-

PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD)
Nursing Notes – Peptic Ulcer Disease PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE (PUD) A peptic ulcer is defined as an excavation (a hollowed-out area) or an erosion that forms in the mucosal wall of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. This lesion occurs specifically in areas that are exposed to the corrosive actions of gastric acid and the digestive enzyme…
-
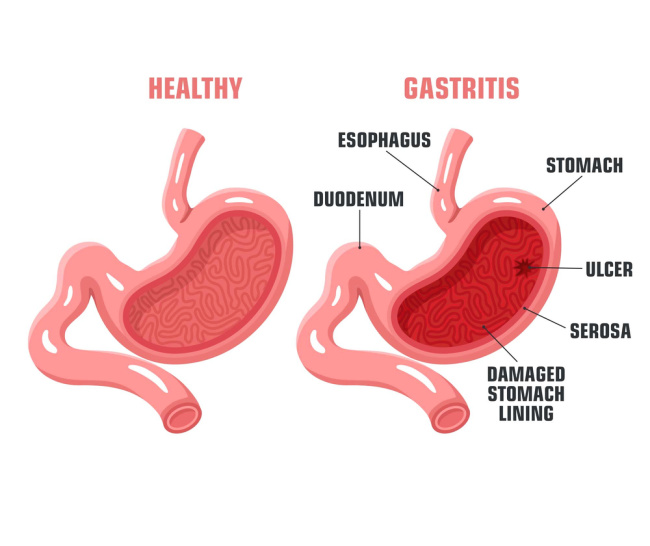
Gastritis Lecture Notes
Nursing Notes – Gastritis GASTRITIS Gastritis is fundamentally an inflammation of the gastric mucosa, which is the delicate inner lining of the stomach. This inflammatory response can be widespread (diffuse) or confined to specific areas (localized) within the stomach, and it represents the body’s reaction to various forms of injury or infection. Gastritis is broadly…
-
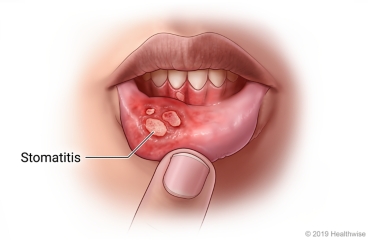
Stomatitis lecture notes
Nursing Notes – Malnutrition STOMATITIS REVIEW: Anatomy of the Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a continuous, hollow, muscular tube that serves as the primary pathway for digestion and absorption. It is approximately 23 to 26 feet (7 to 8 meters) long and extends from the mouth to the anus, passing through the…
-
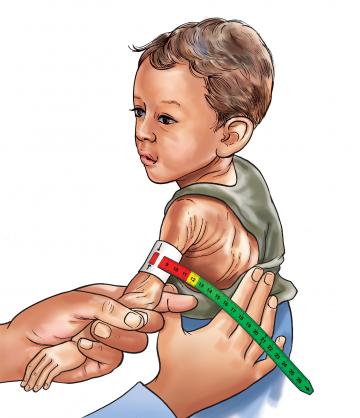
MALNUTRITION IN CHILDREN
Nursing Notes – Malnutrition MALNUTRITION Malnutrition is a pathological state resulting from a relative or absolute deficiency or excess of one or more essential nutrients. It refers to any condition in which the body does not receive enough nutrients for proper function, encompassing both undernutrition and overnutrition. Forms of Malnutrition Undernutrition: An insufficient intake of…
-

Nutrition in Children
Nursing Notes – Child Growth and Development Nutrition in Children Balanced and sufficient nutritional intake is paramount for children. It serves multiple critical functions: promoting optimal growth and development, protecting and maintaining health, preventing nutritional deficiency conditions and various illnesses, and building reserves for periods of starvation or dietary stress. The term ‘nutrition’ itself is…
-
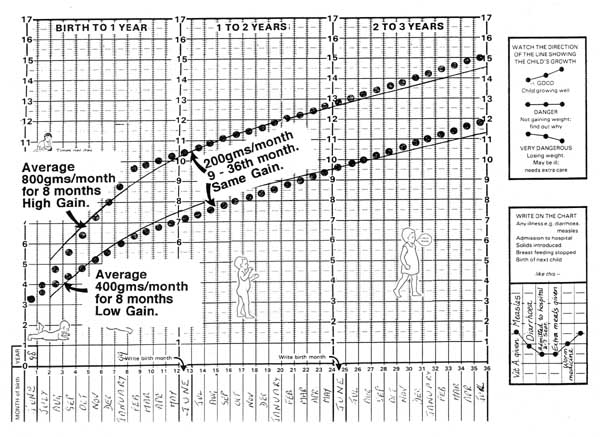
Growth Monitoring and Promotion
Nursing Notes – Child Growth and Development Growth Monitoring and Promotion Growth Monitoring Growth monitoring involves regularly weighing a child, plotting the weight on a child health card (also known as a growth chart), interpreting the results, and counseling parents or caregivers. It’s a proactive and preventative health measure to track a child’s developmental progress…
-
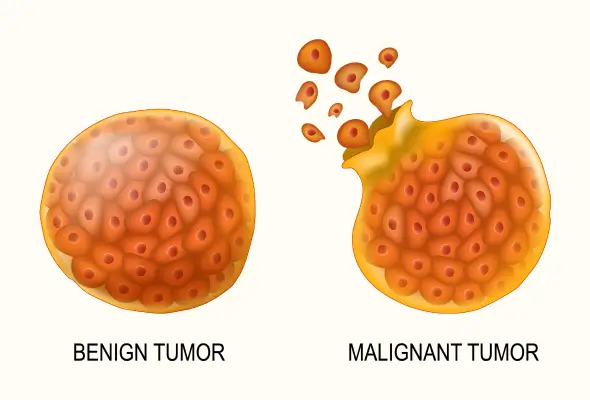
TUMORS (NEOPLASMS)
Nursing Notes – Tumors TUMORS (NEOPLASMS) A Neoplasm is an abnormal mass of tissue whose growth exceeds and is uncoordinated with that of the normal tissues, and which persists in the same excessive manner after the cessation of the stimuli that evoked the change. These new abnormal growths are also commonly referred to as Tumors.…
-
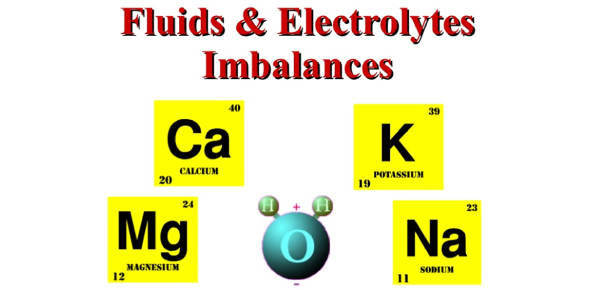
FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE
Nursing Notes – Burns FLUID AND ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE Fluid and electrolyte balance is a dynamic process that is crucial for life and homeostasis. Electrolytes Electrolytes in body fluids are active chemicals (cations that carry positive charges and anions that carry negative charges). The major cations in the body fluid are sodium, potassium, calcium, and hydrogen…
-

HAEMORRHAGE: Nursing Lecture Notes
Nursing Notes – Burns HAEMORRHAGE: Nursing Lecture Notes Haemorrhage, commonly known as bleeding, is the loss of blood from the circulatory system, specifically from blood vessels. It is a critical medical condition that, if uncontrolled, can lead to severe physiological compromise and death. The body possesses intrinsic defence mechanisms, primarily through the process of clotting…
-
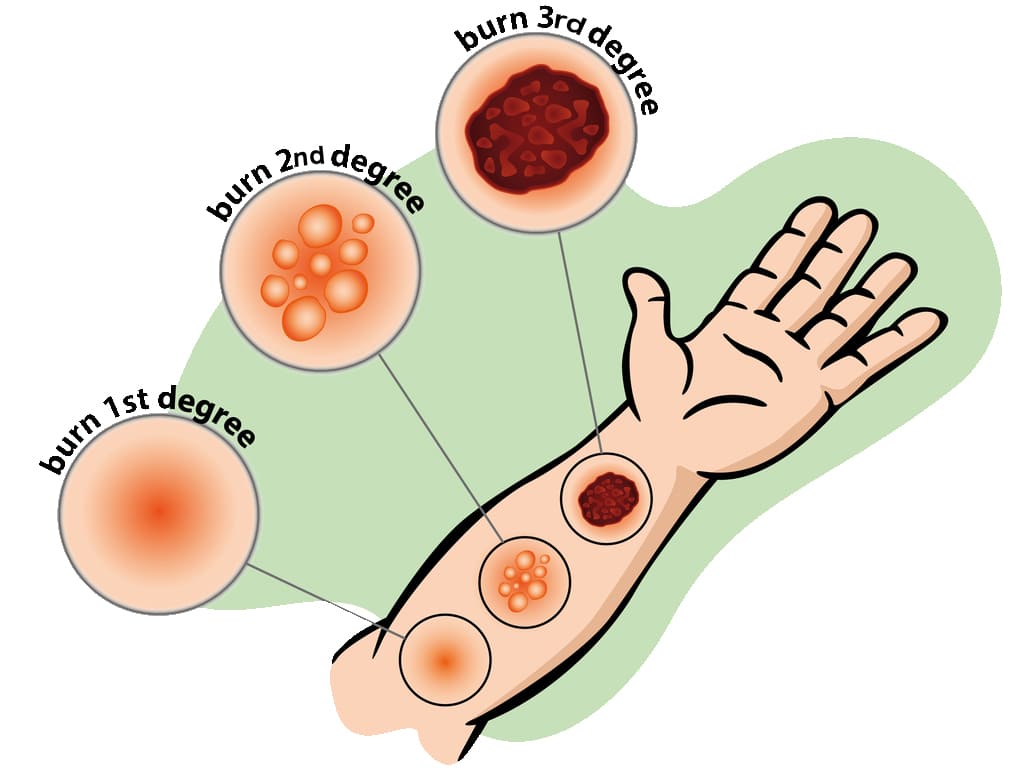
BURNS LECTURE NOTES
Nursing Notes – Burns BURNS Burns are injuries to the skin due to extremes of temperature i.e cold or hot, chemicals or radiations. Burns occur when there is injury to the tissues of the body caused by heat, chemicals, electric current or radiations. Anatomical review of the skin. Skin is the largest organ of the…
