Table of Contents
ToggleBUSINESS IDEA
Business idea is an identified situation that can be changed into a real and profitable activity or business.
It is a concept that can be used for financial gain that is usually centered on a product or service that can be offered for money.
A business idea is a concept that could be used to make money, and an opportunity has proven commercial value.
Coming up with a business idea for start‐up
Every business starts with an idea. That idea is further developed using a five step Process illustrated in the diagram below.

You can decide to take on a business idea because of the following considerations:
- You have a great idea for a small business and you want to learn how to go about its implementation in order to create a successful small business.
- You are already running your own small business and you want to learn about how you could make your business more successful.
Indicators of a viable business Ideas/Opportunities
- Rate of Return on Investment: The business idea should have the potential to yield high profits, motivating entrepreneurs to pursue it.
- Availability of Market: A viable business idea should have a ready market for its products or services.
- Availability of Resources: The necessary resources, such as capital, equipment, and skilled labor, should be available to establish and operate the business.
- Technical Skills: The entrepreneur should possess or have access to the technical skills required to produce the product or deliver the service.
- Legality: The business idea should comply with all applicable laws and regulations. Some ideas are condemned by the laws of the land for instance operating a clinic targeting aborting girls or women is illegal.
Importance of Coming Up with Business Ideas/Opportunities:
- You need an idea for a successful business venture, both to start a business and also to stay competitive afterwards. Sarah wants to start a boutique in her neighborhood. She knows that without a unique business idea, she won’t be able to attract clients and stay competitive in the crowded boutique market.
- They respond to market needs, markets are always composed of customers with different needs to be satisfied. A local farmer notices a growing demand for organic produce in his community. He decides to start an organic farm to meet the needs of health-conscious consumers.
- They respond to natural threats and scarcities that would affect the businesses and communities as a whole for example lack of water, fuel, pollution, pests, diseases etc. A company specializing in water purification systems sees an opportunity in areas affected by water pollution. By providing clean drinking water solutions, they address a critical need while also building a profitable business.
- They also help in responding to changing fashions and requirements. For example, NOKIA responded by changing buttoned and small screened phones to smartphones that support research and other computer support services. In response to the declining popularity of traditional taxis and the rise of ride-sharing apps, a taxi company decided to develop its own mobile app to offer on-demand rides, staying relevant in the evolving transportation industry.
- They help businesses in staying ahead of competition. Innovative business ideas can give businesses a competitive edge and help them differentiate themselves from competitors. A small bakery differentiates itself from larger bakeries by specializing in gluten-free baked goods, attracting health-conscious customers who appreciate the unique offerings.
- It helps in exploiting technology to do better things in an effective and efficient manner. A healthcare startup develops a telemedicine platform that allows patients to consult with doctors remotely.
- Spreading Risk and Allowing for Failure: Generating multiple business ideas allows businesses to spread risk and mitigate the impact of potential failures. A tech company exploring new product ideas invests in multiple projects simultaneously. While some projects may fail, others succeed, allowing the company to spread risk and learn from failures.
- Catering to Specific Groups: Business ideas can be developed to cater to the needs of specific groups, such as the elderly, individuals with disabilities, or niche markets. A clothing brand focuses on adaptive clothing designed for individuals with disabilities. By catering to this specific market segment, they address a need and build a loyal customer base.
Examples of Business Ideas/Opportunities
- − Setting up a grocery
- − Setting up a school, hospital, medical center, clinic.
- − Selling sweet bananas
- − Starting a poultry farm
- − Starting a fumigation service business
- − Opening up a saloon
- − Starting a restaurant
- − Starting up a textile workshop
Sources of Business Ideas/Opportunities:
Entrepreneurs generate business ideas from various sources, and out of the many ideas, they select the most promising business opportunity to pursue. Here are some common sources of business ideas:
- Emerging New Technology and Scientific Knowledge: The development of artificial intelligence (AI) has led to new business ideas in fields such as autonomous vehicles, facial recognition software, and AI-powered customer service chatbots.
- Changes in Consumption Patterns: The growing demand for healthy and organic food products has created opportunities for businesses specializing in these products.
- Trade Fairs, Journals, Press, Magazines: Attending trade fairs and reading industry publications can expose entrepreneurs to new products, trends, and business ideas.
- Social and Economic Trends: The aging population has led to increased demand for products and services tailored to seniors, such as assisted living facilities and home healthcare services.
- Observing the Market Critically: Identifying gaps in the market or unmet customer needs can lead to innovative business ideas. For instance, a lack of convenient and affordable childcare options could inspire an entrepreneur to start a daycare center.
- Market Surveys and Discussions with Entrepreneurs: Conducting market research and engaging in discussions with fellow entrepreneurs can provide insights into customer preferences, industry challenges, and potential business opportunities.
- Creative Mind and Innovative Skills: Entrepreneurs with creative thinking and innovative abilities can come up with unique product or service concepts that appeal to customers.
- Identifying Businesses That Do Not Meet Customer Expectations: Recognizing businesses that fail to satisfy customer needs or provide poor service can inspire entrepreneurs to develop improved offerings in the same market.
- Newspapers, Magazines: Reading business and industry publications can keep entrepreneurs informed about new trends, emerging technologies, and potential business opportunities.
- Hobbies: Turning a hobby or passion into a business can be a rewarding and profitable venture. For instance, a person who enjoys baking could start a home-based bakery.
- Brainstorming: Conducting brainstorming sessions with a team of creative individuals can generate a multitude of business ideas that can be further refined and evaluated.
Reasons for starting a business
- Earning Potential: Business owners have the chance to earn more money compared to traditional jobs, based on their drive, luck, commitment, and ideas.
- Autonomy: Entrepreneurs have the freedom to make their own decisions, set their own schedule, and choose who they work with.
- Team Building: Business owners can select like-minded individuals to complement their skills and contribute to the success of the venture.
- Achievement: Creating a successful business can bring a sense of accomplishment and fulfillment, especially when an idea comes to fruition.
- Innovation: Entrepreneurs have the opportunity to implement their ideas, make changes, and profit from those changes if successful.
- Learning Experience: Starting a business can lead to valuable knowledge and experience, even if it fails initially. Failures provide opportunities for growth and improvement in future endeavors.
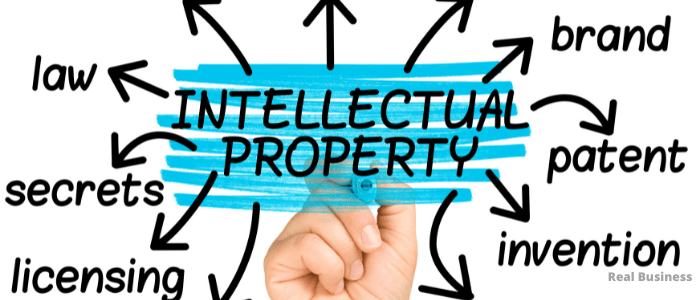
Protecting Your Idea
1. Intellectual Property: Business ideas, inventions, logos, and unique product names can be considered intellectual property if recorded in written, audio, or video format.
2. Legal Forms of Protection:
- Patents: Exclusive rights granted for a fixed period to inventors of new and useful products or processes.
- Trademarks: Names or symbols used in trade that are subject to government regulation.
- Copyright: Exclusive rights regulating the use of original creations, including text, video, audio, and multimedia formats.
3. Importance of Secrecy: Be cautious about disclosing your idea to others, especially those you don’t trust.
4. Written Documentation: Place your idea in writing, including a detailed description and sketches if applicable.
5. Registering Patents and Trademarks:
- Patents: File a patent application with the appropriate government agency.
- Trademarks: Register your trademark in the relevant country or region.
6. Applying Copyright: Copyright protection is automatic in most countries and does not require registration. However, adding the copyright symbol (©) to your work is recommended.
7. Notarization: Consider having your written description of your idea notarized for added legal protection. Notarization is the official act of verifying the authenticity of a signature on a document and confirming the identity of the signer.
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITY
A business plan is essential to translate an idea into a viable opportunity.
A business opportunity refers to a favorable set of circumstances or conditions that exist in the market or industry, which can be leveraged to create value and generate a profit.
A business opportunity is an attractive investment idea or proposition that provides the possibility of a monetary return to the person taking the risk.
Indicators of a Good Business Opportunity:
- Availability of Real demand/market: A good business opportunity should have a market willing and able to buy its goods or services.
- Reasonable Return on Investment: The business should offer profits that justify the risk and effort invested by the entrepreneur.
- Availability of Required Resources: Necessary resources like capital, raw materials, and labor should be accessible for establishing and operating the business.
- Availability of Required Technical Skills: Adequate skills and equipment are needed for production or service delivery, ensuring smooth operations.
- Acceptability in the Community: The business should align with societal norms and preferences to gain acceptance and support.
- Favorable Government Policy: Conducive policies, such as low taxes, can enhance the feasibility and success of the business.
- Availability of Good Infrastructure: Support services like transportation, communication, and banking facilities should be in place to facilitate business operations.
Qualities of Attractive Business Opportunities:
a) Competitive: The business should offer products or services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
b) Good Income Potential: It should have the capability to provide a steady income to support a reasonable lifestyle.
c) Reasonable Ease of Entry: Entry into the market should not be overly challenging, allowing entrepreneurs to leverage their existing skills and resources.
d) Low or Modest Startup Costs: The business should require minimal initial investment.
e) Good Growth Potential: The opportunity should have the potential for long-term survival and income generation.
f) Alignment with Skills and Experience: Entrepreneurs should possess the necessary skills and experience to succeed in the chosen business.
g) Timeliness: The opportunity should address current, unmet customer needs or trends.
h) Sizeable Market Gap: There should be a significant number of potential customers seeking the business’s offerings.
i) Goal Alignment: The opportunity should align with the entrepreneur’s objectives and aspirations.
Types of Business Opportunities:
- Retail and Wholesale: Retail businesses sell directly to consumers, while wholesalers buy goods in bulk and sell them to retailers.
- Franchise and Independent: Franchises involve selling a manufacturer’s goods or services under a special agreement, while independent businesses are created and managed independently.
- Product and Service: Businesses can offer either products, services, or a combination of both.
- Storefront and Non-Storefront: Businesses may operate from physical locations (storefronts) or rely on virtual storefronts (e-commerce websites).
- Industry-Based: Entrepreneurs should choose industries they are interested in and have expertise or experience in to avoid costly mistakes.
Identification Process for a Good Business Opportunity:
Entrepreneurs should conduct a pre-feasibility study to assess the viability of a business opportunity, considering factors like market demand, resources, and competition. This analysis helps determine the potential success of the opportunity and serves as a basis for seeking financial assistance.
EVALUATING BUSINESS OPPORTUNITY
The process of evaluating a business opportunity is what is referred to as feasibility study analysis.
Feasibility study analysis is therefore referred to as a process aimed at assessing the profitability and feasibility of the business opportunity.
Profitability of the business refers to the ability of the business to generate reasonable returns of investment.
Feasibility of the business refers to the ability, applicability and possibility of carrying out the business idea as intended and planned.
Steps in Evaluating Business Opportunities
There are several steps or stages to be considered while evaluating the business opportunity and these include the following;
- Objective analysis: This requires the entrepreneur to find out reasons as to why someone chose that business line. This helps in identifying the benefit ability of the business to the operator or the other stakeholders.
- Market feasibility: This deals with how the products are being priced, branded or packed, how promotion is being handled, the customer’s perception about products. Ask questions on future market prospects, distribution channels among others.
- Technical feasibility: This deals with the production or operations department. Ask questions relating to skills and experience required to perform duty, tools and machinery required, the plant layout, technology, raw materials, storage among others.
- Financial feasibility: This deals with finance analysis and questions expected are; how did you finance this business, how much revenue do you get from sales, how much did you spend on fixed sales, how much working capital is required etc.
- Personnel feasibility: Deals with human resource related issues, for example ask question relating to how many workers do you have, how do you motivate them, how much do you pay them, how did you train them etc
Steps in Starting a Business
- Identify potential business opportunities: Sarah loves baking and notices a growing demand for natural baked goods in her neighborhood.
- Select business opportunities suitable to your background and feasible to the market: Sarah considers her passion for baking and the market demand, deciding to pursue the bakery idea.
- Assess the selected business opportunity: Sarah researches the market further, analyzing the competition, potential customers, and financial feasibility of her bakery idea.
- Prepare a business plan: Sarah creates a detailed business plan outlining her bakery’s concept, target market, products, pricing, and marketing strategies.
- Mobilize the necessary resources: Sarah identifies the resources needed for her bakery, including ingredients, equipment, and skilled staff.
- Complete all legal formalities: Sarah registers her bakery as a legal entity, obtains necessary permits, and ensures compliance with health and safety regulations.
- Acquire land or buildings, equipment, raw materials, skilled and unskilled labor: Sarah leases a commercial kitchen space, purchases baking equipment, and hires staff to assist with baking and customer service.
- Prepare your marketing plan: Sarah develops a marketing plan to promote her bakery through social media, local advertisements, and collaborations with nearby businesses.
- Launch your enterprise: With everything in place, Sarah officially opens her bakery, showcasing her delicious treats to the community.
- Manage all the functions for your enterprise: Sarah oversees all aspects of her bakery, including production, sales, customer service, and finances, to ensure its smooth operation and success.


Please Nurses revision, update for us the notes here, others are not yet highlighted to be opened. I shall appreciate.
Thanks a lot for your endless effort to make us learn.God bless you big
good one