-

Writing Chapter ONE
Chapter One: Introduction (Research Proposal) CHAPTER ONE: Introduction Table of Contents (Click to Expand) ▼ 1.0 Introduction of the Chapter 1.1 Background of the Study 1.2 Problem Statement 1.3 Purpose of the Study 1.4 Specific Objectives 1.5 Research Questions 1.6 Justification of the Study 1.7 Significance of the Study UNMEB Marking Guide (Annex 8) References…
-

PREPARING FOR PROPOSAL DEFENCE
Preparing for Proposal Defence PREPARING FOR PROPOSAL DEFENCE MEANING OF PROPOSAL DEFENCE Proposed Defence refers to a legitimate process organized by the researcher’s institution to assess whether the researchers plan of finding valid solutions to the proposed research question(s) holds academic merit. PROPOSAL DEFENCE PANEL & ITS COMPOSITION The Proposal Defense Panel refers to a…
-

HIV/AIDS Counseling
HIV/AIDS Counseling HIV/AIDS Counseling Counseling is a professional relationship that empowers diverse individuals, families, and groups to accomplish mental health, wellness, education, and career goals. A Professional Relationship: Not a casual chat: It’s distinct from friendly advice or informal conversations. It’s structured, bound by ethical guidelines, and conducted by trained professionals (counselors). Defined roles: The…
-

Epistaxis(Nose Bleed)
Epistaxis Lecture Notes EPISTAXIS This is bleeding from the nostrils/Nasal bleeding which may be arterial venous, or capillary Epistaxis, commonly known as a nosebleed, is defined as hemorrhage from the nasal cavity. More precisely, it refers to bleeding from the blood vessels lining the inside of the nose. This bleeding can range from a minor…
-

Splenomegaly and Hypersplenism
Splenomegaly and Hypersplenism Splenomegaly and Hypersplenism Splenomegaly Splenomegaly is an abnormal enlargement of the spleen. Etymology: The term comes from the Greek words “splen” (spleen) and “megas” (large). Clinical Significance: A normal adult spleen is typically not palpable below the left costal margin (rib cage). Clinical splenomegaly is usually diagnosed when the spleen becomes palpable…
-

Lymphadenitis Lecture Notes
Lymphadenitis Lecture Notes Lymphadenitis Lecture Notes Lymphadenitis is a relatively common condition that refers specifically to the inflammation of one or more lymph nodes. It is characterized by enlargement, tenderness, and often hardening of the affected nodes. While commonly associated with infection, it’s important to remember that not all lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes) is lymphadenitis.…
-

Lymphagitis Lecture Notes
Lymphangitis Lecture Notes Lymphangitis Lecture Notes Lymphangitis is an acute inflammation of the lymphatic vessels, typically caused by a bacterial infection spreading into the lymphatic system from an infected site. It is characterized by the appearance of red streaks or lines, often tender and warm, extending proximally from the site of infection towards regional lymph…
-
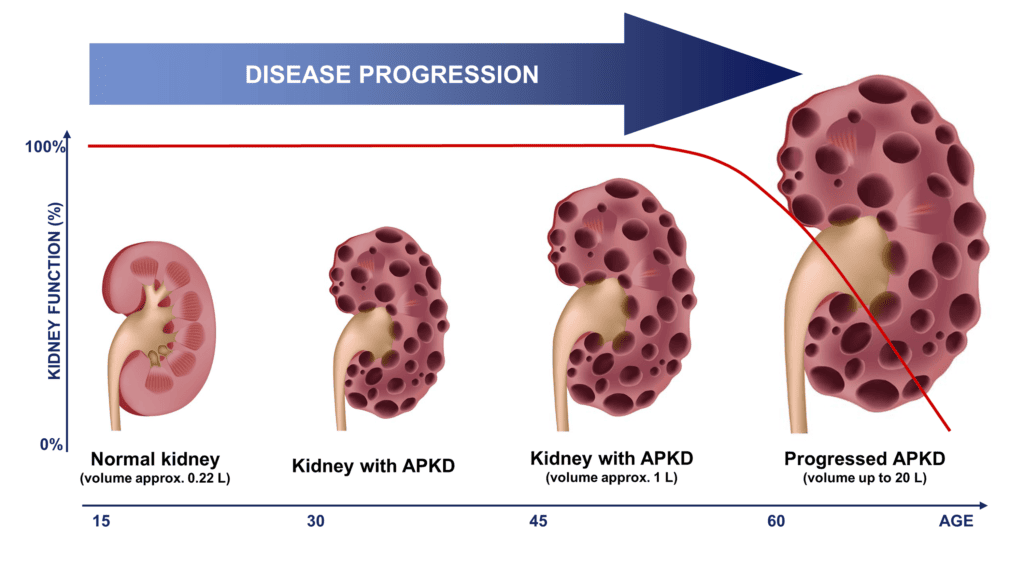
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous fluid-filled cysts within the kidneys. These cysts are non-cancerous but can grow very large and multiply, progressively replacing much of the normal kidney tissue. Progressive Nature: PKD is a progressive disease. Over time,…
-

URETHRITIS Lecture Notes
Urethritis Lecture Notes Urethritis Lecture Notes Urethritis is an inflammatory condition of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. In males, the urethra also carries semen. Inflammation of the urethra can be caused by various factors, but it is most commonly associated with infection. Key characteristics of urethritis…
-
Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Therapy
Nursing Lecture Notes – Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Therapy Introduction to Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Therapy An antibiotic (derived from Greek anti “against” and bios “life”) is a substance produced by microorganisms (e.g., bacteria, fungi) that, in small amounts, inhibits the growth of or kills other microorganisms. Modern Usage (Broader Definition): In modern clinical practice, the term…
