-
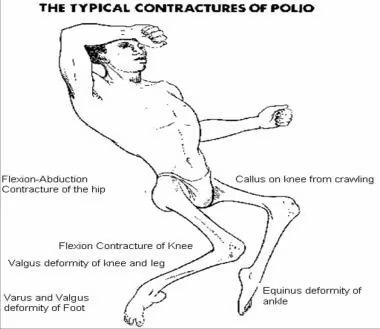
Poliomyelitis Lecture nOTES
Nursing Lecture Notes – Poliomyelitis Introduction to Poliomyelitis Poliomyelitis, commonly known as polio, is an infectious disease that has historically caused widespread fear due to its potential for causing permanent paralysis and death, particularly in children. While significant progress has been made towards its global eradication, understanding the disease remains crucial for healthcare professionals and…
-
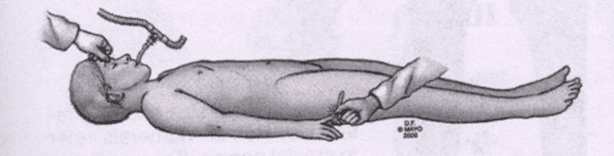
Introduction to Unconsciousness (Coma)
Nursing Lecture Notes – Unconsciousness (Coma) Introduction to Unconsciousness (Coma) Unconsciousness represents a fundamental failure of the brain’s ability to integrate and process information from the internal and external environment, leading to a state of unresponsiveness. It is a neurological emergency that demands immediate attention, as its underlying causes can be life-threatening and rapidly progressive.…
-
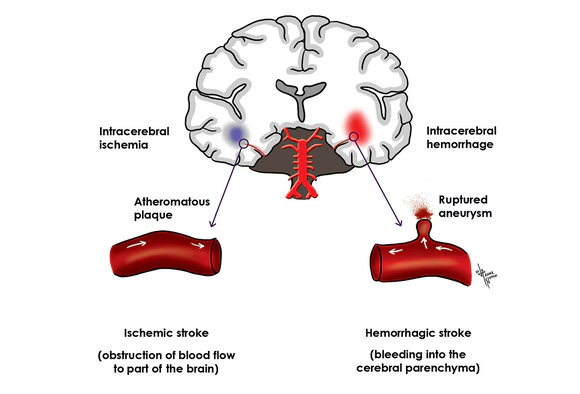
Cerebrovascular accident (Stroke)
Nursing Lecture Notes – Cerebral Vascular Accidents (Stroke) Cerebral vascular accidents (Stroke) Stroke, medically termed a Cerebral Vascular Accident (CVA), represents an acute medical emergency characterized by rapid onset of neurological deficits resulting from a disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This disruption leads to brain cell death due to a lack of…
-
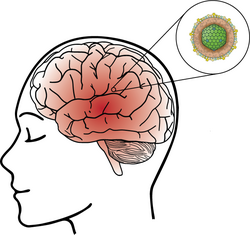
Encephalitis Lecture Notes
Nursing Lecture Notes – Encephalitis Encephalitis Lecture Notes Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain parenchyma (the brain tissue itself). This inflammation directly affects the neurons and other brain cells, leading to neurological dysfunction, as opposed to inflammation primarily of the meninges (membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord) which defines meningitis. Key Differentiating…
-
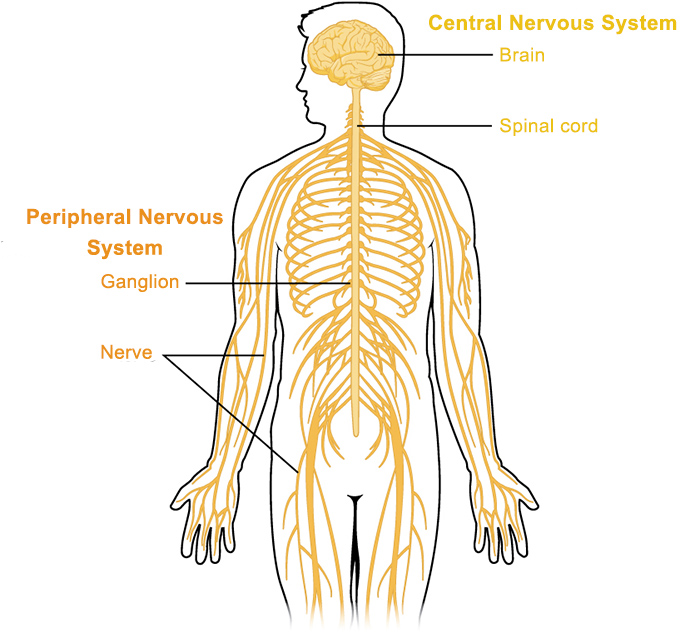
General signs and symptoms of the nervous system disorders
Nursing Lecture Notes – Nervous System Disorders (Part 1) General Signs and Symptoms of Nervous System Disorders Introduction The nervous system, a marvel of biological engineering, orchestrates every thought, movement, sensation, and involuntary bodily function. Its complexity means that disruption at any point—from the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system, CNS) to the peripheral…
-

Teaching Methodology Past Papers Review
Teaching Methodology – Past Papers Review Teaching Methodology Quiz Past Papers Review Test your knowledge with these 54 questions. Start Assessment Teaching Methodology Question 1/54 Submit Next Assessment Complete! Here are your results, . Your Score 27/30 90% Download Full Report
-

IMNCI Cumulative Exam
IMNCI Cumulative Quiz IMNCI Cumulative Quiz Integrated Management of Childhood Illness Test your knowledge with these 50 questions. Start Assessment IMNCI Cumulative Quiz Question 1/50 Submit Next Assessment Complete! Here are your results, . Your Score 27/30 90% Download Full Report
-

IMNCI Session 3 Identify Treatment Quiz
IMNCI – Identify Treatment Quiz IMNCI Identify Treatment Quiz Integrated Management of Childhood Illness Test your knowledge with these 25 questions. Start Assessment IMNCI Treatment Question 1/25 Submit Next Assessment Complete! Here are your results, . Your Score 27/30 90% Download Full Report
-

IMNCI Session One Continuation QUIZ
IMNCI Session One – Assessment IMNCI Session One Cont. Assessment Integrated Management of Childhood Illness Test your knowledge with these 30 questions. Start Assessment IMNCI Session One Question 1/30 Submit Next Assessment Complete! Here are your results, . Your Score 27/30 90% Download Full Report
-

IMNCI Session One Asess and cLASSIFY QUIZ
IMNCI Session One Quiz IMNCI Session One Quiz Integrated Management of Childhood Illness Test your knowledge with these 30 questions. Start Assessment IMNCI Session One Question 1/30 Submit Next Assessment Complete! Here are your results, . Your Score 27/30 90% Download Full Report
