Table of Contents
ToggleCOMMUNICATION IN TEACHING AND LEARNING
Communication🗨️ is a word derived from the Latin word communis or commūnicāre, which means ‘to make common’ or ‘to share’. 🌐
📚 Communication is the act of conveying intended meaning to another person through the use of mutually understood signs and language.
OR Communication is the art of transmitting information, ideas, and attitudes from one person to another. 🗣️
📢 Reasons why we communicate in education:
To 🔄 change in behavior: Communication allows us to convey information and guidance that can lead to changes in how people think or act.
To 🌟 influence others: Through effective communication, we can persuade and inspire others to adopt new ideas or viewpoints.
To 🗯️ express our thoughts and emotions through words & actions: It’s a means of sharing our innermost feelings, thoughts, and ideas, fostering understanding and connection.
It is a 🛠️ tool for controlling and motivating people: Communication helps in managing and motivating individuals by providing direction and feedback.
It is a 🤝 social and emotional process: Communication is the cornerstone of building and nurturing relationships, as it allows us to connect emotionally and socially.
Communication for improving 💪 self-confidence: Expressing oneself and receiving positive feedback can boost self-esteem and confidence.
🎉 Entertain: Communication serves as a medium for entertainment, enabling us to share stories, jokes, and experiences that bring joy and laughter.
📚 Educate: Through communication, we transfer knowledge and information, facilitating the process of learning and understanding.
Establish 🤝 relationships: Communication is essential for forming and maintaining connections with others, be it friendships or professional relationships.
Solve 🧩 problems: Effective communication helps identify issues, discuss solutions, and reach consensus, making it a valuable problem-solving tool.
Make 📝 orders: Communication allows us to give clear instructions and make requests efficiently.
Give 🗺️ directions: Whether it’s navigating physical spaces or guiding someone through a task, communication helps provide directions effectively.
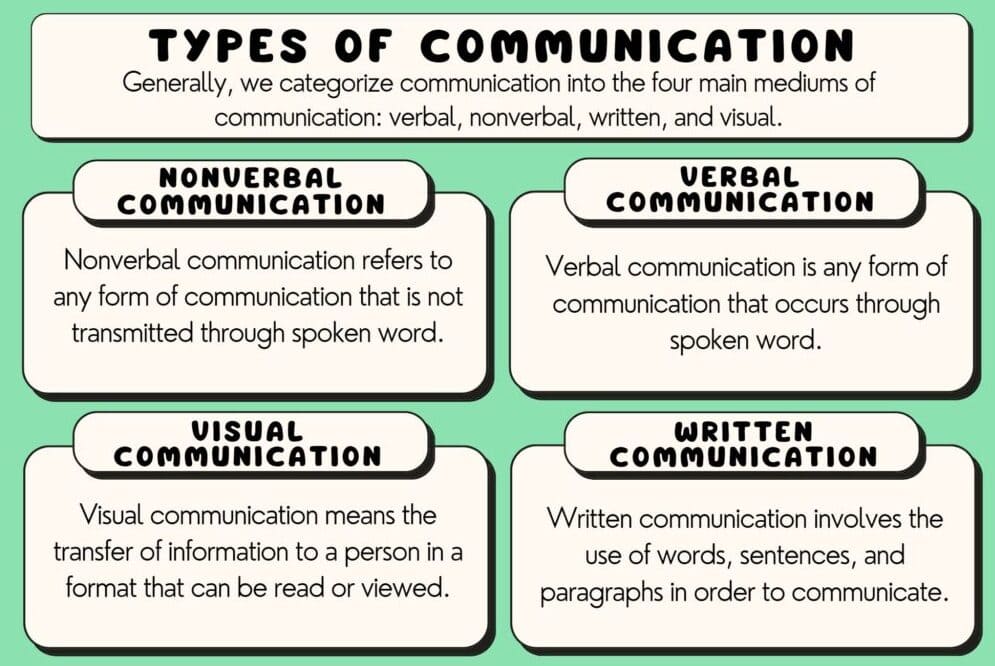
Types/forms of Classroom Communication
Communication within the classroom is important in order for students to learn effectively. Classroom communication exists in four categories: verbal, nonverbal, written, and visual.
Verbal communication refers to sending or receiving a message through sounds and languages. Teachers can address one student or the whole classroom through verbal communication. For example, a teacher may ask a student to stand up, which is verbal communication.
Non-verbal communication refers to communicating without words through body language, gestures, facial expressions, the tone and pitch of the voice, and posture. For example, if a teacher is nodding their head while a student is speaking, this can be encouraging or show that they agree with the student.
Written communication is sending or receiving information through writing. For example, a teacher may arrange a written assignment for students to test their knowledge or present lecture slides or notes for complicated information.
Visual Communication – This form of communication involves the visual display of information, wherein the message is understood or expressed with the help of visual aids. For example, typography, photography, signs, symbols, maps, colors, posters, banners, and designs help the viewer understand the message visually.
Levels of Communication
There are five different levels of communication laid out by the classical theory of communication. Each of these different levels of communication has a different purpose and is used in different situations. However, it is vital to recognize and use all five levels of communication in order to have an effective conversation.
Intrapersonal Communication – This is communication that a person does with themselves. This type of communication is known as self-talk and is the internal process that people use to think, reflect, and make sense of their experiences. It can be considered surface-level communication as both the sender and the receiver of the message are the same person. It includes the silent conversations we have with ourselves. This process of communication, when analyzed, can either be conveyed verbally to someone or stay confined as thoughts.
Interpersonal Communication – This form of communication takes place between two individuals and is thus a one-on-one conversation. Here, the two individuals involved will swap their roles of sender and receiver in order to communicate in a clearer manner.
Small Group Communication – This type of communication can take place only when there are more than two people involved. Here, the number of people will be small enough to allow each participant to interact and converse with the rest. Examples of group communication include class discussions, board meetings, and staff meetings.
Public Communication – This type of communication takes place when one individual addresses a large gathering of people. Public speeches are examples of this type of communication. In such cases, there is usually a single sender of information and several receivers who are being addressed.
Mass Communication – This is communication that is directed toward a very large audience who is not always in the same room or are not always receiving the message at the same time. This would be things like the morning announcements, everyone watching a TV show, looking up something on the internet, reading a book/newspaper/magazine.
Channels/Media of Communication
Educational media refers to channels of communication that carry messages with an instructional purpose. These channels include:
Face-to-face communication: This is the ability to see the other person or people during a conversation. It allows for the exchange of more than just words because both the speaker and listener(s) can observe and adjust based on body language and expression. Examples include classroom teaching and discussion groups.
Print media: This category includes books, journals, magazines, newspapers, workbooks, and textbooks. These materials are easy to use, portable, and inexpensive.
Electronic media: Electronic media is a form of mass media that requires electronic energy to create and distribute informative or entertaining content in the form of audio, visual, or audio-visual formats. These categories include:
a) Audio media: These are teaching-learning devices that appeal to the auditory sense. They carry sounds and can be heard independently. Examples include phone calls, audio tapes, conferencing, record players, and radio.
b) Visual media: These are media that appeal to the sense of sight (eyes) or media that can be seen. Examples include computer work, projected presentations, emails, chats, and messages.
c) Audio-Visual: This category refers to instructional materials that provide learners with audio and visual experiences by engaging both the hearing and seeing senses simultaneously. Examples include television and video tapes.
Factors to consider in communication
Language: 🗣️ To communicate effectively, individuals must share a common language so that each can be understood. In case of a failure to understand the language, an interpreter may be necessary to enhance communication.
Nature of Message: 📜 The means of communication depend on the nature of the message. Urgent, confidential, private, and important messages should be distinguished from ordinary, routine, open, and less important messages, and the means of communication should be chosen accordingly.
Cost: 💰 The cost of sending a message should also be considered when selecting a mode of communication. The result obtained should justify the expenditure.
Record: 📝 If the record of the communication is important, it should be written; otherwise, oral communication is sufficient and can be lost easily.
Distance: 🌍 Distance is another factor for consideration. The mode of communication to be chosen depends on whether the message is to be sent to a nearby place or somewhere at a long distance. Letters and face-to-face communication can be favorable for short distances, while electronic means are suitable for long distances.
Scale of Organization: 🏢 Means of communication in large-scale businesses differ from those in small-scale businesses. In small businesses, most communication is oral, while in large businesses, it is written.
Supporting Technology: 📡 Both the sender and the receiver must have supporting technological communication tools to use a particular media. For example, if individual A sends an e-mail to person B, B should have a personal computer.
Urgency: ⏰ Selection of the means of communication should consider the urgency of the communication. Time available is the main factor here, and higher cost may be justified for sending the message in time. Choose a media that will quickly deliver the information to the receiver.
Secrecy: 🤫 If the message to be communicated is secret or confidential, means that can maintain secrecy should be adopted. In such cases, face-to-face talking may solve the problem.
Safety: 📦 The sender must be careful about the safety of the message. Decisions need to be made about whether the message would be sent by ordinary post or by registered post, through a courier or messenger, etc.
Relationship: 🤝 The relationship between the sender and recipient may be a decisive factor in the choice of the means of communication. Private messages may require personal contact, while formal relationships demand official and conventional modes of communication.
Benefits of Effective Communication
Effective communication is the process of exchanging ideas, thoughts, opinions, knowledge, and data so that the message is received and understood with clarity and purpose. When we communicate effectively, both the sender and receiver feel satisfied. The following are the benefits that result from effective communication:
- Right information is shared 📚
- Minimizes conflicts 🤝
- Resources such as time and money are saved 💰⏰
- Helps in establishing rapport 🤗
- Intended results are achieved 🎯
- Sender is able to provide intended feedback 📢
- Enhances harmonious co-existence, and conflicts are resolved amicably 🤝🕊️
Important Things to Consider When Effective Communicating
Pre-thinking: Pre-thinking about the message is an important quality of effective communication. Pre-thinking enables the sender to develop a creative message and transmit it efficiently. 🤔✍️
Specific Objective: Communication occurs with specific objectives. Therefore, the communicator must know the objective of communication and arrange the message accordingly. 📝🎯
Command of Subject (Mastery of Subject Matter): One should communicate information they have mastered so that, in case of questions or confusion from the receiver, the sender can clarify the information confidently. 📚🧠🗣️
Timeliness: Usefulness of any message depends on its timely transmission. If the message is not transmitted at the appropriate time, its utility is lost. So, the communicator should consider the timing of communication. 🕒⏰
Conciseness: Another important quality of effective communication is that the message should be concise or brief. A concise message contains only relevant and necessary facts, avoids repetition, and is organized properly. ✂️📄
Completeness: Effective communication transmits a complete message so that the receiver can understand the full meaning of the message. The sender should not sacrifice completeness to attain conciseness. 📦🧩
Correctness: Effective communication contains only correct messages. False, manipulated, and exaggerated information irritates the receiver and makes the communication ineffective. ✅❌🤥
Speed and Sequence of Speech: Speaking too fast can make it difficult for the receiver to understand the message. The sender should speak slowly and sequence their words to ensure clear comprehension. 🗣️🎙️
Persuasiveness: Persuasiveness is an important quality of effective communication. It helps develop a positive attitude in the receiver toward the message. 🗣️💡
Feedback: Effective communication always allows for feedback. Feedback ensures that the message has reached the intended receiver and they have understood it clearly. 📣📬
Mutual Interest: Communication is effective when it considers the interests of both the sender and receiver. Ignoring the receiver’s interests can lead to communication failure. 🤝🤝
Use of Appropriate Language: Effective communication uses appropriate language that avoids ambiguity, complex words, misleading non-verbal cues, and technical jargon. The language should be simple and easy to understand. 🗣️📖🗨️
Considering the Receiver: An effective communicator thinks about the receiver’s knowledge, ability, interest, origin, etc. This increases the utility and acceptability of communication. 🧠👥
Use of Appropriate Media: Selecting suitable media is essential for successful communication. The sender should choose written or oral media based on the nature and importance of the message, availability of time, cost, and the receiver’s ability. 📰📻📹
Emphasizing Informal Relationship: Establishing informal relationships with the receiver, in addition to formal ones, ensures the success of communication. Building rapport with the receiver enhances the acceptability of the message. 🤗🤝
Effective Listening: An effective communicator is also an effective listener. They must listen attentively to the response of the receiver, showing patience and understanding. 👂🤝🗣️
Barriers to Communicating in Teaching and Learning
Physical barriers 🚧: These are physical factors that can distract or block the communication process. They include background noise and malfunctioning public address systems.
Physiological barriers 🤕👂👁️: These barriers arise when a sender or receiver of communication is physically unable to express or receive the message with clarity due to physiological issues like severe pain, hearing problems, poor eyesight, or speech impediments.
Emotional and Attitude (Psychological) barriers 😢🤬: Psychological barriers play an important role in interpersonal communication. The state of mind of the sender or receiver can make it difficult to understand conveyed information, often leading to misunderstanding. Emotions like anger, fear, and sadness, as well as attitudes such as the need to be right all the time or beliefs of superiority or inferiority, affect objectivity. Stereotypical assumptions based on cultural backgrounds also contribute to these barriers.
Language (Semantic) barriers 🗣️🌍: Improper communication between the sender and receiver leads to these barriers. Examples include speaking different languages, strong accents, and the use of slang or jargon, which can frustrate communication in teaching and learning.
Organizational barriers 🏢📋: These barriers result from the structure, rules, and regulations within an organization. Superior-subordinate relationships can hinder the free flow of communication and distort information, leading to miscommunication. For instance, a student may need to go through class leaders and student leaders before reaching the principal, making communication less straightforward.
Cultural barriers 🌏🤝: Cultural differences create barriers due to variations in beliefs, practices, and interpretations among different cultures worldwide. What may be harmless in one culture can be perceived as slang in another, and beliefs can vary significantly. Gestures like hugging as a greeting may also be misinterpreted differently in various cultures.
Lack of Common Ground 🧑🤝🧑: When the audience cannot relate to the message because they lack a shared experience with the speaker, communication is hindered. Using examples or stories that students have knowledge or experience of can bridge this gap.
Lack of Eye Contact 👁️🤨: Failure to maintain eye contact with students can raise doubts and make them feel disconnected or suspicious. Maintaining eye contact is crucial for effective communication.
Information Overload and Lack of Focus 📊🧠: Providing excessive information or too many details can overwhelm and distract the audience from the main message, causing a loss of focus.
Lack of Preparation 📊📚: Being unprepared or lacking factual information can erode trust and credibility, affecting the effectiveness of communication.
Talking Too Much 🗣️🤐: Excessive talking without allowing the audience to respond or engage can hinder effective communication. Active listening is vital for balanced communication.
Lack of Enthusiasm 😒🎉: If the communicator lacks interest or enthusiasm for the message, it can affect the audience’s engagement and belief in the message.
Expectations and Prejudices 🤝🙅: Preconceived expectations or biases can lead to false assumptions and stereotyping, causing misinterpretation.
Lack of Trust 🤝❌: Trust is essential for effective communication. When individuals don’t trust their leaders or managers, communication suffers.
Wrong Communication Channels 📡👥: The complexity of communication channels today can make it challenging to select the right ones to deliver relevant information in a timely manner.

