Table of Contents
ToggleMARKETING
Marketing management involves the performance of activities necessary to get goods or services from the producer to customers, resulting in customer satisfaction and profits for the entrepreneur.
It includes identifying, anticipating, and satisfying customer needs effectively and profitably.
Marketing is the action or business of promoting and selling of products or services.
Marketing refers to the activities a company undertakes to promote the buying or selling of its products or services.
The main objective of marketing is to ensure that the customer’s needs or wants are satisfied and at the same time enabling the entrepreneur to make profits.
Objectives of Marketing:
- To recover cash quickly
- To target a new market
- To penetrate the market, especially for new products
- To increase or maintain market share
- For product line promotion
- To increase sales revenue and profitability
- For functional satisfaction
- To maintain or improve the image of products or a business.
- To achieve the four utilities: possession, time, form, and place utilities
- To develop new products or improve existing products.
Conditions of Exchange:
- At least two parties involved
- Each party has something of value to the other
- Both parties are capable of communication and delivery
- Both parties are free to accept or reject the exchange offer
- Both parties believe it’s appropriate or desirable to deal with the other
SELLING FUNCTION
Selling is a two-way communication between the buyer and seller, aimed at persuading the buyer to accept a product at a stated price.
It involves informing the customer how the product meets their needs, its price, usage instructions, and benefits.
Differences between Selling and Marketing:
Feature | Marketing | Selling |
Focus | Customer needs | Seller needs |
Importance | Customer | Product |
Approach | Integrated, long-term | Immediate gains |
Conversion | Customer needs to product | Product to cash |
Emphasis | Customer satisfaction | Sales volume |
Orientation | External market | Internal business |
Mindset | Customer-oriented | Product-oriented |
- Marketing focuses on customer’s needs while selling focuses on the seller’s needs: Marketing aims to understand and fulfill customer needs, while selling is focused on meeting sales targets and generating revenue for the seller.
- In marketing, a customer enjoys supreme importance, while in selling, the product enjoys supreme importance: Marketing prioritizes customer satisfaction and long-term relationships, whereas selling often prioritizes closing deals and achieving short-term sales targets.
- In marketing, there is an integrated approach to achieve long-term goals, while in selling, there is a fragmented approach to achieve immediate gains: Marketing strategies are designed to achieve long-term growth and sustainability, while selling tactics may focus on short-term results without considering broader business objectives.
- In marketing, an entrepreneur converts customer needs into a product, while in selling, they convert the product into cash: Marketing involves identifying and developing products that meet customer needs, while selling involves persuading customers to purchase existing products.
- In marketing, there is caveat venditor (let the seller be aware), while in selling, there is caveat emptor (let the buyer be aware): Marketing promotes transparency and ethical business practices, while selling may sometimes involve aggressive tactics or incomplete disclosure.
- In marketing, profits are realized through customer satisfaction, while in selling, profits are realized through sales volume: Marketing strategies focus on building customer loyalty and repeat business, while selling may prioritize achieving sales targets regardless of customer satisfaction.
- Marketing aims at external market orientation, while selling aims at internal business orientation: Marketing strategies are outward-focused, considering market trends and customer preferences, while selling activities are often internally focused on meeting sales quotas and targets.
- Marketing is based on a customer approach, while selling is based on a product approach: Marketing starts with understanding customer needs and preferences, while selling starts with promoting the features and benefits of a product.
- Marketing is a series of activities an entrepreneur does to find out who his customers are and what they need or want, while selling is a two-way communication between the buyer and seller aimed at persuading the buyer to buy the product: Marketing involves market research, product development, and promotional activities, while selling focuses on direct interaction with customers to close sales transactions.

Marketing Concepts
Marketing concepts refer to the approaches that guide businesses in their marketing activities. These concepts represent different perspectives on how companies should understand and fulfill customer needs, manage their products, and achieve their marketing objectives.
1. Production Concept:
The production concept emerged during the early stages of capitalism until the mid-1950s. Businesses operating under this concept prioritized production, manufacturing, and efficiency. They believed that customers mainly sought products that were affordable and readily available. The core idea behind the production concept is that companies can lower costs and increase supply through mass production, thereby maximizing profits. For example McDonald’s, which revolutionized the fast-food industry by implementing assembly-line production methods to serve customers quickly and affordably.
2. Product Concept:
The product concept operates on the assumption that customers value quality and features above all else, and are willing to pay a premium for superior products. Companies following this concept continuously strive to improve product quality and innovation. A modern example is the technology industry, where companies like Apple and Samsung invest heavily in research and development to enhance product features and performance. Despite higher prices, customers are attracted to these brands for their reputation of offering high-quality products. Another example is luxury fashion brands like Louis Vuitton and Gucci, which focus on crafting premium products with superior craftsmanship and exclusive designs, catering to customers seeking luxury and prestige.
3. Selling Concept:
Unlike the production and product concepts which focus on production and product quality respectively, the selling concept prioritizes making sales regardless of customer needs or product quality. This approach relies on aggressive sales tactics to push products onto customers. For instance, When retailers offer extended warranties on products such as electronics or appliances, they are implementing the selling concept. Rather than emphasizing the quality or suitability of the product for the customer’s needs, the focus is on persuading customers to add an extra layer of protection to their purchase.
4. Marketing Concept:
The marketing concept revolves around putting the consumer at the center of the organization’s activities. It emphasizes understanding and meeting customer needs and wants through market research and customer-centric strategies. An example is Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy, which focuses on creating emotional connections with consumers through storytelling and personalized experiences, leading to brand loyalty and repeat purchases.
5. Societal Marketing Concept:
The societal marketing concept is a relatively new approach that not only considers the needs and wants of target markets but also emphasizes the well-being of society as a whole. In addition to company profits and customer satisfaction, societal marketing incorporates ethical and social considerations into marketing practices. For example, a local supermarket organizing food drives for homeless shelters or sponsoring educational programs for underprivileged children demonstrates a commitment to societal welfare beyond profit generation.
MARKETING MIX
Marketing mix is a combination of factors that can be controlled by a company to influence consumers to purchase its products.
The marketing mix is a strategic framework that consists of four key components, often referred to as the 4 Ps of marketing. These components are product, price, place, and promotion. The marketing mix helps businesses create plans to differentiate their products or services from competitors and create value for customers .
Product:
- The product component focuses on the item or service being sold. It should satisfy a consumer’s need or desire.
- Questions to consider: What is the product? Does it fulfill a need or provide a unique experience? Who are the target customers? What differentiates the product from the competition?.
Product A product is anything offered to the market, which can be a good or a service. Types of ProductProducts can be categorized as goods or services:
The Product Life CycleThe product life cycle refers to the period during which a product remains appealing to customers. Some products last for centuries, while others may only endure for months. Investing in product development and promotion is important to prolonging a brand’s life cycle. Stages of the Product Life Cycle:
|
Price:
- The price component refers to the cost of the product that the consumer pays. It should reflect market trends, be affordable for consumers, and be profitable for the business.
- Questions to consider: How much do competitors charge for similar products? What is the affordability and price range of target consumers? What is the best price fit for the target market?.
PRICING OF GOODS AND SERVICESPricing refers to the activity of assigning monetary values to goods and services offered by an entrepreneur. It’s part of business operations as it directly impacts the entrepreneur’s profit and the purchasing power of consumers. Methods Used By Entrepreneurs When Pricing Their Products:
Objectives for Pricing the Products:
Factors Affecting Price Decisions of a Product / Factors Considered When Determining Price of a Product:
|
Place:
- The place component focuses on where and how the product or service is purchased by customers. It includes distribution channels, physical locations, and online platforms.
- Questions to consider: Which places or venues do buyers frequent for similar products? Where is the competition selling its products? What are the shopping habits of the target audience?.
Place Place refers to the channels of distribution used to deliver products from manufacturers to consumers. Channel members, including manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers, participate in the distribution process. Types of Marketing Intermediaries:
Channels of Distribution:Businesses decide where and how to sell their products, considering factors like cost and efficiency.
|
Promotion:
- The promotion component involves reaching the target audience with the right message at the right time. It includes advertising, sales promotions, and other marketing communication strategies.
- Questions to consider: When is the right time to reach the target audience? Which channels or mediums will the target audience get their information from? What advertising approaches will be the most fruitful?.
Product Promotion Product promotion involves informing, persuading, and influencing customers’ decisions to buy goods or services. Objectives of Promotion
Methods of Sales Promotion:
|

Types of Marketing
- Paid Advertising: This includes paying for ads to promote products or services. For example, a clothing brand may invest in TV commercials, social media ads, or Google Ads to reach potential customers.
- Cause Marketing: This involves associating a company’s offerings with a social cause. For instance, a coffee chain might donate a portion of its proceeds to support education in underprivileged communities with each cup of coffee sold.
- Relationship Marketing: This focuses on building strong connections with customers to foster loyalty. An example would be a local bakery that remembers customers’ days and offers or thank-you notes or birthday messages.
- Undercover Marketing: Also known as stealth marketing, promotes products without advertising. An example is a popular video game character wearing branded clothing during a movie scene, stealthy exposing viewers to the brand without directly marketing it.
- Word of Mouth: This relies on satisfied customers spreading positive experiences to others. For instance, if a friend recommends a restaurant based on their enjoyable dining experience, it may prompt others to visit the restaurant.
- Internet Marketing: Internet marketing leverages online platforms to promote products or services. For example, an online bookstore may use social media advertising, email newsletters, and content marketing to attract book lovers to its website.
- Transactional Marketing: This strategy offers incentives to encourage immediate purchases. An example is a retail store offering limited-time discounts or buy-one-get-one-free deals to entice shoppers to make on-the-spot purchases.
- Diversity Marketing: This involves tailoring marketing strategies to diverse audience segments. For instance, a beauty brand may create inclusive advertising campaigns featuring models from various ethnic backgrounds or body sizes to appeal to a wider range of consumers.

MARKETING SURVEY / RESEARCH
Market research is a systematic process of collecting and analyzing information relating to markets and opinions of the public about the products of a firm to enable present and future decision making.
Market research is the process of collecting and analyzing information relating to demand for a good or service in order to identify market opportunities and problems.
Market research is an organized effort to gather information about target markets or customers.
A target market refers to a fairly similar group of customers to whom a business product or service is aimed at.
Potential customers are a group of people sharing common needs and characteristics that a business decides to serve.
Aims / Objectives Of Carrying Out Market Research Of A Product
1. Understanding Customer Preferences: This involves researching what kind of products people want, what features are important to them, what quality they expect, how much they are willing to pay, and where and when they want to buy. This helps businesses develop products and marketing strategies that meet the needs and desires of their target customers.
2. Assessing the Market: This involves analyzing the size of the market for a particular product, the level of competition, the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, and the effectiveness of current marketing and sales strategies. This helps businesses identify opportunities for growth and make informed decisions about how to compete effectively.
3. Making Informed Decisions: This involves using market research data to make decisions about product development, pricing, marketing, distribution, and other business strategies. This helps businesses make data-driven decisions that are likely to lead to success.
4. Reducing Risk: Market research helps businesses identify and mitigate potential risks associated with new products or markets. This can save businesses time, money, and resources.
5. Identifying Opportunities: Market research can help businesses identify new opportunities for product development, market expansion, and other growth opportunities. This can help businesses stay ahead of the competition and achieve their long-term goals.
6. Testing and Improving: Market research can be used to test the effectiveness of marketing campaigns or product designs. This helps businesses improve their products and marketing strategies over time.
7. Gaining a Competitive Advantage: By understanding the market and its customers better than competitors, businesses can gain a big advantage. This can lead to increased sales, market share, and profitability.
8. Boosting Sales and Distribution: This involves identifying the best ways to distribute products to reach the most consumers, and understanding how to increase sales and turnover. This helps businesses optimize their distribution and sales strategies for maximum impact.
9. Increasing Profitability: By improving product development, marketing, and distribution based on market research data, businesses can maximize their efficiency and profitability. This then leads to increased revenue.
10. Understanding Market Trends: Market research helps businesses identify emerging trends and anticipate future changes in the market. This allows them to adapt their strategies and stay relevant.
15. Building a Strong Brand: Market research helps businesses understand how consumers perceive their brand and identify opportunities to strengthen their brand image. This leads to increased brand awareness, loyalty, and big market share.
Methods / Tools Of Market Research
- Observation method. This is where the entrepreneur watches the behaviour and attitudes of the public towards his product and products of competitors. It involves making an informal survey by observing business activities in the community. It reveals the need for the particular business.
- Experimental method. This is where an entrepreneur sells his products within a small selected area before selling on a large scale. If the product is liked within a small selected area, then the entrepreneur can distribute nationwide.
- Interviewing method. Under this method, the entrepreneur asks oral questions either face to face or by telephone to obtain response from people towards his products. It is a formal discussion which can identify the shortcomings of the business.
- Telephone surveys. Under this method, an entrepreneur calls different groups of customers to obtain information about aspects of the product to establish the market stand.
- Questionnaire method. Under this method, an entrepreneur carefully designs questions which are printed on paper then sent to possible respondents to give answers. It is a formal survey which obtains market information.
- Personal contacts. This involves making an informal survey by talking to family members and friends. These provide information about the best business to set up and the best products to be purchased in the locality.
- Surfing / use of the internet. This is where information is gathered through surfing from different websites from the internet.
- SWOT analysis. This method involves collecting data by a business through gathering information about its strengths, weaknesses, as well as information about opportunities and threats from the outside environment.
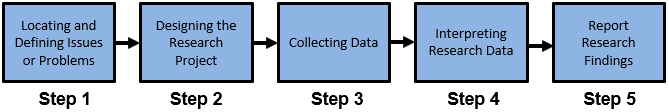
Steps Taken In Carrying Out Market Research / Survey
Imagine you’re a hospital administrator looking to improve patient satisfaction and attract new patients. You decide to conduct market research to understand your target audience’s needs and preferences.
- Define the Problem: You want to know what factors influence patients’ choice of hospital, what services they value most, and what areas of improvement they see.
- Define the Sample: You decide to survey 200 patients who have recently been discharged from your hospital, as well as 100 patients who have chosen to receive care at a competitor’s hospital.
- Collect Data: You create a survey with questions about patient satisfaction with various areas of care, including wait times, communication with staff, cleanliness, and hospital experience. You also ask about patients’ reasons for choosing your hospital or a competitor’s.
- Analyze the Results: You analyze the survey data to identify trends and patterns. For example, you might find that patients value attention, clear communication from doctors and nurses, and a comfortable environment. You might also discover that some patients choose competitors due to shorter wait times or more specialized services.
- Make the Research Report: You create a report summarizing the findings of your survey. You clearly present the data. For example, you might recommend investing in additional staff to reduce wait times, improving communication, and trying new service offerings to better meet patient needs.
- Make Decisions: Based on your research, you decide to implement several initiatives to improve patient satisfaction. You hire additional nurses to reduce wait times, conduct training for staff on effective communication, and invest in new equipment to offer more specialized services. By understanding patients’ needs and preferences, you can make informed decisions that will improve their experience and attract new patients to your hospital.
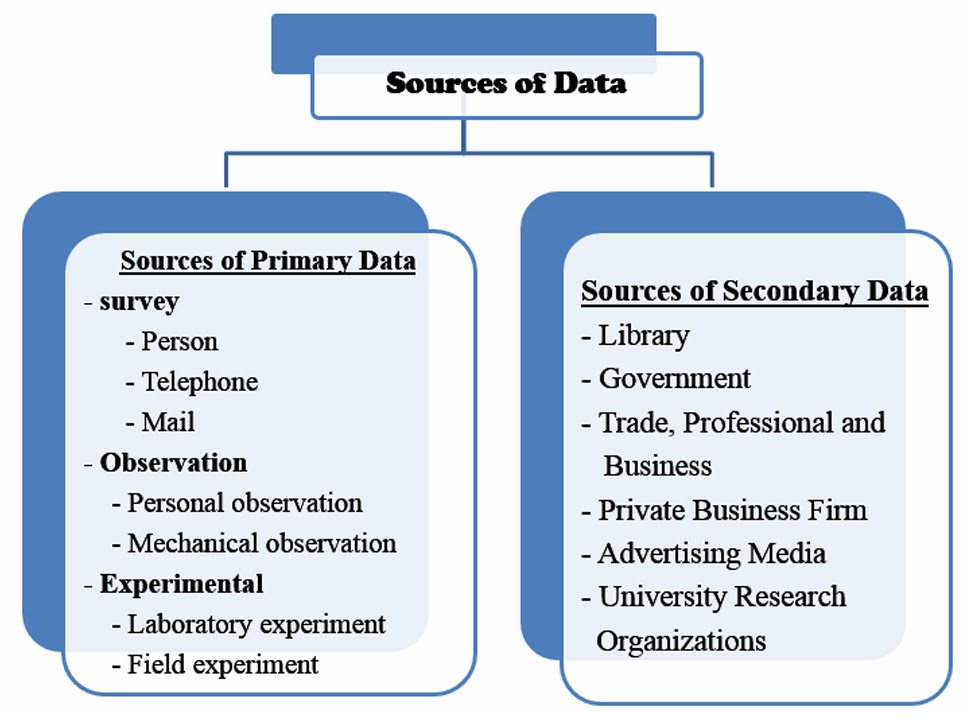
Sources Of Data For Conducting Market Research
- Competitors / competition. This is where data is collected by monitoring the activities of competitors in the same line of business. This may provide important information about customers’ demands that were overlooked and they may be capturing part of the market by offering something unique.
- Customers. The entrepreneur should talk to customers to get their feelings and ask them where improvement can be made. Encouraging and collecting customers’ comments is an effective form of research which involves asking customers to explain how the product could be improved to satisfy their needs.
- Employees (workers). This is one of the best sources of information about customers’ feelings, likes and dislikes, usually employees work more directly with the customers and hear their complaints that may not reach the owner. They are in most cases aware of the items customers request for that the business does not offer.
- Company records and files. Examining company records and files can be very informative e.g looking at the sales records, complaints, receipts or any other records can show an entrepreneur where his customers live and work, what their preference is, amount purchased etc. Using suggestion boxes can also be a source of information.
Problems Faced When Conducting Market Research Of A Given Product
- Language difference. Given that Uganda lacks a national language, researchers sometimes miss the information they desire to get due to inability to communicate in the languages understood by the different respondents / consumers.
- Inadequate financial resources. It is very expensive to carry out market research. Small firms with limited capital may not be able to undertake it and this greatly affects their planning.
- Inadequate skills to handle data collection due to limited man power to effectively and efficiently handle market research. This leads to inaccurate interpretation of information from the public.
- Inadequate communication facilities. Accessibility of some areas of the country is difficult due to poor road networks. Therefore, information from such areas cannot easily be obtained by researchers.
- Inadequate co-operation from the customers or public. Some people refuse to answer the questions; others give wrong answers while some chase away the researchers. All these distort research findings and conclusions.
- Insecurity / hostility in some areas which hinder effective data collection.
- Bias. There is also a possibility of getting information from a biased sample / source.
- Wrong target group. Choice of wrong sample target group of customers or people from where to get information.
- Inaccurate data. Most people or customers do not keep records of their sales or purchases and therefore not being able to get accurate information from them.
- Political instabilities also affect research as the researchers may not be able to go to the areas of their choice.

