-

Introduction to environmental hygiene
Nursing Lecture Notes – Environmental Hygiene Introduction Topic 1.16: Environmental Hygiene/Sanitation Introduction to Environmental Hygiene in Healthcare Objectives This module will provide the knowledge necessary to: Explain why there is a need to maintain a clean environment to prevent the spread of infections. Discuss cleaning and disinfection requirements for clinical settings like ambulatory surgery centers.…
-
Introduction to personal hygiene
Nursing Lecture Notes – Personal & Communal Health Personal Hygiene Module Unit Description: Covers elements of personal health and principles of maintaining a healthy environment, including hygiene practices for health promotion and behavior changes for proper sanitation. Learning Outcomes for this Unit: By the end of this unit, the student shall be able to: Describe…
-

Personal and Communal Health (PCH)
Nursing Lecture Notes – Personal & Communal Health Module Unit CN-1105: Personal and Communal Health (PCH) Contact Hours: 45 Module Unit Description: Covers elements of personal health and principles of maintaining a healthy environment, including hygiene practices for health promotion and behavior changes for proper sanitation. Learning Outcomes for this Unit: By the end of…
-
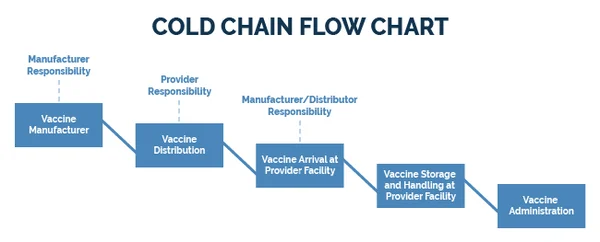
Cold Chain
The Vaccine Cold Chain – A Guide for Health Workers The Vaccine Cold Chain Definition and Importance The cold chain is a system of storing, transporting, and distributing vaccines at specified low temperatures—typically between +2°C and +8°C—from the point of manufacture to the point of administration. Its purpose is to ensure that vaccines remain in…
-

Simple laboratory tests
Simple Laboratory Tests – Microbiology Study Guide Simple Laboratory Tests in Microbiology Accurate diagnosis of infectious diseases relies heavily on laboratory analysis. For nurses and midwives, understanding the principles of laboratory tests, especially how to properly collect and handle specimens, is a critical skill. The quality of a lab result is only as good as…
-

Pathological effects of microorganisms
Pathological Effects of Microorganisms – Complete Study Guide Pathological Effects Of Microorganisms Microorganisms are a ubiquitous part of our world. While many are harmless or even beneficial (like our normal flora), a subset known as pathogens possess the ability to cause disease. The pathological effects of microorganisms refer to the full spectrum of harmful changes…
-

Normal flora
Expanded Microbiology Notes: Flora and Disease Normal Flora and Host-Microbe Interactions Concept of Normal Flora The human body is not sterile; it is home to a vast and complex community of microorganisms. Normal Flora (also called the normal microbiota or commensals) are the microorganisms that live on or inside the body of a healthy person…
-

Introduction & Concepts of Microbiology
Complete Microbiology Lecture Notes Module Unit: CN-1104 – Microbiology Contact Hours: 30 Credit Units: 2 Module Unit Description: This module introduces students to the concept of Microbiology and its importance to medical science. It covers the classification of microorganisms, their characteristics, their role in spreading infection and disease, simple microbial laboratory tests, and concepts of…
-

Maintenance of the computers and their components
Nursing Lecture Notes – Topic 4: Computer Maintenance Topic 4: Maintenance of Computers and their Components Why is Computer Maintenance Important? Just like you perform regular checks on medical equipment to ensure it functions correctly and safely, your computer also needs regular maintenance. Proper care helps your computer to: Run faster and more efficiently. Last…
-

Introduction to internet use
Nursing Lecture Notes – Topic 3: Introduction to Internet Use Topic 3: Introduction to Internet Use What is the Internet? The Internet is a massive, global network connecting millions of computers, allowing them to communicate with each other and share information. Think of it as a worldwide library, post office, and marketplace all in one.…
