as accountants, lawyers, underwriters, and others.
5. Proper planning and documentation: Risk management encourages proper planning and documentation of assets and their associated risks.
6. Facilitates trade: Risk management, particularly in the context of international trade, plays a crucial role in ensuring that goods are insured before transit.
7. Promotes professionalism: Effective risk management cultivates professionalism in business, as entrepreneurs adopt proactive approaches to managing risks.
8. Protects against risks: Risk management safeguards businesses against potential losses by implementing appropriate risk responses.
9. Enhances business continuity: By transferring risks to third parties through insurance, risk management helps ensure business continuity.
10. Prioritization and decision-making: Risk management aids in setting priorities by guiding the allocation of scarce resources and capital. This helps in effective decision-making and planning.

Reasons for Poor Risk Management by Ugandan Entrepreneurs:
- Ignorance: Many entrepreneurs lack awareness of the importance of risk management and its benefits.
- Limited finances: Some organizations may have limited financial resources to invest in comprehensive risk management strategies.
- Inadequate government policies: The government’s policies regarding insurance enforcement may not be robust enough to encourage effective risk management practices.
- Negligence: Many business practitioners may neglect risk management due to a lack of understanding or prioritization.
- Traditional beliefs: Traditional norms, values, and cultures may influence entrepreneurs to rely on traditional risk management methods rather than modern approaches.
- Limited insurance firms: The number of insurance firms operating in Uganda may be limited, reducing the accessibility and affordability of insurance products.
- Excessive compensation procedures: Complex and time-consuming compensation procedures may discourage entrepreneurs from insuring their assets.
- Negative perception: The general public may have negative perceptions about risk management procedures, hindering its adoption.

