Table of Contents
ToggleAndrogens
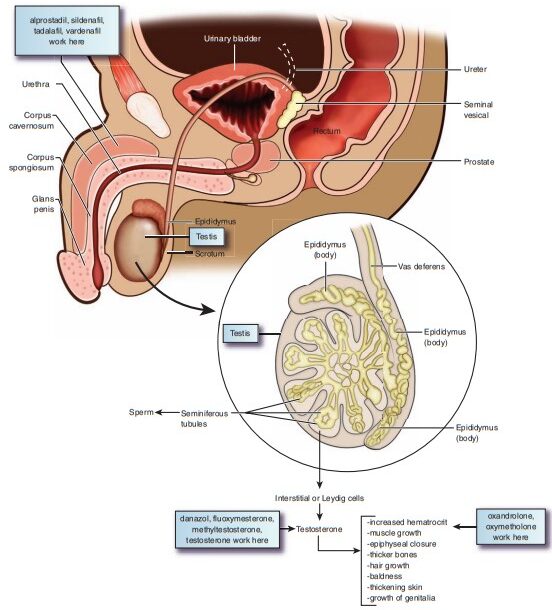
Androgens are male sex hormones
Androgens include Testosterone, which is produced in the testes, and the Androgens, which are produced in the Adrenal glands.
Androgens are chiefly produced in the testes and small amounts in adrenal cortex. In female, small amounts are produced in the ovary and adrenal cortex.
Testosterone is the most important natural androgen and in adult male, 8-10mg is produced daily. Its secretion is regulated by gonadotropins and gonadotrophic releasing Hormone (GnRH). Inadequate production of androgens is due to pituitary malfunction or atrophy, injury to or removal of testicles. Androgens stimulate the development of male characteristics.
Naturally occurring androgens hormones are;
- Testosterone, the principal androgenic hormone produced by the leydig cells of the testes.
- Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) produced by adrenal cortex.
Common Terms
Anabolic steroids: androgens developed with more anabolic or protein-building effects than androgenic effects.
Androgenic effects: effects associated with development of male sexual characteristics and secondary characteristics (e.g., deepening of voice, hair distribution, genital development, acne)
Androgens: male sex hormones, primarily testosterone; produced in the testes and adrenal glands
Hirsutism: hair distribution associated with male secondary sex characteristics (e.g., increased hair on trunk, arms, legs, face)
Hypogonadism: underdevelopment of the gonads (testes in the male)
Penile Erectile Dysfunction: condition in which the corpus cavernosum does not fill with blood to allow for penile erection; can be related to aging or to neurological or vascular conditions
Examples of Androgens
| Drug Name | Usual Dosage | Usual Indications |
|---|---|---|
| danazol (Danocrine) | 100–600 mg/d PO, depending on use and response | Prevent ovulation for treatment of endometriosis; prevention of hereditary angioedema |
| fluoxymesterone (Androxy) | 5–20 mg/d PO for replacement therapy; 10–40 mg/d PO for certain breast cancers | Treatment of delayed puberty in male patients and certain breast cancers in postmenopausal women |
| testosterone (Androderm, Depo-testosterone) | 50–400 mg IM every 2–4 weeks, dose varies with preparation (check more below) | Replacement therapy in hypogonadism (check more below) |
| methyltestosterone (Testred, Virilon) | Males: 10–50 mg/d PO Females: 50–200 mg/d PO | Replacement therapy in hypogonadism; treatment of delayed puberty in male patients and certain breast cancers in postmenopausal women |
TESTOSTERONE (depo-testerone, androderm)
Classification:
Therapeutic: Hormone
Pharmacological: Androgen
Pregnancy; Category-x
Schedule: III controlled substance.
Effects of Testosterones.
Anabolic Effects (Growth and Metabolic Functions)
- Maintains bone density.
- Regulates fat distribution.
- Helps in Red Blood Cell production.
- Supports muscle growth, strength and body mass.
- Speeds up recovery from injury.
- They act to increase the retention of nitrogen, sodium, potassium, and phosphorus.
- They decrease the urinary excretion of calcium.
- Testosterones increase protein anabolism and
decrease protein catabolism (breakdown).
Androgenic Effects ( Sexual Characteristics and Functions)
- Enhances sex drive and libido.
- Increases aggression.
- Acne.
- Beard and body hair.
- Male pattern boldness.
- Development and maintenance of male sex organs.
- Spermatogenesis.
- Increased size of the prostate.
Control of Testosterone Secretion.
Hypothalamus releases GnRH, which stimulates the Anterior Pituitary gland to secrete FSH an LH which in turn stimulate the Leydig cells to secrete testosterone. High levels of serum testosterone exerts a negative feedback i.e.
- APG suppresses secretion of LH.
- Hypothalamus suppresses the GnRH.
Indications of Testosterone.
- Hypogonadism and impotence in males due to testicular/pituitary/hypothalamic deficiency.
- Testosterone deficiency .
- Breast cancer treatment in post menopausal women, who cant be operated.
- Treatment of delayed male puberty.
- Prevention of postpartum breast engorgement.
- Illegally, sportsmen often use anabolic steroids for promoting their musculature and sporting abilities.
- Blockage of follicle-stimulating hormone and luteinizing
response hormone release in women to prevent ovulation for
treatment of endometriosis. - Prevention of hereditary angioedema
Contraindications of Testosterone.
- Allergy to androgens or other ingredients in the drug. Prevent hypersensitivity reactions.
- Pregnancy, lactation. Potential adverse effects on the neonate. It is not clear whether androgens enter breast milk.
- Presence or history of prostate or breast cancer . Aggravated by the testosterone effects of the drug.
- Liver dysfunction, Cardiovascular disease. Can be exacerbated by the effects of the hormones.
- Topical forms of testosterone have a Black Box Warning alerting user to the risk of virilization (Female develops male characteristics) in children who come in contact with the drug.
- Danazol has Black Box warning regarding the risk of thromboembolic events, fetal abnormalities, hepatitis, and intracranial hypertension.
- For use with caution in patients with Diabetes Mellitus, BPH and Sleep apnea.
Side Effects and Adverse Effects of Testosterone
In men,
- Administration of an androgen may result in breast enlargement
- (gynecomastia),
- testicular atrophy,
- inhibition of testicular function,
- impotence,
- enlargement of the penis,
- nausea and vomiting,
- jaundice,
- headache,
- anxiety,
- male pattern baldness,
- acne and depression,
- fatigue,
- abdominal cramps,
- confusion,
- deepening of the voice,
- edema,
- drug-induced hepatitis,
- gingivitis.
- hirsutism (increased hair distribution)
In women,
- receiving an androgen preparation for breast carcinoma the most common adverse reactions are;
- amenorrhea and virilization (acquisition of male sexual characteristics such as changes in body and facial hair, a deepening voice, acne, menstrual irregularities and enlargement of the clitoris).
Drug Interactions
May increase action of warfarin (anti-coagulants), oral hypoglycemic agents and insulin.
Concurrent use with corticosteroids may increase the risk of edema formation.
Nursing intervention/ involvement:
- If the androgen is to be administered as a buccal tablet, the nurse demonstrates the placement of the tablet and warns the patient not to swallow the tablet but to allow it to dissolve in the mouth.
- The nurse reminds the patient not to smoke or drink water until the tablets is dissolved. Oral and parenteral androgens are often taken or given by injection outpatient basis.
- When given by injection, the injection is administered deep I.M into the gluteus muscle.
- Oral testosterone is given with or before meal to decrease gastric upset.
- When testosterone Trans -dermal system testostederm is prescribed, the nurse places the system on clean, dry scrotal skin. Optimal skin contact of the Trans dermal system is achieved by shaving scrotal hair before placing the system.
- Monitor fluid input and output
- Weigh the patient twice a week
- Assess for edema and report
- Monitor secondary sexual characteristics in men
- Monitor menstrual irregularities, deepening of the voice, in females.
- Monitor Hemoglobin and hematocrit periodically
- Monitor urine and serum calcium levels
Patient/family teaching:
- Advise the patient to report signs of priapism, difficulty in urinating, hypercalcemia, edema, unexpected weight gain, swelling of the fee, hepatitis, unusual bleeding.
- Explain rationale for prohibiting use of testosterone for increasing athletic performance
- Notify Doctor of pregnancy.
- DM patients to monitor blood sugar.
- Regular follow up, laboratory tests and physical examination
- For ladies to notify doctor if signs of body hair distribution, deepening of voice menstrual irregularities occur.
ANABOLIC STEROIDS
These are agents that are not easily converted to the potent androgen 5 alpha o-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) hence their effects on sex are less but their anabolic effect are high.
Drugs commonly used by athletes include; nandolone, stanozolol, and mithenelone. All of this drugs are regulated as controlled substances, making their use by athletes illegal.
Clinical uses/indications of anabolic steroids.
- Osteoporosis
- Appetite improves and there is a feeling of well being.
- To counteract osteoporosis seen in chronic glucocorticosteroid therapy.
- Stimulates linear growth in prepubertal boys (height).
- Used in renal diseases.
NANDROLONE
This is another steroid naturally produced by body, it is often synthesized and sold under the trade names Deca- Durabolin and Durbolin.
Professional athletes like Berry Bonds and Roger Clemens alleged used nandrolone to illegally enhance their performance.
STANOZOLOL:
This synthetic steroid goes by the brand name Winstrol. This steroid is unusual in that it can be taken orally. Base ball players like Rafael. Palmeiro have tested positive for illegal use of stanozolol and strength athletes often use it illegally to quickly get stronger.
OXANDROLONE:
Is a synthetic steroid retailed as the drug Anavar, which is approved for use in osteoporosis. Body builders use this steroid illegally to create greater muscle.
Contraindications:
- Male patients with cancer of the breast or with known or suspected carcinoma of the prostate.
- Carcinoma of the breast in female with hypercalcemia; androgenic anabolic steroids may stimulate osteolytic resorption of bones.
- Pregnant because of masculinization of the fetus.
- Nephrosis or the nephritic phase of nephritis.
Side effects of anabolic steroids:
- Severe acne, oily skin and hair – hair loss.(virilization)
- Liver diseases resulting into complications such as heart attack and stroke.
- Altered mood, irritability, increased aggression, depression or suicidal tendencies.
- Alteration in cholesterol and other blood lipids
- High blood pressure
- Gynecomastia- abnormal development of mammary glands in men causing breast enlargement.
- Shrinking of testicles.
- Azoospermia (absence of sperm in semen)
- Menstrual irregularities in women
- Infertility
- Excess facial or body hair, deeper voice in women.
- Stunted growth and heat in teens
risk of viral or bacterial un function due to unsterile injections - Edema
- Prostate cancer
- Injury from skin-to-skin transfer of topical testosterone
Drug interactions:
- Anti-coagulants. Anabolic steroids may increase sensitivity to oral anti-coagulants. Dosage of the anti-coagulants may have to be decreased in order to maintain the prothrombin time at the desired therapeutic level. Patients receiving oral anti-coagulant therapy require close monitoring, especially when anabolic steroids are started or stopped.
Patient’s information:
- The physician should instruct patients to report any of the following effects of androgenic anabolic steroids,
- hoarseness,
- acne,
- changes in menstrual periods,
- more hair on the face,
- Nausea and vomiting,
- changes in skin colour or ankle swelling.
ANTI ANDROGENS
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens from mediating their biological effects in the body.
They act by blocking the androgen receptor and/or inhibiting or suppressing androgen production. They include:
- Danzol
- Finasteride
- Spironolactone
- Flutamide
- Cyproterone
- Ketoconazote
- Bicalutamide and Nilutamide
Finasteride
Available preparations: Tablets 5mg
Available brands: Finest, Proscar
The androgen hormone inhibitor finasteride is a synthetic drug that inhibits the conversion of testosterone into the androgen 5 alpha o-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). The development of the prostate glands is dependent on DHT. The lowering of serum levels of DHT reduces the effect of this hormone on the prostate gland, resulting in decrease in the size of the gland and this synthesis associated with prostate gland enlargement.
Indications;
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia(BPH)
- Androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness) in men only
Mechanism of action:
It inhibits the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase which is responsible for converting testosterone to its potent metabolite 5-alpha dihydrotestosterone in prostate, liver and skin since 5-alphs dihydrotestosterone is partially responsible for prostatic hyperpiesia and hair loss.
Dose:
- In BPH 5mg o.d
- Alopecia 1mg/day for 3 months or more. Available in tablets of mg and 5mg
Side effects;
- Decreased libido
- Decreased volume of ejaculation
- Erectile dysfunction/impotence
- Breast tenderness and enlargement
- Testicular pain
Contraindications/precautions;
- Known hypersensitivity to finasteride
- Use with caution on hepatic impairment
Nursing implications:
- Assess for symptoms of prostatic hyperplasia e.g. feeling of incomplete bladder emptying, interruption of the urinary stream
- Digital rectal examination should be done before and periodically during BPH therapy.
- Laboratory tests of prostate specific antigen cancer concentration which is used to screen for cancer of prostate.
- Take this drug without regard to meals.
Patient/ family teaching;
- Finasteride possesses risk to male fetus; tell males not to have sex with pregnant women to avoid the risk of absorption
- Inform the Doctor immediately if sexual partner is or may become pregnant because additional measures such as discontinuing the drug or use of condom may be necessary.

I’m extremely impressed with your writing skills
and also with the layout on your weblog. Ιs this a paid theme or did you customize it yoᥙrself?
Anyway keep up thе nice quality wrіting, іt is rare to sеe a
great blog like this one today.