-

Medicines Acting on Specific Body Systems
Medicines Acting on Specific Body Systems Medicines play a big role in modern healthcare, providing solutions to a wide range of diseases and disorders. The human body is a network of interconnected systems, each with its functions and challenges. To address these challenges, pharmacologists have developed drugs that act on specific body systems, ensuring targeted…
-

Specific Anti-microbial Agents
ANTIBIOTICS Antibiotics are chemical substances derived from microorganisms that either inhibit the growth of or destroy other microorganisms. They are pivotal in combating bacterial infections and are divided into two primary categories: Bacteriostatic Antibiotics: Inhibit bacterial growth. Bactericidal Antibiotics: Directly kill bacteria. Classification of Antibiotics Antibiotics can be classified based on their: Mechanism of Action…
-

DRUGS USED IN PAEDIATRICS
DRUGS USED IN PAEDIATRICS The field of pediatric pharmacology focuses on the safe and effective use of medications in children, from infancy to adolescence. Pediatric patients require special consideration due to their developing physiology, which affects how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted. Here is an introduction to the key aspects of drugs used…
-
DRUGS USED IN MIDWIFERY
DRUGS USED IN MIDWIFERY Drugs used in midwifery are drugs specifically used during pregnancy, labor, delivery, and postpartum care to ensure the health of the mother and baby. They may induce labor, prevent complications, manage pain, or treat postpartum conditions. Examples; Oxytocics: e.g., Oxytocin (induces or augments labor), Misoprostol (induces labor or manages postpartum hemorrhage).…
-

Legal aspects and national policies
The National Drug Authority (NDA) The National Drug Authority (NDA) is a regulatory body comprised of individuals of high integrity, tasked with overseeing the implementation of the national drug policy. Its core objective is to ensure the availability, quality, and safe use of pharmaceuticals across the country. The NDA plays a big role in maintaining…
-

Drug Classification
Classifications of Drugs A drug is any substance that, when introduced into a living organism, alters its structure or function. This includes anything from medications used to treat illnesses to recreational substances. Drugs are used for various reasons: Treatment: To cure or manage diseases and health conditions. Prevention: To protect against illnesses (e.g., vaccines). Diagnosis:…
-

Terminologies and Sources of Drugs
TERMINOLOGIES Pharmacology: The scientific study of drugs, their origins, chemical properties, actions, and uses in the treatment, diagnosis, and prevention of disease. Pharmacology is the scientific study of drugs and their use in medicine. This includes pharmacokinetics (what the body does to the drug) and pharmacodynamics (what the drug does to the body). In midwifery,…
-

Psychiatric disorders related to maternal child health
Psychiatric disorders related to maternal child health Psychiatric disorders that can affect mothers include: Depression: A common disorder that can occur during pregnancy and the postpartum period Anxiety: A common disorder that can occur during pregnancy and the postpartum period Postpartum psychosis(Puerperal or postnatal psychosis) : A disorder that usually manifests as bipolar disorder Post-traumatic…
-

Therapeutic Modalities in Psychiatry
THERAPEUTIC MODALITIES IN PSYCHIATRY Therapeutic modalities refers to different types of care provided by psychiatric nurses to individual patients, groups and families. Therapy is the treatment of someone with mental or physical illness without the use of drugs or operations. Psychiatric treatment aims to manage mental health disorders, alleviate symptoms, and improve patients\’ overall quality…
-
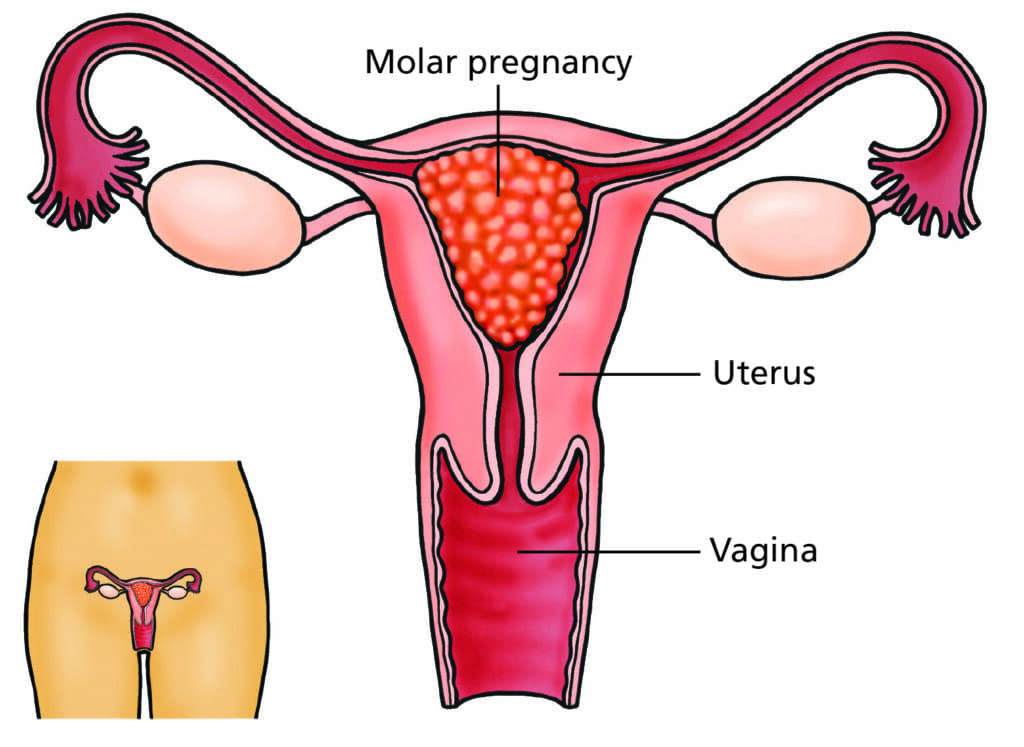
HYDATIDIFORM MOLE (Molar Pregnancy)
HYDATIDIFORM MOLE (VESICULAR) This condition occurs when the uterus is filled with a mass of cysts, and the chorionic villi grows into a mass of cysts. This process begins around 6 weeks of pregnancy, and the embryo is absorbed. Hydatidiform mole is an abnormal placental condition characterized by partly degenerative and partly proliferative changes in…
