Table of Contents
ToggleGONADOTROPINS
Gonadotropins are fertility medications given by injection that contain follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) alone or combined with luteinizing hormone (LH).
Gonadotropins are hormones that stimulate the gonads, which are the sex organs in the body.
Gonadotropins are produced by the pituitary gland, which is a small gland located at the base of the brain. The release of gonadotropins is regulated by the hypothalamus.
In females, the gonads are the ovaries, and in males, they are the testes.
Gonadotropins are a class of medications used to treat infertility and disorders associated with reproductive functions.
Types of Gonadotropins
There are two main types of gonadotropins:
1. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): This hormone stimulates the growth and development of follicles in the ovaries of females and sperm production in the testes of males.
Females | Males |
– Normal Ovarian Function: FSH is useful for the development and maturation of follicles in the ovaries, which contain the eggs. This ensures regular ovulation and fertility. – Estrogen Production: FSH stimulates the production of estrogen by the growing follicles. Estrogen is for the development of female secondary sexual characteristics, menstrual cycle regulation, and overall reproductive health. – Improved Egg Quality: FSH contributes to the development of healthy eggs, increasing the chances of successful fertilization and pregnancy. – Fertility Treatment: FSH is a key component of fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF) to stimulate multiple egg production. | – Sperm Production: FSH is essential for the production of sperm in the testes. It stimulates the Sertoli cells, which are responsible for nourishing and supporting sperm development. – Improved Sperm Quality: FSH contributes to the production of healthy, motile sperm, increasing the chances of fertilization. |
2. Luteinizing hormone (LH): This hormone triggers ovulation in females and testosterone production in males.
Females | Males |
– Ovulation: LH triggers the release of the mature egg from the follicle (ovulation), which is essential for fertilization. – Corpus Luteum Formation: After ovulation, LH stimulates the formation of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone is for maintaining the uterine lining for potential pregnancy. – Hormonal Balance: LH plays a role in regulating the production of estrogen and progesterone, contributing to hormonal balance in the female body. – Fertility Treatment: LH is used in fertility treatments to trigger ovulation and support the development of the corpus luteum. | – Testosterone Production: LH stimulates the Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone. Testosterone is essential for male sexual development, sperm production, and overall health. – Secondary Sexual Characteristics: LH-driven testosterone production is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics like facial hair, muscle mass, and deepening of the voice. – Libido and Sexual Function: Testosterone, produced under the influence of LH, plays a crucial role in libido and sexual function. |
GONADOTROPIN DRUGS (Fertility Drugs)
Gonadotropin Drugs/Fertility drugs are agents that stimulate the female reproductive system.
Fertility drugs are medications used to help women who are having trouble getting pregnant. They work by stimulating the ovaries to produce more eggs, increasing the chances of conception.
Indications for Fertility Drugs:
1. Treatment of infertility in women with functioning ovaries whose partners are fertile: This is a broad category encompassing various causes of infertility, including:
- Anovulation: When a woman doesn’t ovulate regularly, fertility drugs can stimulate ovulation and increase the chances of pregnancy.
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): PCOS often causes irregular ovulation. Fertility drugs can help regulate ovulation and improve fertility.
- Endometriosis: This condition can affect ovulation and egg quality. Fertility drugs can help stimulate ovulation and improve chances of conception.
- Premature Ovarian Failure: In some cases, women experience premature ovarian failure, leading to low egg reserves. Fertility drugs can help stimulate limited egg production.
- Unexplained Infertility: When the cause of infertility is unknown, fertility drugs can be used to stimulate ovulation and see if it improves chances of pregnancy.
2. Used to stimulate multiple follicle development for harvesting of ova for in vitro fertilization (IVF): This is a crucial aspect of IVF, where multiple eggs are needed for fertilization and embryo transfer.
3. Menotropins are used to stimulate spermatogenesis in men with low sperm counts and otherwise normally functioning testes: While not directly related to female fertility, this highlights the broader application of fertility drugs in both men and women.
Contraindications for Fertility Drugs:
- Allergy to fertility drug: Prevent hypersensitivity reactions.
- Primary ovarian failure: These drugs only work to stimulate functioning ovaries.
- Ovarian cysts: Can be stimulated by the drugs and can become larger.
- Pregnancy: Due to the potential for serious fetal effects.
- Idiopathic uterine bleeding: Can represent an underlying problem that could be exacerbated by the stimulatory effects of these drugs.
- Lactation: Risk of adverse effects on the baby.
- Thromboembolic disease: Increased risk of thrombus formation.
- Women with respiratory diseases: Alterations in fluid volume and blood flow can overtax the respiratory system.
Adverse Effects:
- Greatly increased risk of multiple births and birth defects.
- Ovarian overstimulation: abdominal pain, distention, ascites, pleural effusion.
- Others: headache, fluid retention, nausea, bloating, uterine bleeding, ovarian enlargement, gynecomastia, and febrile reactions possibly due to stimulation of progesterone release.
Fluid retention is a common side effect of fertility medications, because;
Hormonal Changes: Fertility drugs increase estrogen levels, which can lead to fluid retention. Estrogen promotes sodium retention in the body, and sodium attracts water, causing fluid buildup.
Increased Blood Flow: Fertility drugs increase blood flow to the ovaries and uterus, which can lead to fluid buildup in the pelvic area.
Drugs used in treatment of infertility
Name | Clinical uses and dosage | Contraindications |
Clomifene
| Infertility due to failure to ovulate. Given 50 mg daily × 5/7 Starting from the 5th day of the cycle , Increase to 100mg ×5/7 From day 5-10 if no response. | Pregnancy. |
Bromocriptine
| Female infertility associated with hyperprolactinemia Dosage 1.25 – 2.5mg Bid × 3-7 days with food. Inhibition of lactation 2.5mg bid with meals × 14 days.
| Severe ischemic heart disease Uncontrolled hypertension Pregnancy Breast feeding. |
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM DRUGS
Drugs that affect the female reproductive system typically include hormones and hormonal-like agents.
These drug types include;
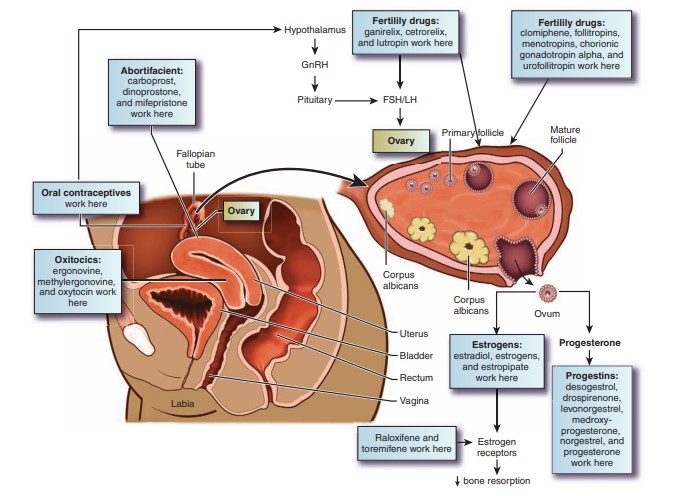
Gonadotropin Sites of Action
Female Sex Hormones
The female sex hormones can be used to replace hormones that are missing or to act on the control mechanisms of the endocrine system to decrease the release of endogenous hormones.
Drugs that act like estrogen, particularly at specific estrogen receptors, are also used to stimulate the effects of estrogen in the body with fewer of the adverse effects.
Female sex hormones include;
- Estrogens
- Progestins
Estrogens.
This hormone is naturally produced by the ovaries, placenta and adrenal glands. It stimulates the development of female sex characteristics, prepares the body for pregnancy, affects the release of FSH and LH, and is responsible for proliferation of the endometrial lining.
Low estrogen in the body is responsible for the signs and symptoms of menopause, in the uterus, vagina, breast and cervix.
Other Functions of estrogen include;
- Breast development.
- Increase cholesterol in bile, to prevent damaging effects of bile salts.
- Increases fat storage, such as in breast tissue.
- Maintains bone mineral density.
- Maintains muscle strength.
- Prevents atherosclerosis, by increasing HDL concentration and lowering LDL.
- Estrogen is responsible for maintaining libido, memory, and mental health.
- It stimulates ovulation, maintains the uterine walls and is important in vaginal lubrication.
Indications of Estrogen Therapy.
- Estrogens are used for hormone replacement therapy (HRT) when ovarian activity is blocked or absent.
- Is used to control the signs and symptoms of menopause.
- They can also be used in therapy for prostate cancer and inoperable breast cancer, also as palliative care.
- Treatment of female hypogonadism(when the body produces little or no hormones).
- Treat ovarian failure.
- Oral contraceptives (estrogen and progestin)
- Morning after pill (emergency pills)
- Endometriosis
- Dysmenorrhea, used with progestin.
Progestin/Progesterone.
This promotes maintenance of pregnancy and it is called a pregnancy hormone.
Its functions include;
- Transforms proliferative endometrium into secretory endometrium.
- Prevents follicle maturation, ovulation and uterine contractions.
- Used in contraceptives. It inhibits release of GnRH, FSH and LH, hence follicle development and ovulation are prevented.
Indications of Progestin.
- Used as a contraceptive.
- Maintains pregnancy and development of secondary sex characteristics.
- Use to treat primary and secondary amenorrhea, and functional uterine bleeding.
- Treatment of acne and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD).
- For the relief of signs and symptoms of menopause .
Contraindications of Female Sex hormones.
Estrogen
- Known allergies
- Idiopathic vaginal bleeding.
- Breast Cancer(Estrogen dependant cancer)
- CVA since it increases clotting factor prodn.
- Hepatic dysfunction.
- Pregnancy.
- Lactation.
Progestin/Progesterone
- PID
- STD
- Endometriosis
- Renal and hepatic disorders.
- Epilepsy.
- Asthma.
- Migraine headaches
- Cardiac Dysfunction —potential excerbation.
Adverse Effects.
- Corneal Changes.
- Photosensitivity.
- Peripheral edema.
- Chloasma ( patches on the face)
- Hepatic adenoma.
- Nausea
- Vomiting.
- Abdominal cramps.
- Bloating.
- Withdraw bleeding.
- Changes in menstrual flow.
Important aspects/issues to remember.
- Women receiving any of these drugs should receive an annual medical examination, including
breast examination and Pap smear, to monitor for adverse effects and underlying medical
conditions. - Women taking estrogen should be advised not to smoke because of the increased risk of
thrombotic events. - Women who are receiving these drugs for fertility programs should receive a great deal of psychological support and comfort measures to cope with the many adverse effects associated
with these drugs. The risk of multiple births should be explained. - Drugs are used in treatment of specific cancers in males and they should be advised about the
possibility of estrogenic effects. - Not indicated during pregnancy or lactation because of potential for adverse effects on the fetus
or neonate.
Examples of female sex hormones and dosages.
Estrogen
- Estradiol, 1–2 mg/day orally or 1–5 mg IM every 3–4 weeks or 2–4 g intravaginal cream daily.
- Estrogens, conjugated (C.E.S., Premarin), 0.3–1.25 mg/day orally.
- Estropipate (Ortho-Est, Ogen), 0.625–5 mg/day orally.
Progestin/Progesterone.
- Etonogestrel (Implanon) 68 mg implanted sub dermally for up to 3 yr, replaced or changed when needed.
- Medroxyprogesterone (Provera) 5–10 mg/day PO for 5–10 days for amenorrhea or 400–1000 mg/week IM for cancer therapy or 150 mg of deep IM every 3 months (13 weeks) for contraception.
Clinically important Drug Interactions
- Barbiturates, rifampin, tetracyclines, phenytoin: decreased serum estrogen levels
- Corticosteroids: increased therapeutic and toxic effects of corticosteroids.
- Nicotine: Increased risk of thrombi and emboli
- Grapefruit juice: inhibition of metabolism of estradiols
- St. John’s wort: can affect metabolism of estrogens and can make estrogen-containing
contraceptives less effective.
- Barbiturates, carbamazepine, phenytoin, griseofulvin, penicillin, tetracyclines, rifampin: reduced
effectiveness of progestins - St. John’s wort: can affect the metabolism of progestins and can make progestin-containing
contraceptives less effective..


Am in love with what I read thanks
Gdwork done and well simplied thnks
Great notes
Perfect notes. I just need pdf
excellent
well written