-
Anatomy Introduction
BNS 111: Anatomy & Physiology – Introduction Notes BNS 111: Anatomy & Physiology SEMESTER I – Introduction Key definitions and Levels of Organization Alright, let’s start with the very basics of studying the body. When we talk about Anatomy, we are talking about the **structure** of the body. Think of it like building a house…
-

PYELONEPHRITIS
PYELONEPHRITIS The term “Pyelonephritis” originates from Greek: “Pyelum” (or “Pyelos”) meaning renal pelvis. “Nephros” meaning kidney. “-itis” meaning inflammation. Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the kidney parenchyma (the functional tissue) and the renal pelvis (the collecting system). It is fundamentally an upper urinary tract infection (UTI). It most commonly results from an ascending infection, where…
-

General Paralysis of the Insane (GPI)
General Paralysis of the Insane (GPI) General Paralysis of the Insane (GPI), also known as general paresis, paralytic dementia, or syphilitic paresis, is a severe neuropsychiatric disorder classified as an organic mental disorder. It is a late-stage manifestation of untreated syphilis, resulting from chronic meningoencephalitis and progressive cerebral atrophy. GPI primarily affects the frontal and…
-

Traction in Nursing
TRACTION Traction is a pull exerted on the part of the limb against a pull of compared strength in the opposite direction. This is a system in fracture management in which a continuous pull is applied and maintained on a limb or other parts of the body by the use of cords and weights. It…
-

SUTURING OF THE WOUND
Suturing Suturing is the process of closing a wound by stitching the wound edges together using a surgical needle and thread. It is a fundamental technique in wound management and surgical procedures to facilitate healing, prevent infection, and restore tissue integrity. Purpose of Suturing The primary goals of suturing are: To approximate wound edges until…
-

HIV AND PREGNANCY
HIV AND PREGNANCY HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that attacks the body\’s immune system, specifically the CD4 cells (T cells), which are important for immune defence. If untreated, HIV can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), a condition where the immune system is severely weakened. HIV is a lenti-virus (slow and long acting)…
-

Tuberculosis in Pregnancy
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Pulmonary Tuberculosis is an infectious disease of the lungs caused by acid-fast bacilli known as Mycobacterium. INCIDENCE: The incidence ranges between 1% and 2% amongst the hospital deliveries in the tropics, being confined predominantly to the underprivileged sectors of society. Incidence of tuberculosis is rising worldwide with the rising prevalence of HIV infected…
-
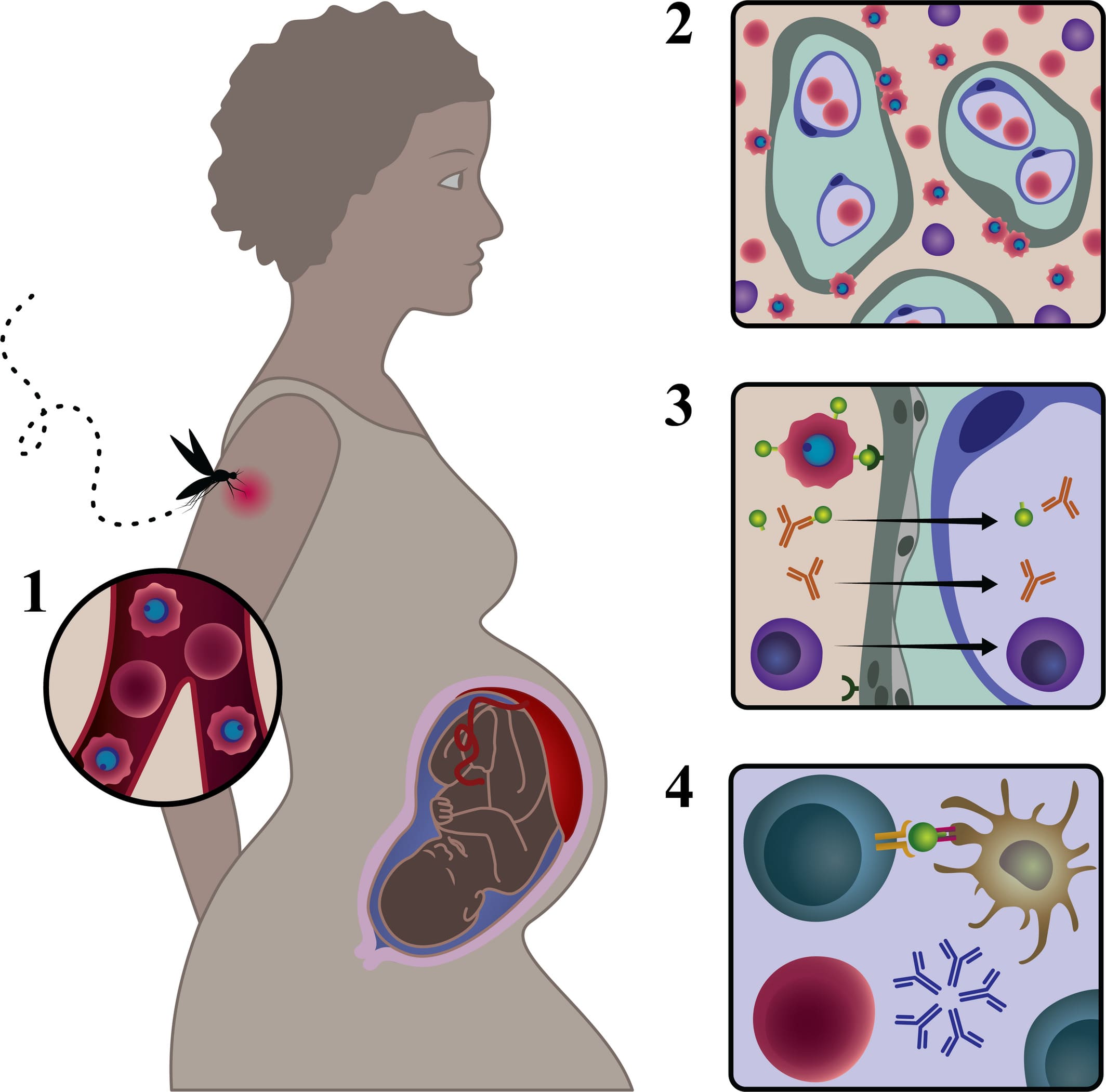
MALARIA IN PREGNANCY
MALARIA IN PREGNANCY Malaria is a febrile condition/disease caused by a Plasmodium parasite and is the most common cause of pyrexia in tropical regions, usually associated with rigors. CAUSES Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites (protozoa), which are of four types: Plasmodium falciparum: This is the most dangerous species, responsible for the majority of malaria…
