To understand tonsillitis, it's essential to first know what the tonsils are and their role in the body.
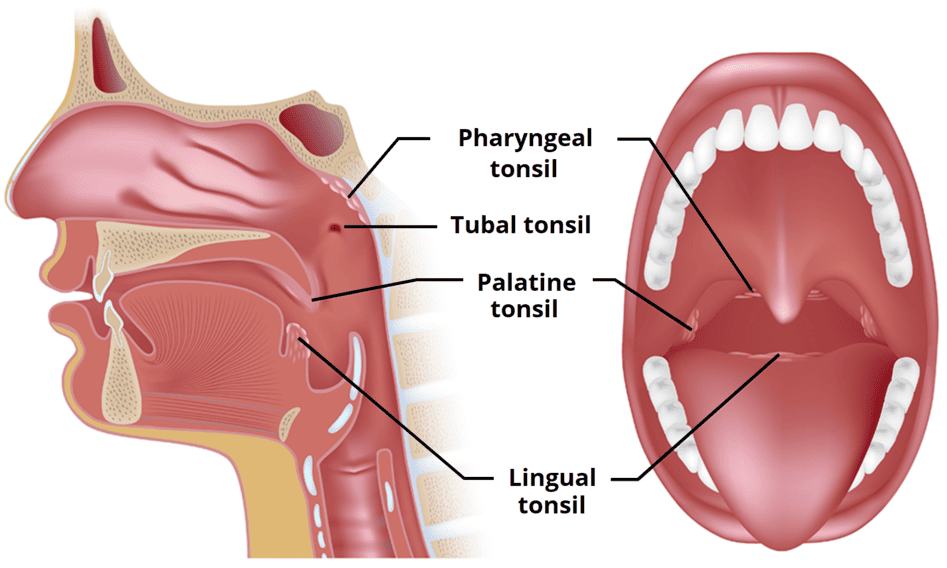
- Location: The tonsils are lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. The most commonly referred to tonsils are the palatine tonsils, which are two oval-shaped pads of tissue located on either side of the back of the throat, visible upon examination. Other tonsils include the lingual tonsils (at the base of the tongue) and the pharyngeal tonsil (adenoid, located behind the nasal cavity).
- Structure: Each palatine tonsil is covered by mucous membrane and contains crypts (invaginations or pockets) where lymphocytes are present.
- Function: Tonsils are part of the body's lymphatic system and play a crucial role in the immune system. They act as a first line of defense against pathogens (bacteria, viruses) that enter the body through the mouth or nose. They contain immune cells (lymphocytes) that can identify and trap germs, producing antibodies to fight infections. They are particularly active in early childhood when the immune system is developing.
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, most commonly affecting the palatine tonsils. This inflammation results from an infection, which can be caused by either viruses or bacteria.
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils, two oval-shaped pads of tissue located at the back of the throat (one tonsil on each side). Tonsillitis is contagious especially before signs and symptoms show up. Tonsils act as filters, trapping germs that could otherwise enter the air and cause infection in our body. They also make antibodies. Tonsillitis may be acute or chronic.
- Inflammation: The tonsils become swollen, red, and often painful.
- Infection: It is primarily an infectious process, leading to the body's immune response in the tonsillar tissue.
- Symptoms: Typically characterized by a sore throat, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), and sometimes fever.
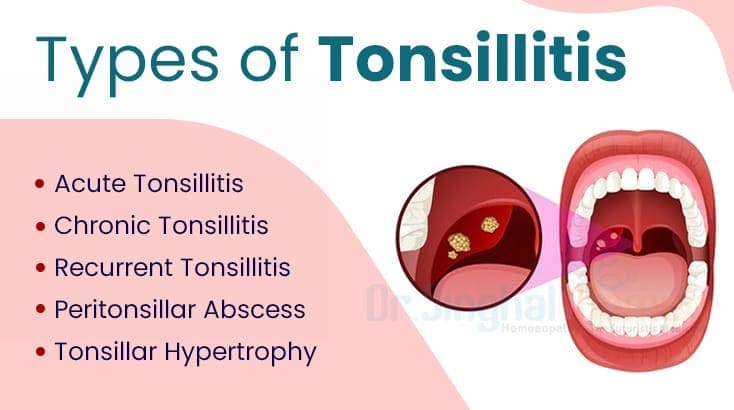
When discussing "types" of tonsillitis, it's helpful to classify them in a few ways:
- Based on Duration and Frequency: This is the most common medical classification.
- Based on Etiology (Cause): Viral vs. Bacterial.
- Related Conditions/Complications often seen in conjunction with Tonsillitis: Conditions that can either be confused with tonsillitis or arise from it.
This is the primary way medical professionals categorize tonsillitis episodes.
- Acute Tonsillitis: A sudden onset of tonsil inflammation due to infection. Symptoms are severe but short-lived. It is usually accompanied by inflammation of the fornices and pharynx. It is more common in children than adults, normally caused by group A Beta streptococcus and sometimes viruses. Presents with Severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, often headache, malaise.
- Recurrent Tonsillitis: Multiple, distinct episodes of acute tonsillitis occurring frequently over a specific period. This isn't a continuous state but rather repeated acute infections.
- Common Criteria (often used for considering tonsillectomy):
- 7 episodes in the past year, OR
- 5 episodes per year in the past 2 years, OR
- 3 episodes per year in the past 3 years.
- Common Criteria (often used for considering tonsillectomy):
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Persistent low-grade infection or inflammation of the tonsils that lasts for an extended period, often weeks to months. It may not have the severe acute symptoms but rather a persistent sore throat, bad breath, and sometimes enlarged tonsils with crypts. It is defined as persistent progressive inflammation of the tonsils. If an acute attack re-occurs 5-6 times a year, it indicates that some one has failed to develop immunity and it is considered to be chronic. Presents with Chronic sore throat, bad breath (halitosis), feeling of something stuck in the throat, persistent tenderness of neck lymph nodes.
- Tonsillar Hypertrophy: Enlargement of the tonsils without necessarily being acutely or chronically infected. This can occur due to previous infections, or simply be a normal variation, especially in children. When significantly enlarged, they can obstruct breathing, especially during sleep (sleep apnea). Presents with Snoring, difficulty breathing during sleep, muffled voice, difficulty swallowing large foods.
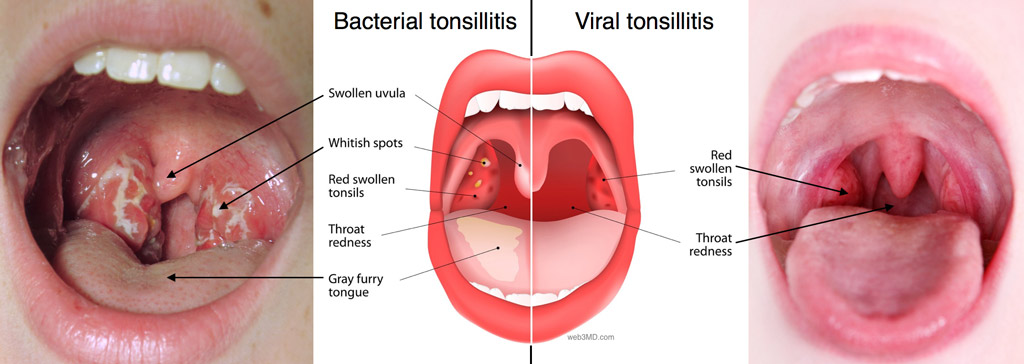
- Viral Tonsillitis: Caused by various viruses (e.g., adenoviruses, rhinoviruses, influenza, parainfluenza, coronaviruses, Epstein-Barr virus). This is the most common cause of tonsillitis. "Viral" tonsils as red and swollen, but generally without the prominent white patches/exudates often seen in bacterial infections. They may appear more diffusely red. Often accompanied by other viral symptoms like runny nose, cough, hoarseness, conjunctivitis.
- Bacterial Tonsillitis: Most commonly caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus, or GAS), leading to "Strep Throat." Other bacteria can also cause it. "Bacterial" clearly depicts red, swollen tonsils with white spots or exudates. Presents with Sudden onset sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, headache, stomach ache/vomiting (especially in children). Often without prominent cough, runny nose, or hoarseness.
These are not "types" of tonsillitis themselves, but important related conditions that are often considered in the grand of tonsillar inflammation.
- Peritonsillar Abscess (Quinsy): A serious complication of acute tonsillitis where an infection spreads behind the tonsil, forming a collection of pus. This is a medical emergency. Presents with Severe unilateral sore throat, fever, difficulty opening the mouth (trismus), muffled "hot potato" voice, drooling, uvula deviation.
- Tonsilloliths (Tonsil Stones): Small, often yellowish-white, calcified masses that form in the crypts (pockets) of the tonsils. They are composed of bacteria, food debris, and mucus. They are not an infection themselves but can be associated with chronic inflammation or contribute to bad breath. Presents with Bad breath, sensation of something stuck in the throat, chronic sore throat, can sometimes cause pain or discomfort.
- Acute Mononucleosis (Glandular Fever): While a systemic viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), it very commonly presents with severe tonsillitis as a prominent feature, often with significant exudates and lymph node enlargement. It's often classified as a viral cause of severe tonsillitis.
Understanding the causes (etiology) and contributing factors (risk factors) of tonsillitis is crucial for prevention, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment.
- Adenoviruses: Very common cause of upper respiratory infections, often causing pharyngitis and tonsillitis.
- Rhinoviruses: The most frequent cause of the common cold.
- Influenza Virus: Causes the flu, often with severe sore throat.
- Parainfluenza Virus: Another common cause of respiratory infections.
- Coronaviruses: Including those that cause common colds.
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV): The cause of infectious mononucleosis (glandular fever). This often presents with particularly severe tonsillitis, prominent exudates, and significant lymphadenopathy.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): Can cause herpetic gingivostomatitis, which can involve the tonsils.
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV): Another virus that can cause a mono-like illness.
- Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Streptococcus or GAS): This is by far the most common bacterial cause, leading to "Streptococcal pharyngitis" or "Strep Throat." It is clinically significant due to potential non-suppurative complications (e.g., Rheumatic Fever, Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis) if left untreated.
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Moraxella catarrhalis
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae
- Corynebacterium diphtheriae (rare in developed countries due to vaccination, but causes diphtheria with a characteristic pseudomembrane).
- Anaerobic bacteria (especially in peritonsillar abscesses).
- Age:
- Children: Tonsillitis is most common in school-aged children (5-15 years old) due to their developing immune systems and increased exposure to germs in school or daycare settings. Viral tonsillitis is more common in very young children, while bacterial tonsillitis (Strep) is more prevalent in children over 3.
- Infants/Toddlers: Rarely get strep throat before age 3.
- Adults: While less common than in children, adults can still get tonsillitis.
- Frequent Exposure to Germs:
- School/Daycare: Children in these environments are in close contact with many other children, facilitating the spread of viral and bacterial infections.
- Crowded Environments: Living or working in crowded conditions can increase exposure to pathogens.
- Compromised Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems (e.g., due to illness, medications, or chronic conditions like HIV) may be more susceptible to recurrent or severe infections, including tonsillitis.
- Smoking/Exposure to Secondhand Smoke: Irritants from smoke can inflame the mucous membranes of the throat and tonsils, making them more vulnerable to infection.
- History of Recurrent Tonsillitis: Individuals who have had tonsillitis multiple times are at higher risk for future episodes. This might be due to genetic predisposition, chronic infection in tonsillar crypts, or persistent exposure.
- Close Contact with an Infected Individual: Tonsillitis-causing pathogens are spread through respiratory droplets (coughing, sneezing, talking). Close proximity to someone with tonsillitis increases the risk of transmission.
- Poor Hygiene: Infrequent handwashing, especially after coughing, sneezing, or before eating, can contribute to the spread of infectious agents.
- Allergies: While not a direct cause, chronic irritation and inflammation from allergies can potentially make the tonsils more susceptible to infection.
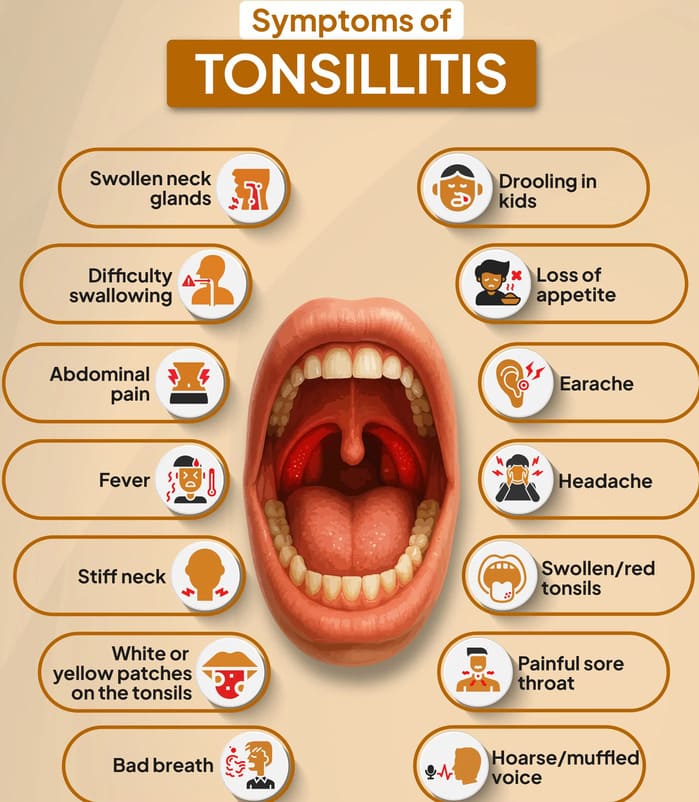
The clinical presentation of tonsillitis can vary depending on whether the infection is viral or bacterial, and if it's acute or chronic.
- Sore Throat (Pharyngalgia): This is the most common and often the first symptom. It can range from mild discomfort to severe pain, making swallowing difficult.
- Difficulty Swallowing (Dysphagia/Odynophagia): Pain or discomfort when swallowing food, liquids, and even saliva. Patients may avoid eating and drinking due to this.
- Fever: Often present, ranging from low-grade (common in viral) to high (more common in bacterial). Associated with Chills, body aches (myalgia), headache.
- Red, Swollen Tonsils: The palatine tonsils (visible at the back of the throat) appear enlarged, inflamed, and bright red. This is the defining visual sign.
- Tender, Swollen Lymph Nodes (Cervical Lymphadenopathy): The lymph nodes in the neck, particularly those under the jaw and at the sides of the neck, often become enlarged and painful to the touch as they fight the infection.
- Voice Changes: A muffled or "hot potato" voice can occur due to the swelling in the throat, making articulation difficult.
- Malaise/Fatigue: A general feeling of being unwell, tired, and lacking energy.
While there can be overlap, some signs are more indicative of one cause over the other.
- Runny Nose (Rhinorrhea): Clear or sometimes thicker nasal discharge.
- Cough: Often a dry or productive cough.
- Hoarseness/Laryngitis: Inflammation of the voice box leading to a rough voice.
- Conjunctivitis: Red, watery eyes.
- Oral Ulcers/Vesicles: Small blisters or sores in the mouth (e.g., in herpangina caused by coxsackievirus).
- Absence of Exudates (Often): While viral tonsillitis can have exudates (as seen in severe cases like mononucleosis), they are less consistently present and often less prominent than in bacterial infections.
- White Patches or Streaks on Tonsils (Exudates/Pus): These are collections of pus or fibrin, appearing as white, yellowish, or gray spots or streaks on the surface of the tonsils. This is a classic sign of bacterial tonsillitis.
- Red Spots on the Soft Palate (Petechiae): Tiny, pinpoint red spots on the roof of the mouth, behind the tonsils. This is a strong indicator of Strep Throat.
- Strawberry Tongue: The tongue may appear red and bumpy, resembling a strawberry (early phase white coating, later red and shiny).
- Rash (Scarlatiniform Rash): In some cases of Strep Throat, a fine, red, sandpaper-like rash can develop, indicating Scarlet Fever.
- Nausea, Vomiting, Abdominal Pain: More common in children with Strep Throat.
- Absence of Viral Symptoms (often): Unlike viral tonsillitis, Strep Throat is less likely to be accompanied by cough, runny nose, or conjunctivitis.
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Persistent sore throat, halitosis (bad breath), persistently enlarged tonsils, and sometimes the presence of tonsilloliths (tonsil stones) in the tonsillar crypts.
- Peritonsillar Abscess (Quinsy): Extremely severe, typically unilateral (one-sided) sore throat, severe difficulty swallowing, drooling, trismus (difficulty opening the mouth), muffled "hot potato" voice, and marked deviation of the uvula to the opposite side due to the pus collection pushing the tonsil forward.
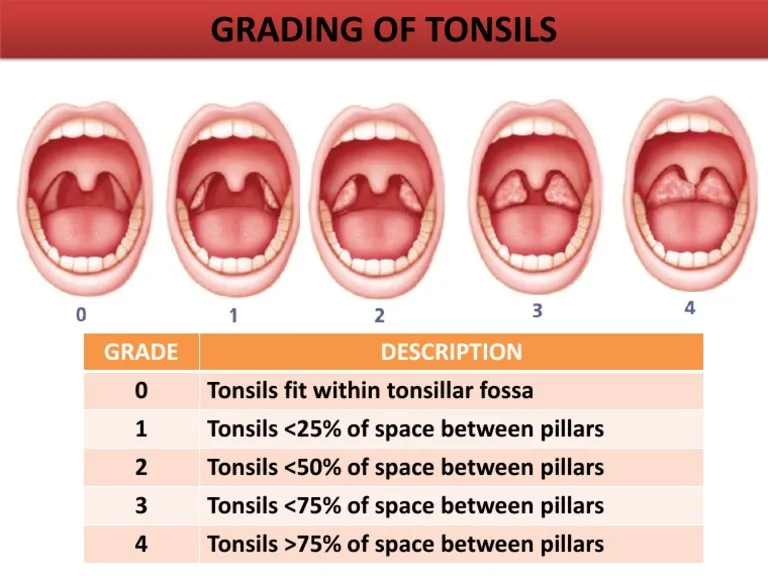
Diagnosing tonsillitis involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The primary goal is to determine if the tonsillitis is viral or bacterial, as this impacts treatment.
- Symptom Onset and Duration: Acute vs. chronic, gradual vs. sudden.
- Specific Symptoms: Sore throat severity, difficulty swallowing, fever (measured temperature), headache, body aches, cough, runny nose, hoarseness, abdominal pain, nausea/vomiting.
- Exposure History: Recent contact with sick individuals (especially those with strep throat or mono).
- Past Medical History: History of recurrent tonsillitis, allergies, immunosuppression, rheumatic fever.
- Risk Factors: Age, exposure to daycare/school, smoking.
- General Appearance: Assess for signs of distress, dehydration, fever, and overall well-being.
- Head and Neck Exam:
- Oropharyngeal Examination (Thorough Throat Inspection):
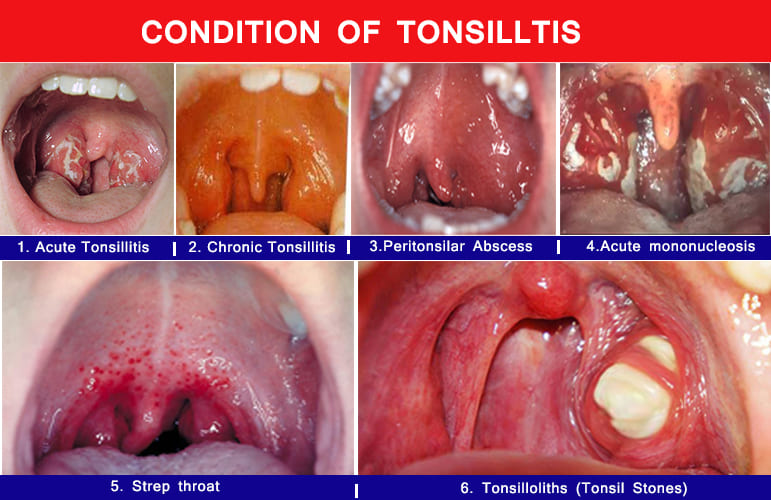
- Tonsils: Visual inspection for size, redness, swelling, presence of exudates (white patches or streaks), petechiae on the soft palate, or ulcerations. Your images "1. Acute Tonsillitis," "4. Acute mononucleosis," "5. Strep throat," and the "Bacterial" vs. "Viral" diagrams are excellent examples of what to look for.
- Uvula: Check for deviation, which could indicate a peritonsillar abscess. Your image "3. Peritonsilar Abscess" is a good visual.
- Pharynx: Assess for general redness or inflammation.
- Tongue: Look for "strawberry tongue" (red and bumpy), or any coating.
- Cervical Lymph Nodes: Palpate the neck for tenderness and enlargement of lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy).
- Oropharyngeal Examination (Thorough Throat Inspection):
- Skin Exam: Check for any rashes (e.g., scarlatiniform rash suggestive of scarlet fever).
Since viral and bacterial tonsillitis often present similarly, laboratory tests are crucial, especially to identify Group A Streptococcus (GAS), which requires antibiotic treatment.
- Procedure: A quick swab of the tonsils and posterior pharynx is taken. The swab is then tested for the presence of GAS antigens.
- Results: Results are typically available within 5-15 minutes.
- Sensitivity/Specificity: High specificity (meaning a positive test is very likely true positive), but variable sensitivity (meaning a negative test might miss some cases, especially in children).
- Usage: If positive, usually indicates GAS infection and antibiotics are prescribed. If negative, especially in children, a throat culture is often recommended due to sensitivity concerns.
- Procedure: Similar to RADT, a swab of the tonsils and pharynx is taken and sent to a lab to grow any bacteria present.
- Results: Takes 24-48 hours for results.
- "Gold Standard": Throat culture is considered the gold standard for diagnosing GAS pharyngitis due to its high sensitivity.
- Usage: Often performed when RADT is negative, especially in children, or when there's a strong clinical suspicion of strep despite a negative RADT. Not routinely needed if RADT is positive.
- Usage: Not routinely performed for uncomplicated tonsillitis. However, it can be helpful in cases of severe or atypical presentations.
- Findings: Elevated white blood cell count (leukocytosis) with a predominance of neutrophils suggests bacterial infection. Atypical lymphocytes and lymphocytosis may suggest a viral infection like infectious mononucleosis.
- Usage: Performed if infectious mononucleosis is suspected (e.g., prolonged fatigue, marked lymphadenopathy, significant splenomegaly, very severe tonsillar exudates, particularly in adolescents/young adults).
- Results: Monospot is a rapid test, but can be negative early in the illness or in very young children. EBV serology is more definitive.
- Tonsillar Exudates
- Swollen, Tender Anterior Cervical Lymph Nodes
- History of Fever
- Absence of Cough
- A point is given for each present criterion. Higher scores increase the probability of Strep Throat. (McIsaac score adds age modification).
When a patient presents with a sore throat, fever, and tonsillar inflammation, it's nice to consider a range of other conditions that can mimic tonsillitis. Differentiating these helps in avoiding misdiagnosis and ensuring appropriate management.
These are often confused with bacterial tonsillitis due to overlapping symptoms.
- Common Cold (Viral Pharyngitis): Sore throat is usually milder, often accompanied by prominent "cold" symptoms like runny nose, nasal congestion, cough, and sneezing. Tonsils may be mildly red but rarely have significant exudates.
- Infectious Mononucleosis (EBV Pharyngitis): While it often presents with severe tonsillitis , it's accompanied by extreme fatigue, prolonged fever, diffuse lymphadenopathy (especially posterior cervical), and sometimes splenomegaly. Symptoms tend to be more protracted than typical tonsillitis.
- Herpangina: Caused by Coxsackievirus. Characterized by small, painful blisters (vesicles) or ulcers on the tonsils, soft palate, and uvula, rather than diffuse exudates. seen in young children.
- Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD): Also caused by Coxsackievirus. Features include oral lesions (blisters/ulcers anywhere in the mouth, not just tonsils) and a characteristic rash on the hands and feet.
- Influenza (Flu): Abrupt onset of high fever, body aches, headache, fatigue, and dry cough, often preceding or accompanying sore throat.
- Diphtheria: (Rare in vaccinated populations). Formation of a tough, grayish-white pseudomembrane on the tonsils, pharynx, or larynx that bleeds if attempts are made to remove it. Can cause severe systemic toxicity.
- Gonococcal Pharyngitis: Sexually transmitted infection. May be asymptomatic or present with a sore throat and exudative pharyngitis. History is key.
- Peritonsillar Abscess (Quinsy): A complication of tonsillitis, not a primary tonsillitis. Characterized by severe, often unilateral, throat pain, trismus (difficulty opening mouth), "hot potato" voice, drooling, and deviation of the uvula.
- Allergies/Post-Nasal Drip: Chronic irritation from post-nasal drip can cause a persistent sore throat, throat clearing, and cough. Typically no fever, exudates, or marked tonsillar swelling.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) / Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR): Acid reflux can irritate the throat, leading to chronic sore throat, hoarseness, sensation of a lump in the throat, and chronic cough. Worse at night or after eating.
- Oral Thrush (Candidiasis): White, creamy patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and sometimes tonsils that can be scraped off, revealing reddened, sometimes bleeding, tissue underneath. Common in infants, immunocompromised individuals, or those on antibiotics/steroids.
- Agranulocytosis: A severe reduction in white blood cells (neutrophils), leading to profound immunosuppression and severe, often necrotic, pharyngitis/tonsillitis. Patients are usually very ill and may have a history of certain medications.
- Foreign Body: Sharp localized pain, especially with swallowing, often unilateral, due to a fish bone or other foreign object lodged in the tonsil or pharynx.
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS) / Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN): Severe mucocutaneous reactions, often drug-induced, causing painful blistering and erosion of mucous membranes (including oral and pharyngeal) and skin. Patients are very unwell with widespread symptoms.
The management and treatment of tonsillitis are guided by the underlying cause (viral vs. bacterial), the severity of symptoms, and the frequency of recurrence. The goals/aims are:
- To limit and prevent the spread of infection.
- To relieve signs and symptoms such as pain and fever.
- To treat the underlying cause (if bacterial).
- To prevent complications.
This involves symptomatic relief for all types of tonsillitis and specific antimicrobial treatment for bacterial cases.
- Reassurance: Reassure the patient and relatives about the nature of the condition and the plan of care.
- Patient Isolation & Barrier Nursing:
- Rationale: To limit the spread of infection (especially bacterial or highly contagious viral forms) to other patients or healthcare providers.
- Practice: Admit the patient to a medical isolation ward if deemed necessary. Emphasize isolation precautions and barrier nursing techniques (e.g., hand hygiene, masks, gloves) depending on the pathogen.
- Observations:
- Vital Signs: Monitor and record temperature, pulse, respiration (TPR), and blood pressure (BP) regularly.
- Specific Observations: Note the degree of tonsillar enlargement and inflammation.
- Complication Monitoring:
- Observe for facial edema, particularly in the morning, which may suggest nephritis (a potential complication of strep throat).
- Observe for painful joints, suggestive of rheumatic fever (another potential strep complication).
- Monitor fluid intake and output for diminished urine output and albumin, which could indicate renal involvement.
- Continuously observe for the development of other complications (e.g., peritonsillar abscess).
- Fever Management:
- Tepid Sponging: Use tepid (lukewarm) water sponging to help reduce high fever, particularly in children.
- Antipyretics: Administer analgesics that also reduce fever (antipyretics) like Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) or Ibuprofen.
- Pain Management:
- Analgesics: Administer appropriate analgesics, such as Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen, to relieve pain and discomfort. Note: Aspirin is generally avoided in children and teenagers due to the risk of Reye's Syndrome.
- Hydration:
- Encourage Oral Fluids: Emphasize and encourage plenty of oral fluids (at least 4-5 liters in 24 hours if tolerated) to prevent dehydration and soothe the throat. Cold fluids, popsicles, and warm teas can be comforting.
- Oral Hygiene & Throat Soothers:
- Mouth Gargling: Encourage frequent throat gargling with warm normal saline (salt water) solution to soothe the throat and maintain oral hygiene.
- Mouth Care: Perform regular mouth care to ensure oral hygiene.
- Diet:
- Highly Nourishing, Soft, Light Diet: Gradually introduce a highly nourishing, soft, and light diet as tolerated. Avoid foods that are sharp, spicy, or difficult to chew and swallow.
- Support for Children:
- If the patient is a child, provide support for the neck while swallowing to ease discomfort.
- General Nursing Care: Provide daily nursing care as for any other patient, focusing on comfort and hygiene.
- Antibiotics:
- Indication: Prescribed only when bacterial tonsillitis (most commonly Group A Streptococcus) is confirmed or highly suspected. Antibiotics are ineffective against viral tonsillitis.
- First-Line: Penicillin V (e.g., 500 mg every 6 hours for 10 days) is the antibiotic of choice for Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Alternatives:
- For those allergic to penicillin: Macrolides (e.g., Erythromycin, Azithromycin) or Cephalexin may be used.
- For severe cases or specific situations: Broader spectrum antibiotics like IV Ceftriaxone might be used initially, particularly if admitting for complications.
- Compliance: Emphasize the importance of completing the entire 10-day course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve earlier, to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria and prevent complications like rheumatic fever.
Tonsillectomy, the surgical removal of the tonsils, is indicated for specific, usually chronic or severe, conditions where conservative medical management has failed or complications arise.
Tonsillectomy is not indicated for simple tonsillar enlargement unless it causes significant problems, as tonsils naturally decrease in size with age, especially in children. Indications are typically for:
- Chronic Recurrent Tonsillitis:
- Frequency: When the disease chronically interferes with schooling or daily life due to fear of complications or constant recurrence. Specific criteria often include:
- 7 episodes in the preceding year, OR
- 5 episodes per year for the preceding 2 years, OR
- 3 episodes per year for the preceding 3 years.
- Each episode must be clinically well-documented (e.g., by a physician with specific symptoms and/or positive rapid strep test/culture).
- Frequency: When the disease chronically interferes with schooling or daily life due to fear of complications or constant recurrence. Specific criteria often include:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) / Upper Airway Obstruction:
- When enlarged tonsils cause significant breathing difficulties during sleep, leading to snoring, apneas (pauses in breathing), or hypopneas (shallow breathing).
- Recurrent Peritonsillar Abscess:
- After the acute management of a peritonsillar abscess, if there is a history of recurrent PTAs.
- Chronic Tonsillitis:
- Persistent sore throat, chronic halitosis (bad breath), or presence of tonsilloliths that are resistant to conservative management and significantly impact quality of life.
- Unilateral Tonsil Enlargement (Suspicion of Malignancy):
- Especially in adults, if one tonsil is significantly larger than the other without apparent cause, to rule out lymphoma or squamous cell carcinoma.
The patient is prepared like any other patient for general anesthesia and surgery, with special emphasis on:
- Thorough Medical History & Physical Exam: To assess overall health and identify any contraindications or risk factors.
- Laboratory Tests: Routine pre-operative blood tests (e.g., CBC, coagulation profile) to ensure the patient is fit for surgery and to assess bleeding risk.
- Oral Care: Emphasis on excellent oral hygiene before surgery to reduce bacterial load.
- Pre-operative Antibiotics: May be administered (e.g., IV Ceftriaxone) to reduce the risk of post-operative infection, although not universally practiced for all tonsillectomies.
- NPO (Nil Per Os): Patient is instructed not to eat or drink for a specified period before surgery.
- Patient Education: Explain the procedure, potential risks, and post-operative expectations to the patient and family.
- Anesthesia: Carried out under general anesthesia.
- Procedure: The tonsil is carefully dissected and removed from the underlying pharyngeal tissue using various surgical techniques (e.g., cold knife dissection, electrocautery, radiofrequency ablation, microdebrider).
After surgery, meticulous care is essential for patient recovery and complication prevention.
- Preparation of Recovery Area: A post-operative bed with all necessary accessories (suction, oxygen, vital sign monitor) is prepared.
- Positioning:
- Upon transfer from the operating room, the patient is received and nursed in the lateral (side) position with the head down (recovery position).
- Rationale: This position helps prevent the patient from inhaling blood or tonsil fragments, thus avoiding aspiration, until they are fully alert.
- Post-operative Observations:
- Frequent Monitoring: Vital signs (TPR & BP) are monitored frequently in the immediate post-operative period.
- Skin Color: Observe skin color for any signs of pallor or cyanosis.
- Bleeding: Crucial observation. Observe for signs of bleeding, which is most commonly detected by:
- Frequent Swallowing: The patient may be constantly swallowing small amounts of blood, even if not overtly spitting it out. This is a key indicator of bleeding and requires immediate attention.
- Restlessness: Unusual restlessness can also be a sign of bleeding.
- Overt Blood: Spitting up fresh blood.
- If significant bleeding is suspected, the patient will need to be returned to the theatre for ligation of the bleeding points immediately.
- Secretion Management: Encourage the patient to spit out secretions rather than swallowing them, to help monitor for bleeding.
- Antibiotics:
- Prophylaxis/Treatment: Continue with antibiotics for prophylaxis or to treat potential infections (e.g., IV Ceftriaxone initially, then possibly oral Penicillin V 6 hourly if needed for a longer course).
- Fluid & Diet Progression:
- Hydration: Encourage sips of cold water or clear fluids as soon as the patient is fully awake and swallows without difficulty. This helps prevent dehydration and may soothe the throat.
- Diet: On the next day, the patient is encouraged to drink and eat soft, bland foods. Avoid hot, spicy, or hard/crunchy foods for at least 1-2 weeks.
- Oral Care: Continue oral care, often with warm saline water gargling (if old enough and able to gargle effectively).
- Pain Management: Provide regular and adequate pain relief, as post-tonsillectomy pain can be significant.
- Discharge & Advice: When the patient improves and meets discharge criteria, they are discharged with clear instructions on pain management, diet, activity restrictions, and signs of complications (especially bleeding) requiring immediate medical attention.
Nursing Diagnoses are clinical judgments about individual, family, or community responses to actual or potential health problems/life processes. They provide the basis for selection of nursing interventions to achieve outcomes for which the nurse has accountability.
- Related To: Inflammation and swelling of the tonsils, pharyngeal irritation.
- As Evidenced By: Patient verbalizing pain (e.g., "my throat hurts"), difficulty swallowing, grimacing, restlessness, increased heart rate, refusal to eat/drink.
| Intervention | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Assess Pain | Regularly assess pain level using a pain scale (e.g., 0-10) and observe non-verbal cues. |
| Administer Analgesics | Administer prescribed pain medications (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen) as ordered, ensuring proper dosage and timing. Educate patient/parents on avoiding aspirin in children. |
| Provide Comfort Measures |
|
| Encourage Rest | Promote a quiet environment for rest to conserve energy. |
| Educate | Teach patient/family about pain management techniques and when to report worsening pain. |
- Related To: Difficulty/painful swallowing (odynophagia), fever leading to increased insensible fluid loss.
- As Evidenced By: (Potential signs of dehydration) dry mucous membranes, decreased urine output, poor skin turgor, patient expressing reluctance to drink.
| Intervention | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Monitor Intake and Output (I&O) | Accurately record all fluid intake and urine output. |
| Encourage Oral Fluid Intake |
|
| Assess Hydration Status | Monitor mucous membranes, skin turgor, fontanelles (in infants), and urine specific gravity. |
| Administer IV Fluids | If oral intake is severely compromised or signs of dehydration are present, administer intravenous fluids as prescribed. |
| Educate | Instruct patient/family on recognizing signs of dehydration and the need to increase fluid intake. |
- Related To: Painful swallowing, loss of appetite due to illness, difficulty consuming solid foods.
- As Evidenced By: Weight loss (if chronic), reluctance to eat, verbalization of inability to eat, poor intake recorded.
| Intervention | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Assess Nutritional Status | Monitor weight (daily if possible), review dietary intake, and assess for signs of malnutrition. |
| Offer Soft, Bland Diet | Provide foods that are easy to swallow, non-irritating, and nutritionally dense (e.g., pureed foods, mashed potatoes, cooked cereals, yogurts, soups). Avoid spicy, acidic, or hard/crunchy foods. |
| Small, Frequent Meals | Offer smaller, more frequent meals/snacks rather than large meals. |
| High-Calorie, High-Protein Supplements | Consider liquid nutritional supplements if oral intake remains poor. |
| Encourage Oral Hygiene | Good mouth care before meals can improve appetite and comfort. |
| Educate | Advise family on appropriate food choices and strategies to encourage intake. |
- Related To: Presence of infectious organisms (bacterial/viral), close contact with others.
| Intervention | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Implement Isolation Precautions |
|
| Educate on Hand Hygiene | Emphasize meticulous handwashing for the patient, family, and healthcare providers. |
| Avoid Sharing | Instruct patient not to share eating utensils, drinks, or food. |
| Contain Respiratory Secretions | Teach patient to cover mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and dispose of tissues properly. |
| Administer Antibiotics (if bacterial) | Ensure adherence to the prescribed antibiotic regimen to eradicate the bacteria and reduce contagiousness. Educate on completing the full course. |
| Restrict Contact | Advise patient to avoid close contact with others, especially during the contagious period (until afebrile and on antibiotics for 24 hours for bacterial tonsillitis). |
- Related To: Infectious process, inflammation.
- As Evidenced By: Elevated body temperature, flushed skin, tachycardia, tachypnea, warm to touch.
| Intervention | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Monitor Temperature | Assess body temperature regularly. |
| Administer Antipyretics | Administer prescribed fever-reducing medications (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen). |
| Tepid Sponging | Use tepid water for sponging if fever is very high and other measures are insufficient. |
| Provide Light Clothing/Bedding | Avoid overheating. |
| Maintain Hydration | Encourage fluid intake as discussed under risk for deficient fluid volume. |
| Monitor for Seizures | Especially in young children susceptible to febrile seizures. |
- Related To: Lack of exposure to information regarding tonsillitis, its management, and prevention of complications.
- As Evidenced By: Patient/family asking questions, expressing misconceptions, inappropriate behaviors (e.g., not completing antibiotics).
| Intervention | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Assess Learning Needs | Determine what the patient/family already knows and what information they require. |
| Provide Education |
|
| Use Teach-Back Method | Ask the patient/family to explain information in their own words to ensure understanding. |
| Provide Written Materials | Supplement verbal instruction with written handouts. |
- Related To: Untreated/inadequately treated infection, severe inflammation.
- As Evidenced By: (Potential for) signs of peritonsillar abscess, rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, airway obstruction.
| Intervention | Rationale |
|---|---|
| Monitor for Specific Signs |
|
| Prompt Reporting | Report any signs of complications to the physician immediately. |
| Patient Education | Emphasize to the patient/family the importance of completing antibiotics and recognizing early signs of complications to seek urgent medical care. |
Information needed for patients and their caregivers to effectively manage tonsillitis, prevent recurrence, and ensure a healthy recovery, particularly following surgical intervention.
- Complete Antibiotic Courses: For bacterial tonsillitis, strict adherence to the full course of antibiotics is paramount to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria and prevent recurrence.
- Good Hygiene Practices:
- Hand Washing: Emphasize frequent and thorough hand washing, especially after coughing, sneezing, and before eating.
- Avoid Sharing: Discourage sharing of eating utensils, drinks, and personal items.
- Avoid Irritants: Minimize exposure to environmental irritants like cigarette smoke, which can irritate the throat and increase susceptibility to infection.
- Boost Immune System:
- Balanced Diet: Encourage a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Adequate Sleep: Promote sufficient rest.
- Regular Exercise: Encourage moderate physical activity.
- Identify and Manage Triggers: If certain factors consistently precede tonsillitis episodes (e.g., allergies, exposure to specific environments), discuss strategies to minimize exposure or manage these triggers.
- Consider Tonsillectomy: For patients with recurrent, well-documented episodes of tonsillitis that significantly impact quality of life, tonsillectomy becomes a long-term management strategy to eliminate the source of infection.
This is a critical period requiring specific guidance to ensure a smooth recovery and prevent complications.
- Pain Management:
- Medication: Provide clear instructions on prescribed pain medications (analgesics), including dosage, frequency, and potential side effects. Emphasize taking medication before pain becomes severe.
- Non-Pharmacological: Advise on soothing measures like cold liquids, popsicles, ice chips, and sometimes a cool compress to the neck.
- Hydration:
- Crucial: Stress the extreme importance of adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration and aid healing. Even if painful, encourage frequent small sips of water or other clear, non-acidic fluids.
- Signs of Dehydration: Educate parents/patients on signs of dehydration (e.g., decreased urination, dry mouth, lethargy) and when to seek medical attention.
- Diet Progression:
- Initial: Start with clear, cold liquids immediately post-op.
- Gradual Advancement: Progress to soft, bland foods (e.g., mashed potatoes, yogurt, scrambled eggs, well-cooked pasta, pureed fruits) as tolerated over the first week.
- Avoid: Hard, crunchy, sharp (e.g., chips, toast), spicy, or highly acidic foods (e.g., citrus juices, tomatoes) for at least 1-2 weeks, as these can irritate the surgical site and increase bleeding risk.
- Activity Restrictions:
- Rest: Emphasize rest for the first few days.
- Avoid Strenuous Activity: Advise against vigorous activities, heavy lifting, contact sports, and excessive talking/shouting for 10-14 days to minimize bleeding risk.
- School/Work: Discuss appropriate return to school or work schedules, often after 7-10 days depending on recovery.
- Monitoring for Complications:
- Bleeding: This is the most serious complication. Educate on signs of bleeding:
- Frequent Swallowing: The most important sign, often indicative of slow internal bleeding.
- Fresh red blood or blood clots from the mouth.
- Vomiting blood.
- Increased pain that is not relieved by medication.
- Instruct to seek immediate medical attention (e.g., go to the emergency room) if any signs of bleeding occur.
- Fever: A low-grade fever is common; persistent high fever may indicate infection and warrants medical consultation.
- Dehydration: As above.
- Signs of Infection: Increased redness, swelling, pus, or foul odor from the throat.
- Bleeding: This is the most serious complication. Educate on signs of bleeding:
- Oral Hygiene: Gentle mouth rinses with plain water (not vigorous gargling) may be advised to keep the mouth clean. Avoid harsh mouthwashes.
- Follow-up Appointments: Stress the importance of attending all scheduled post-operative follow-up appointments with the surgeon.
- Understanding the Disease: Ensure a clear understanding of whether the tonsillitis is viral or bacterial and why specific treatments (e.g., antibiotics) are or are not used.
- Medication Adherence: Reinforce the importance of taking all medications as prescribed.
- When to Seek Medical Attention: Provide clear guidelines on signs and symptoms that warrant a return visit to the clinic or an emergency department visit (e.g., worsening pain, difficulty breathing, rash, signs of dehydration, signs of complications).
- Preventive Measures: Reiterate hygiene practices and lifestyle choices that can reduce the risk of future infections.
- Coping Strategies: Offer emotional support and practical advice for coping with the discomfort of tonsillitis or the recovery from tonsillectomy.
While tonsillitis is a common and usually self-limiting or easily treated condition, it can lead to various complications if left untreated, improperly treated, or in severe cases.
- Peritonsillar Abscess (Quinsy): This is the most common local complication. It's a collection of pus that forms behind the tonsil, typically on one side, pushing the tonsil and uvula towards the opposite side (as seen in your image "3. Peritonsilar Abscess").
- Symptoms: Severe unilateral throat pain, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), painful swallowing (odynophagia), trismus (difficulty opening the mouth), muffled "hot potato" voice, drooling, and fever.
- Treatment: Requires urgent medical attention, typically involving needle aspiration or incision and drainage of the abscess, along with antibiotics.
- Parapharyngeal Abscess: A more serious, deeper infection in the space alongside the pharynx, which can extend into the neck and chest.
- Symptoms: High fever, severe sore throat, neck swelling, dysphagia, and potentially airway obstruction.
- Treatment: Requires aggressive intravenous antibiotics and often surgical drainage.
- Retropharyngeal Abscess: An abscess in the space behind the pharynx, usually seen in young children. Can be life-threatening due to potential for airway compromise.
- Symptoms: Fever, stridor (noisy breathing), neck stiffness, refusal to eat, and drooling.
- Treatment: Surgical drainage and intravenous antibiotics.
- Airway Obstruction: Severely enlarged tonsils, especially during an acute infection or in cases of infectious mononucleosis, can physically block the airway, leading to difficulty breathing. This is particularly concerning in children.
- Symptoms: Stridor, labored breathing, snoring, cyanosis, and in severe cases, respiratory distress.
- Treatment: May require corticosteroids to reduce swelling, and in extreme cases, intubation or tracheostomy.
- Tonsillar Cellulitis: Inflammation and infection of the tissue around the tonsil, without pus formation (precursor to peritonsillar abscess).
- Symptoms: Similar to tonsillitis but more severe localized pain and swelling.
- Treatment: Aggressive antibiotics.
- Tonsilloliths (Tonsil Stones): Small, often foul-smelling, calcified deposits that form in the crypts of the tonsils (as shown in your image "6. Tonsilloliths").
- Symptoms: Chronic bad breath (halitosis), feeling of something stuck in the throat, chronic sore throat.
- Treatment: Usually conservative (gargling, manual removal), but persistent cases can be an indication for tonsillectomy.
These "non-suppurative" complications are immune-mediated and occur as a delayed reaction to an untreated or inadequately treated Streptococcus pyogenes infection.
- Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF): A serious inflammatory disease that can affect the heart, joints, brain, and skin. It's a leading cause of preventable heart disease worldwide (rheumatic heart disease).
- Onset: Typically occurs 2-3 weeks after an untreated strep throat infection.
- Symptoms: Migratory polyarthritis (joint pain that moves from joint to joint), carditis (inflammation of the heart, which can lead to permanent damage), chorea (involuntary movements), subcutaneous nodules, and erythema marginatum (a specific rash).
- Prevention: Prompt and complete antibiotic treatment of strep throat is crucial for preventing ARF.
- Acute Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis (APSGN): An inflammatory kidney disease that occurs as an immune reaction to certain strains of GAS.
- Onset: Typically occurs 1-3 weeks after a strep throat or skin infection.
- Symptoms: Hematuria (blood in urine, often making it dark or cola-colored), edema (swelling, especially in the face and ankles), hypertension (high blood pressure), and proteinuria (protein in urine).
- Prevention: Unlike ARF, antibiotic treatment of strep throat does not reliably prevent APSGN, although it can limit the spread of nephritogenic strains.
- Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal Infections (PANDAS): A controversial theory suggesting that in some children, a strep infection can trigger or exacerbate certain neuropsychiatric disorders, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and tic disorders.
- Symptoms: Abrupt onset or exacerbation of OCD and/or tics, often following a strep infection.
- Treatment: Management is complex and often involves a combination of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory agents, and psychiatric therapies.
- Dehydration: Due to difficulty swallowing (odynophagia), patients may avoid drinking, leading to dehydration.
- Weight Loss: In chronic tonsillitis or recurrent severe episodes, persistent pain and difficulty eating can lead to inadequate caloric intake and weight loss.
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Persistent or recurrent inflammation, often leading to chronic sore throat, halitosis, and development of tonsilloliths.
- Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): Infection can spread from the throat to the Eustachian tube, leading to ear infections.
- Sinusitis: Infection can spread to the paranasal sinuses.


Good work
I have already started to love your work
Maybe for Diploma remember we have both directs and extension
Maybe you can see how to handle that
Thanks
You are welcome
Remember this website is just 1 month and a few days old, that means we are still developing the site. We shall incorporate all nursing courses very soon and we really appreciate your feedback.
I love 💕 every about this,greatest appreciate
Am great ful for the work and help
Thanks for the best work we appreciate
grateful
Am great ful for the work and help
GREAT TEAM
Great work and well organized
I really love the approach and answering of the question
You are welcome, anything you would like us to improve?
Good luck….simple and precice approach
Thanks for the summarized notes ….I have really understood…God bless you so much
Thank you so much family for supporting the nursing family I always read your content