Table of Contents
ToggleWASTE MANAGEMENT
Waste is any material – solid, liquid, or gas – that is unwanted and/or unvalued, and has been discarded or discharged by its owner.
Healthcare Waste refers to all types of waste from all health care activities; waste generated by the health care facilities, research facilities and laboratories.
Healthcare waste is also known as biomedical waste, infectious waste or medical waste. Healthcare waste is also known as biomedical waste, infectious waste or medical waste.
The large volumes of health care waste if not managed properly can lead to a global hazard. This could not only lead to the spread of highly contagious diseases but the hazardous chemical waste produced by the use of items can cause considerable damage to the ecosystem and the environment.
Classification of wastes
Classification according to matter state (properties)
- Solid waste includes common household waste (including kitchen and garden waste), commercial and industrial waste, sewage sludge, construction and demolition waste, waste from agriculture and food processing, and mine and quarry tailings.
- Liquid waste includes domestic waste water (liquid kitchen, laundry, and bathroom waste), storm water, used oil, and waste from industrial processes.
- Gaseous waste comprises gasses and small particles emitted from open fires, incinerators, and vehicles, or produced by agricultural and industrial processes.
Classification of wastes- general according to their degradability
- Bio-degradable : Whether they can be degraded by physical or biological means (paper, wood, fruits and others)
- Non-biodegradable; These cannot be degraded easily by physical or biological means (plastics, bottles, old machines, cans, Styrofoam containers and others)
Classification according to their Effects on Human Health and the Environment
- Hazardous wastes: Substances unsafe to use commercially, industrially, agriculturally, or economically that are shipped, transported to or brought from the country of origin for dumping or disposal in, or in transit through, any part of the world.
- Non-hazardous: Substances safe to use commercially, industrially, agriculturally, or economically that are shipped, transported to or brought from the country of origin for dumping or disposal in, or in transit through, any part of the world.
Type of Waste | Percentage |
Non-infectious Waste | 80% |
Pathological and Infectious Waste | 15% |
Sharps Waste | 1% |
Chemical or Pharmaceutical Waste | 3% |
Pressurized Cylinders, Broken Thermometers | Less than 1% |
SOURCES OF HEALTHCARE WASTE
Major Sources | Minor Sources | ||
Hospitals | Clinics | Dental Clinics | Physician’s Office |
Laboratories | Research Centers | Home Health-care | Nursing Homes |
Animal Research | Blood Banks | Acupuncturists | Psychiatric Clinics |
Nursing Homes | Mortuaries | Cosmetic Piercing and Tattooing | Funeral Services |
Autopsy Centers | Paramedic Services | Institutions for Disabled Persons |
Sources of health care waste
Major sources
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Laboratories
- Research centers
- Animal Research
- Blood banks
- Nursing Homes
- Mortuaries
- Autopsy centers
Minor sources
- Dental clinics
- Physician’s office
- Home health-care
- Nursing homes
- Acupuncturists
- Psychiatric clinics
- Cosmetic piercing and tattooing
- Funeral services
- Paramedic services
- Institutions for disabled persons
WASTE MANAGEMENT HIERARCHY
Waste management hierarchy is a structured approach to prioritize and manage waste by minimizing its environmental impact.
It consists of several key steps, listed in descending order of priority

Waste management hierarchy is defined as the order of preference for action to reduce and manage waste and is usually presented diagrammatically in the form of a pyramid.
The aim of waste hierarchy is to extract the maximum practical benefits from products and to generate a minimum amount of waste.
- Prevention/avoidance: This concept focuses on the measures to be taken so as not to create any type of wastes in the first place e.g. avoiding to eat from the ward. This is given the top priority in the waste management program.
- Reduction of Wastes/minimization: According to this concept, the health care setting should reduce or minimize the amount of waste or the toxicity of wastes e.g. avoiding to use gloves in procedures that don’t necessary need one to use gloves and companies should take action to make changes in the type of materials that are being used for the production of the specific products, so as to ensure that the by-products are of the least toxicity.
- Reuse: Reuse is another effective Solid waste management strategy, in which the waste is not allowed to enter into the disposal system. The wastes are collected in the middle of the production phase and are again fed along with the source to aid in the production process e.g. Autoclaving metal instruments or sterilization of medical equipment.
- Recycle: In the recycling strategy, the waste materials are implemented in the production of a new product. In this process, the waste materials of various forms are collected and then processed. Post processing, they enter into the production lines to give rise to new products. This process prevents pollution and saves energy.
- Energy Recovery: The energy recovery process is also called waste to energy conversion. In this process; the wastes that cannot be recycled are being converted into usable forms of energy such as heat, light and electricity etc. This helps in the saving of various natural resources. Various processes such as combustion, anaerobic digestion, landfill gas recovery, pyrolization and gasification are being implemented to carry out the conversion process.
- Treatment and Disposal: The disposal process holds the last position in the waste management hierarchy. Landfills are the common form of waste disposal.
Waste Management Steps/Waste Stream
Waste stream refers to the systemic steps followed in health care solid waste management from its generation to its final disposal.
1. Generation:
Non-Hazardous waste/General waste: Office, Kitchen, Administrative, Municipal/Public Areas, Hostels, Store Authorities, Restrooms, etc.
Hazardous (Infectious & toxic waste): Wards, Treatment Rooms, Dressing Rooms, OT ICU, Labour Room, Laboratory, Dialysis Room, CT Scan, Radio-imaging, etc.
WHO Classification | Description of Waste | Examples |
1. General Waste | No risk to human health | Office paper, wrappers, kitchen waste, general sweeping, etc. |
2. Pathological Waste | Human tissue or fluid | Body parts, blood, body fluids, etc. |
3. Sharps | Sharp waste | Needles, scalpels, knives, blades, etc. |
4. Infectious Waste | May transmit bacterial, viral, or parasitic diseases | Laboratory culture, tissues (swabs), bandages, etc. |
5. Chemical Waste | Chemical waste | Laboratory reagents, disinfectants, film developer, etc. |
6. Radioactive Waste | Radioactive waste | Unused liquid from radiotherapy or lab research, contaminated glassware, etc. |
7. Pharmaceutical Waste | Expired or outdated drugs/chemicals | Expired medications and chemicals |
8. Pressurized Container | Waste from pressurized containers | Gas cylinders, aerosol cans, etc. |
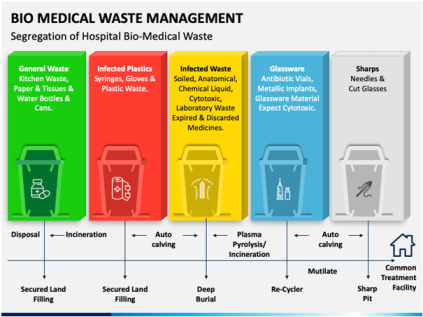
2. Segregation:
Waste segregation is the practice of separating different types of waste at the source to ensure proper handling and disposal.
Done at the point of waste generation and placed in separate colored bags. Color coding may vary by nation or hospital.

|
Type of Waste Category |
Examples |
Type of Bin |
|
Infectious and Highly Infectious Waste |
|
RED BIN |
|
Non-Infectious Waste |
|
BLACK BIN |
|
Pharmaceutical and Chemical Waste |
|
BROWN BIN |
3. Collection or Handling of Waste:
Waste collection is the systematic gathering of various types of medical waste.
Handling concerns the collection, weighing and storing conditions.
Trained sanitation personnel, often supervised by nursing staff and sanitation supervisors, manage this process. They ensure waste is correctly segregated at the point of generation into appropriate color-coded bins.
Proper documentation is maintained in a register to track waste quantity and type. Regular cleaning and disinfection of garbage bins are essential for maintaining hygiene.
The waste collection process is conducted in compliance with safety regulations and guidelines, ensuring the protection of personnel and the environment. This systematic collection is a crucial step in the safe and efficient management of medical waste.
Waste should not be stored in the generation area for more than 4-6 hours. Waste collected in various areas is prepared for transport or disposal/treatment.
4. Transportation:
Hospitals should have a separate corridor and lift dedicated to carrying and transporting waste.
General waste is deposited at municipal dumps.
- Waste designated for autoclaving and incineration is disposed of at a separate site for external transport (using distinct colored plastic bags).
- Transportation is carried out in sealed containers to prevent leakage.
5. Treatment & Disposal:
Waste disposal in hospitals is the final phase in the systematic management of medical waste.
It involves the safe and environmentally responsible removal or destruction of waste, ensuring it no longer poses health risks to patients, staff, and the community.
- General waste is dumped at municipal dumping sites.
- The sanitation officer is responsible for coordinating with municipal authorities for proper disposal.
- Use of labels/symbols helps in identifying waste for treatment (e.g., Risk of Corrosion, Danger of Infection, Toxic Hazards, Glass Hazards, Radioactive Materials, etc.).
TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL TECHNIQUE FOR HEALTH CARE WASTE
- Incineration
- Chemical disinfection
- Wet & dry thermal treatment (Autoclave)
- Microwave irradiation
- Land disposal
- Inertization
Technique | Description |
Incineration | – High temperature dry oxidation process of over 800 °C. – Reduces organic and combustible waste to inorganic and incombustible waste – Used for most hazardous waste and waste that can’t be recycled – Results in significant reduction of waste volume and weight |
Disinfection
| – Kills or inactivates pathogens contained in waste – Suitable for liquid waste like urine, blood, stool, and hospital sewage |
| – Wet Thermal Treatment: Steam autoclave sterilization process, and any waste contaminated with microorganisms. – Dry Thermal Treatment: Non-burn, dry thermal disinfection process suitable for infectious waste and sharps, not to be used for pathological, cytotoxic, or radioactive waste |
Microwave Irradiation | – Most organisms destroyed by microwaves of specific frequency and wavelength – Efficiency checked through bacteriological and virological tests |
Land Disposal Burial | – Used when hazardous healthcare waste cannot be treated or disposed elsewhere – Investigate more suitable treatment methods – May include land open dumps and sanitary landfills |
Inertization OR Encapsulation | – Mixing waste with cement and other substances before disposal – Inhibits waste from migrating into surface and groundwater – Mixture proportions: 65% pharmaceutical waste, 15% lime, 15% cement, 5% water |