-

MENOPAUSE
MENOPAUSE The term menopause originates from the Greek words: Mens – meaning \”monthly\” Pausis – meaning \”cessation.\” Menopause is a natural stage in a woman’s aging process, characterized by a decline in ovarian function, leading to reduced production of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. This physiological change results in the permanent cessation of menstruation and…
-

Money matters for Small Business
MONEY MATTERS FOR SMALL BUSINESSES Money matters involve issues related to finances, particularly personal and business finances. Money Matters For Small Businesses means that financial management is important for the success and survival of small businesses. Money is the most essential resource for starting and operating a business. It acts as the lifeblood of any…
-
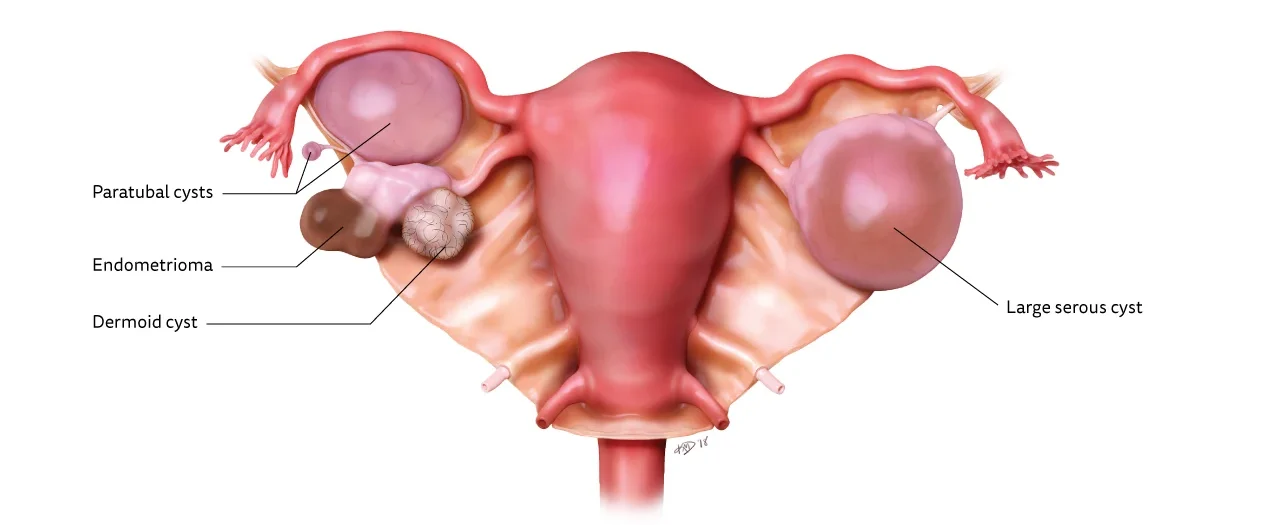
Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian Cysts Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets within or on the surface of an ovary. An ovarian cyst is a semi-solid or fluid-filled sac within the ovary. Many women will have them at some point during their lives. Most ovarian cysts present little or no discomfort and are harmless. The majority disappear without…
-
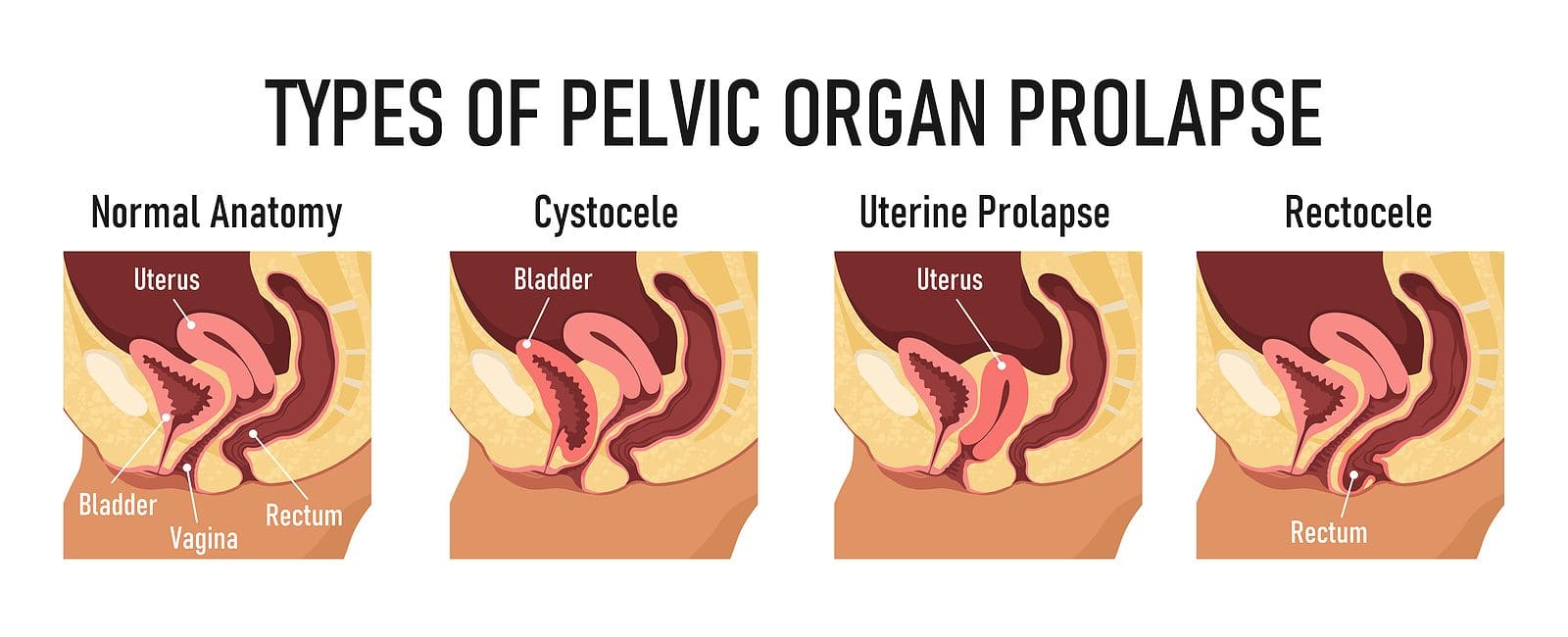
Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP)
Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP): POP occurs when the muscles and ligaments that support the pelvic organs weaken, allowing these organs to bulge or drop into the vagina. It is divided into three main categories: 1. Anterior Vaginal Wall Prolapse: Cystocele: This is the most common type of POP. It happens when the bladder bulges into…
-
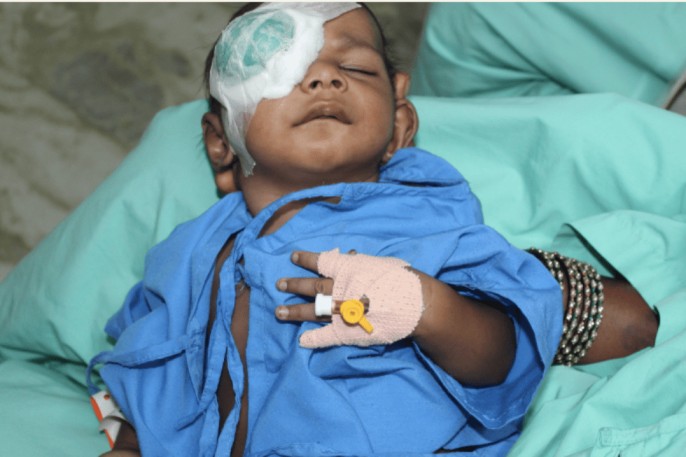
Care of a child under going eye surgery
EYE CARE Eye care is characterized as the special attention given to the eyes to prevent complications. Natural Cleansing: The production of tears and the blinking mechanism provide a natural cleansing process for the eyes (Harrison, 2006). When this process is interrupted, the eyes may need to be artificially cleansed to remove debris, prevent dryness,…
-
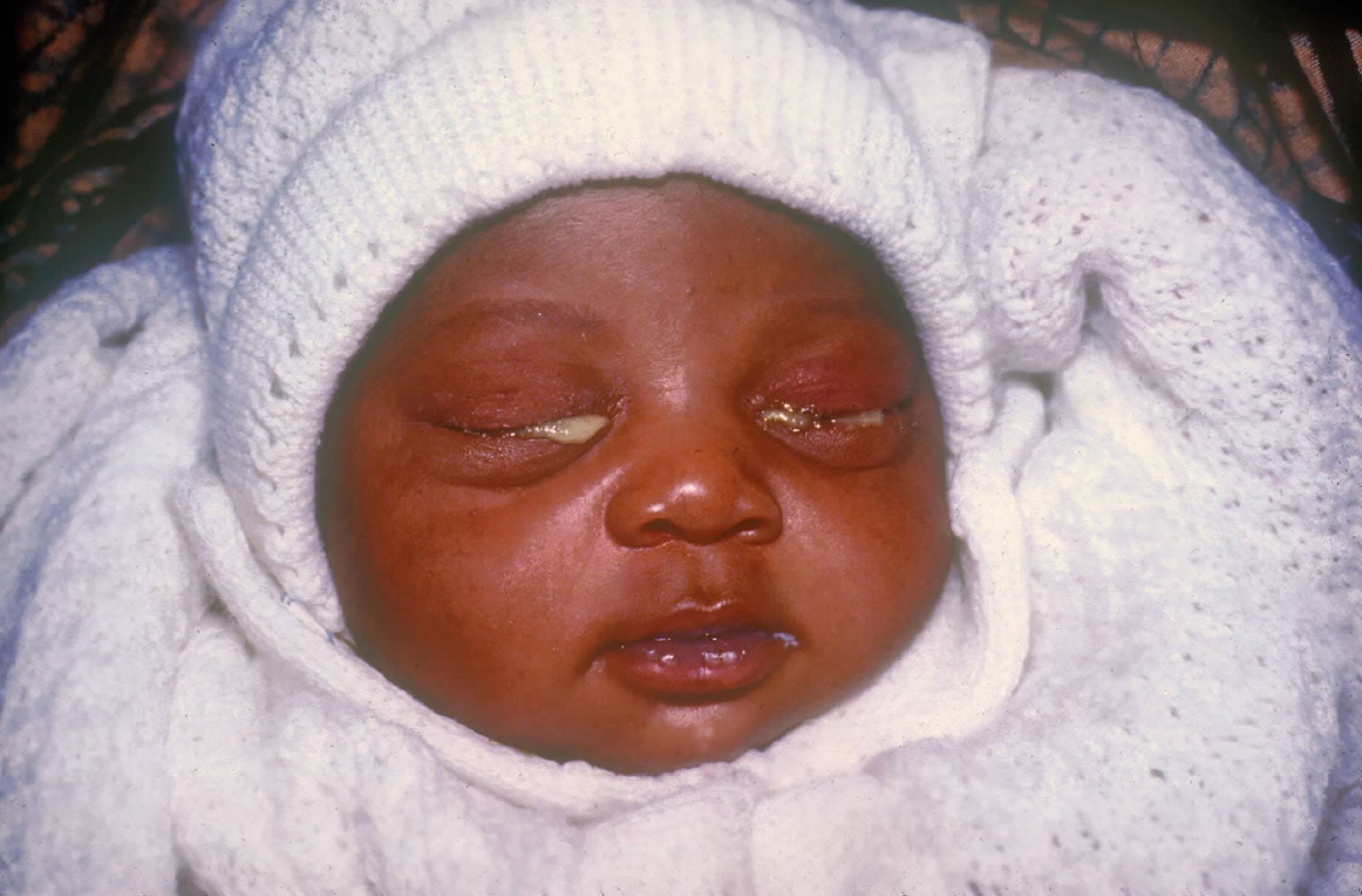
Eye Infections in Children
EYE INFECTIONS Eye infections occur when bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other microorganisms invade the tissues of the eye or its surrounding structures. These infections can range from mild to severe and may involve various parts of the eye, including the conjunctiva, cornea, eyelid, or internal ocular structures. Conjunctivitis: Conjunctivitis, commonly known as ‘pink eye’, is…
-
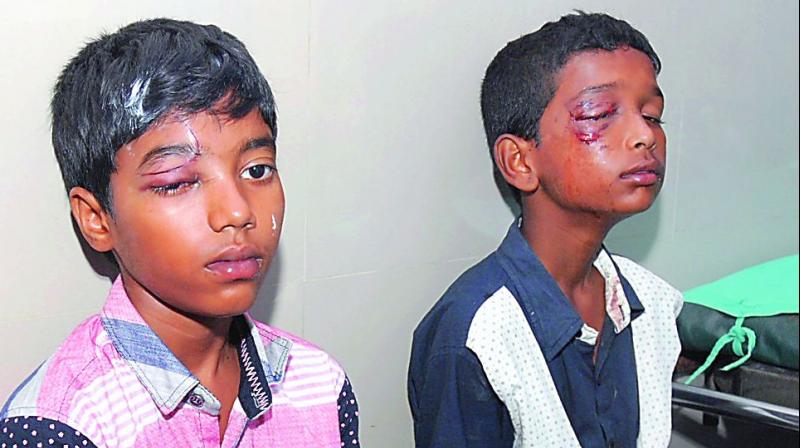
Eye Injuries in Children
EYE INJURIES IN CHILDREN An eye injury refers to any trauma or damage to the eye or its surrounding structures, including the eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea, sclera, iris, lens, retina, or optic nerve. These injuries may result from mechanical, chemical, or thermal causes, and can range from minor irritations to vision-threatening conditions. Injuries to the eye,…
-
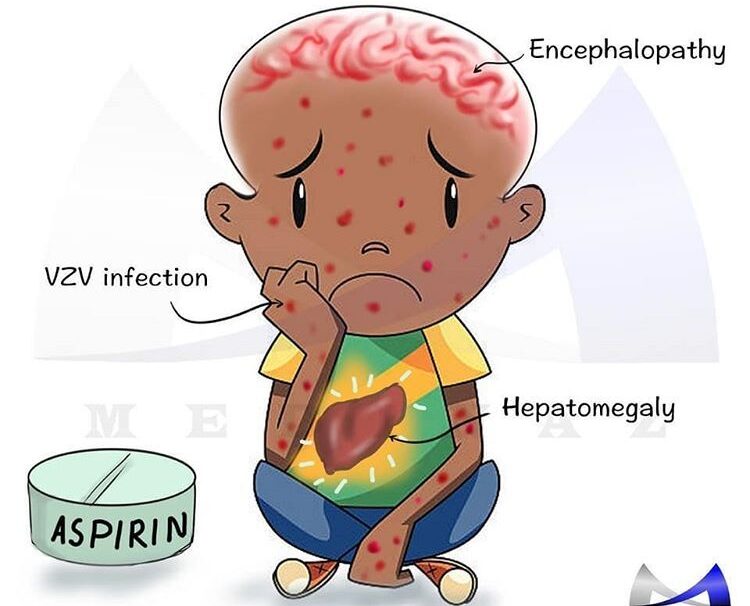
Reye’s Syndrome
REYE’S SYNDROME Reye’s syndrome is characterized by acute noninflammatory encephalopathy and fatty degenerative liver failure. I.e It is characterized by swelling in the liver and brain. Reye’s syndrome commonly affects children recovering from viral infection, most commonly flu or chickenpox. Pathogenesis Viral Infection: Reye’s syndrome often occurs during the recovery phase of a viral infection,…
-
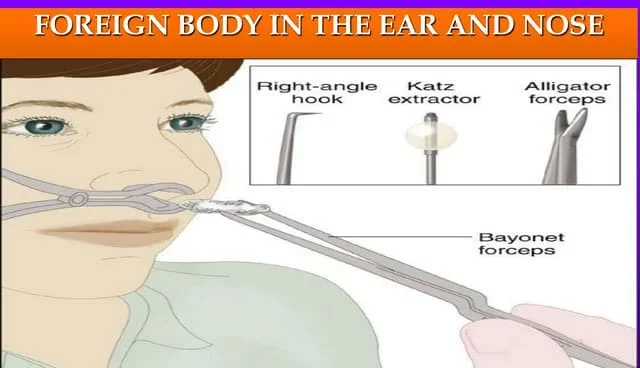
Removal of foreign bodies from the ear and nose
FOREIGN BODY IN THE EAR AND NOSE A foreign body refers to any object that is not naturally present in a specific area of the body. Foreign bodies can be objects that are accidentally inserted or lodged in these areas, causing discomfort, obstruction, and potential complications. FOREIGN BODY IN THE EAR: A foreign body in…
-
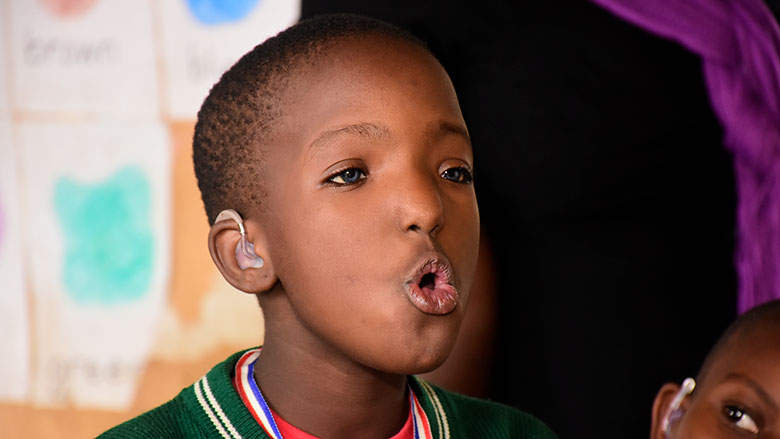
HEARING IMPAIRMENT
HEARING IMPAIRMENT Hearing impairment is defined as an impairment in hearing, whether permanent or fluctuating, that adversely affects a person’s ability to hear and understand sounds. It can range from mild to profound. But let’s first see what Hearing means Hearing starts when sound waves traveling through the air reach the outer ear, also called…
