-

Aggression and Violence
Aggression: It is harsh physical or verbal action intended to harm or injure another person. OR Aggression is verbal expression of readiness to cause an attack with threats. Violence: is threat with physical attack that results into harm. OR Violence is showing marked physical force causing harm being inflicted on another person…
-

Suicide and Suicidal Behaviour
Suicide Suicide is the deliberate act of ending one’s life Suicide refers to deliberate act of self harm that result into death. Reasons for committing suicide To solve problems like adultery for his/her spouse, poverty, stigma, discrimination, To harm others incase of anger to parents decisions for children. To end life in-case of terminal illnesses…
-

Research
Introduction to research Research is the systematic collection, analysis and interpretation of data to answer a certain question or solve a problem Research is a term derived from the combination of two words: “re” and “search.” “Re” is a prefix meaning “again” or “anew,” and “search” is a verb signifying a close and careful examination, testing, probing,…
-
Concepts of Primary Health Care
Concepts of Primary Health Care – PHC Essential Health Care: This is the care that meets the local needs of majority that enable individual to live a socially and economically productive life. Practically, scientifically sound methods and technology: The health care system should be able to solve the health problems in that community. Accessibility Health…
-

Anaemia in Pregnancy
ANAEMIA IN PREGNANCY Anaemia during pregnancy refers to a condition where the red blood cell count or haemoglobin level in the mother’s blood is lower than normal. Anaemia in pregnancy is defined as haemoglobin (Hb) concentration is less than 11 g/dl. Anaemia means a reduction in oxygen carrying capacity or in quantity of red blood…
-
Domiciliary Care
Domiciliary care is an obstetric care given to a mother in her home during pregnancy, labour and puerperium Types of Domiciliary Care Type one domiciliary midwifery care “continuity:; In this type the woman is cared for in her home all through during antenatal period delivery and postnatal care. The woman will only visit a health…
-

Terms used in Anatomy and Physiology
Module Unit CN-111: Anatomy and Physiology (I) Contact Hours: 60 Module Unit Description: Introduces students to the anatomy and physiology of the human body, covering the structure and function of different body parts and systems, specifically skeletal, muscular, circulatory, and digestive systems. Learning Outcomes for this Unit: By the end of this unit, the student…
-

Pulmonary Hemorrhage
PULMONARY HEMORRHAGE Pulmonary hemorrhage (PH) is a serious condition in children, characterized by bleeding into the alveoli and airways of the lungs. Pulmonary haemorrhage is an acute bleeding from the lung, from the upper respiratory tract, the trachea, and the alveoli. Pulmonary hemorrhage (PH) in infants is a serious condition characterized by bleeding into the…
-
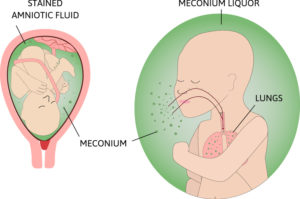
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) Lecture Notes Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) Meconium Aspiration Syndrome (MAS) is a condition of respiratory distress in a newborn infant, typically born at or near term, caused by the aspiration of meconium-stained amniotic fluid into the tracheobronchial tree. Let’s break down this definition: Meconium: This refers to the newborn’s first stool.…
-

Broncho pulmonary dysplasia
Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) Lecture Notes Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic lung disease that affects premature infants who have received prolonged respiratory support, usually mechanical ventilation and oxygen, for conditions like Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS). Broncho Pulmonary Dysplasia (BPD) is also known as Chronic lung disease of premature babies Chronic lung disease…
