-

Uterus, Fallopian tubes and Ovaries
THE NON-PREGNANT UTERUS The uterus is a hollow muscular organ of the female reproductive system where offspring gestate.A pear-shaped organ, the uterus lies posterior-superior to the bladder and anterior to the rectum in the female pelvis. It consists of the fundus (top), body (middle), and cervix (lower). The uterus is composed of the endometrium (inner…
-
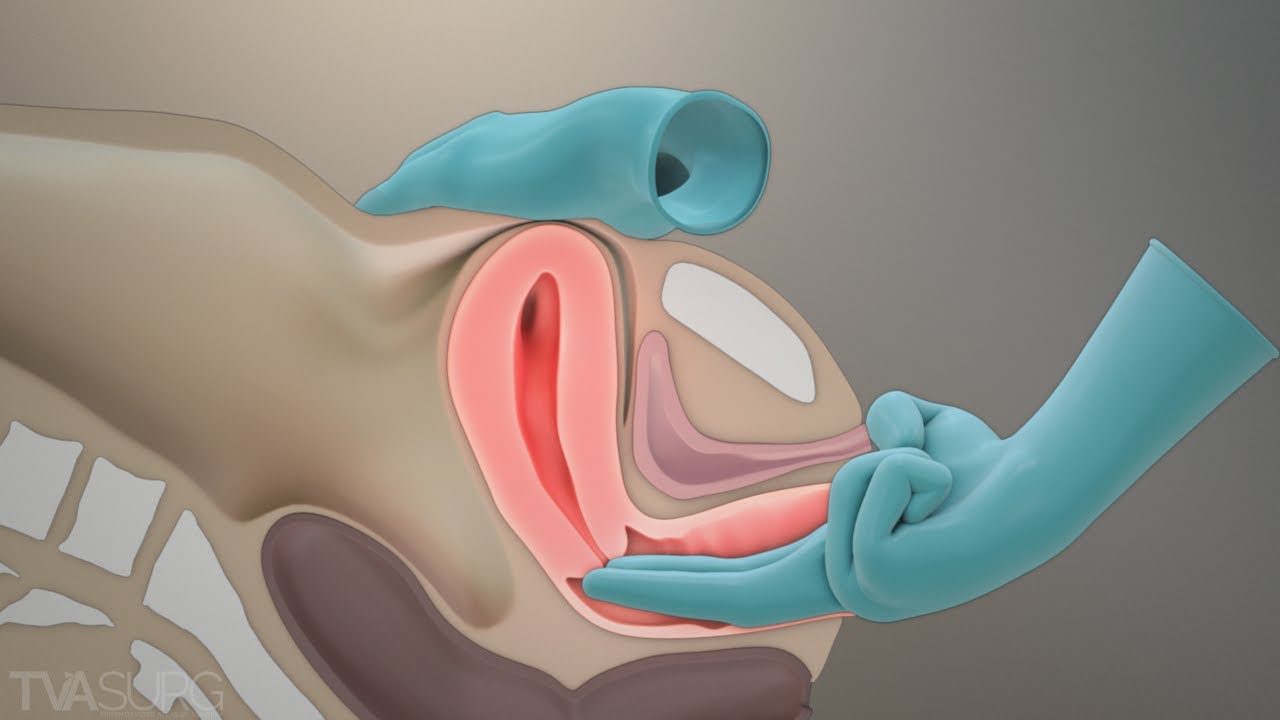
PELVIC ASSESSMENT
Pelvic Assessment During Labor A mother who is pregnant for the second time (Gravida 2, Para 1+0) reports with labor pains. Your task is to perform an internal pelvic assessment and create a plan for the mode of delivery. Pelvic Assessment Pelvic assessment is a process to determine whether a mother’s pelvis is wide enough…
-
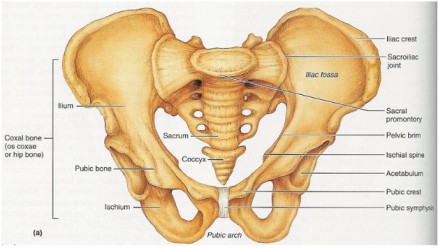
Female Pelvis
Introduction To Obstetric Anatomy This field focuses on the anatomical structures involved in pregnancy, labor, and the postpartum period. Key areas of study include the pelvis, pelvic floor, female reproductive system, female breast, male reproductive system, embryology, fetal skull, and the female urinary system. Definition of Terms Anatomy: The study of the structures of the…
-

Post-Operative Nursing Care
Post-Operative Nursing Care Post-operative nursing care refers to the specialized care provided to patients following a surgical procedure. This care focuses on monitoring, managing, and supporting the patient’s recovery through a variety of interventions and assessments. Aims or principles of post-operative care Prevent, Recognize, and Treat Complications: Through skillful observation and application of knowledge, proactively…
-
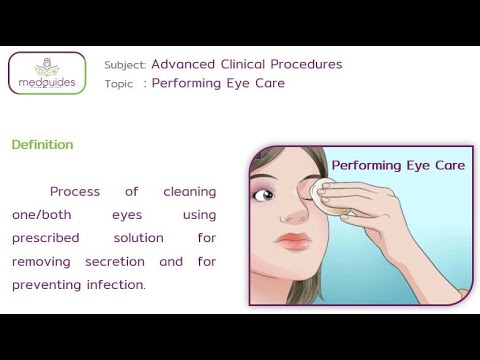
CARE OF THE PATIENT’S EYES
CARE OF THE PATIENT’S EYES. Care of the patient’s eyes includes a range of procedures and practices aimed at maintaining the cleanliness, comfort, and health of the eyes. It Involves: Cleaning of the Eye: This includes removing debris, discharge, and crusting from the eyelids and eyelashes. It’s done gently using sterile wipes or cotton balls…
-
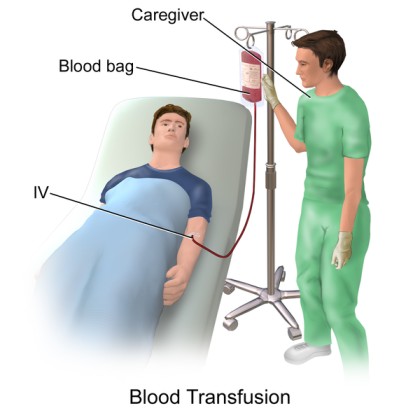
BLOOD TRANSFUSION
BLOOD TRANSFUSION Blood transfusion refers to the intravenous replacement of lost or destroyed blood with compatible human blood. TYPES OF BLOOD PRODUCTS 1. Whole Blood: Whole blood is indicated to the patient experiencing acute massive loss or hypovolemic shock. Whole blood restores volume and raises hemoglobin count and therefore oxygen capacity. Indication: Acute massive blood…
-
INSTIlLING MEDICATION
INSTILLING MEDICATION INTO EAR Requirements Tray Cotton tipped applicators. Cotton balls. Bowl with warm normal saline. Medication bottle with dropper. Receiver. Clean gloves. At the side Screen Vomit bowl Procedure. Step Action Rationale 1 Refer to general rules on nursing procedure and medicine administration. 2 Obtain assistance in case of children or infants. Prevents…
-
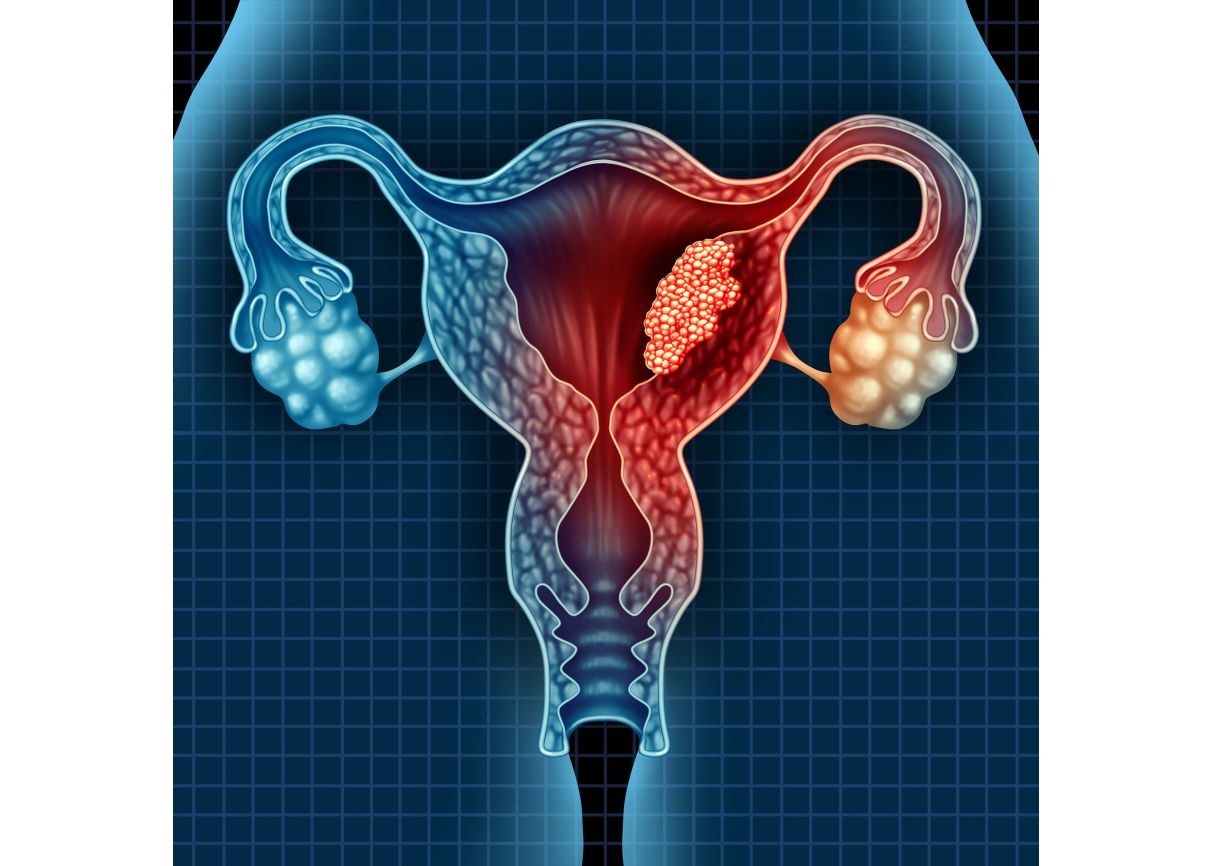
Cancers of Reproductive Health Organs
Breast Cancer Breast cancer occurs when cells in the breast grow and divide uncontrollably, forming a mass of tissue known as a tumour. Breast cancer can invade nearby tissues and travel to other body parts, forming new tumours, a process called metastasis. Clinical Manifestations Early Signs of Breast Cancer Asymptomatic: Sometimes, breast cancer shows…
-
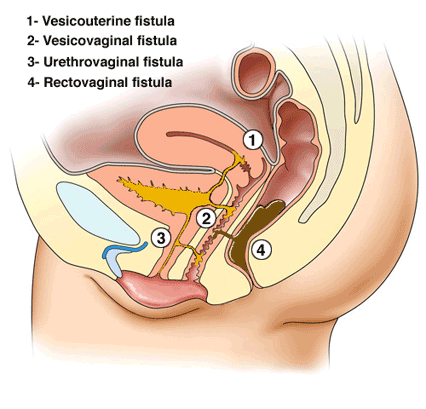
OBSTETRIC/VAGINAL FISTULA
OBSTETRIC/VAGINAL FISTULA Vaginal Fistula is an abnormal communication (opening) of the vagina and the neighbouring -pelvic organs as a result of obstetrical causes e.g. delivery. Urogenital Fistula: Abnormal communication between the urinary (ureters, bladder, urethra) and genital (uterus, cervix, vagina) systems. A fistula is an abnormal communication between two or more epithelial surfaces. Types of…
-

SUPPORT SUPERVISION
SUPPORT SUPERVISION Support supervision is the process of helping, guiding, teaching and learning from staff at their places of work and helping them to improve performance in a joint problem solving manner. Support supervision is a way of helping people learn and grow in their work. It combines two important elements: support and supervision. Support…
