Table of Contents
TogglePOLYMENORRHOEA/ EPIMENORRHOEA
Polymenorrhea, also known as epimenorrhoea, is a medical condition characterized by frequent menstrual periods that occur more frequently than the normal menstrual cycle.
Polymenorrhoea also refers to menstruation periods that occur at shorter intervals than usual (14-21 days), but they are frequent and regular.
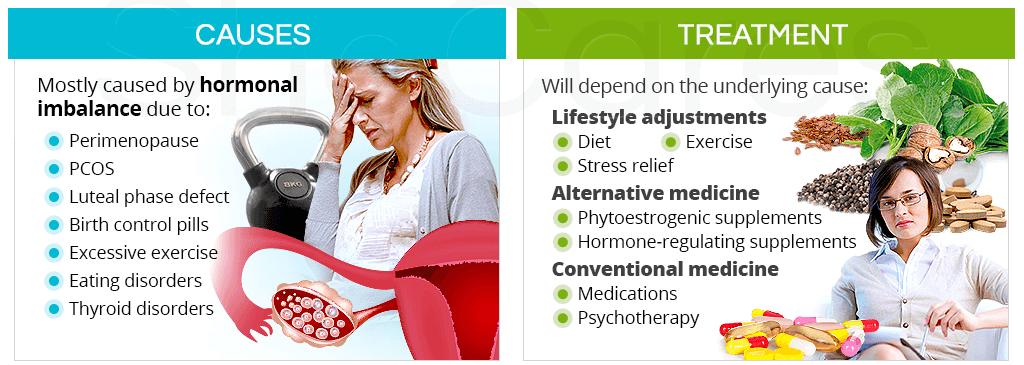
Causes of Polymenorrhea/Epimenorrhoea:
- Hormonal imbalances: Fluctuations in oestrogen and progesterone levels can disrupt the normal menstrual cycle and result in more frequent periods.
- Thyroid disorders: Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) or underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism) can affect hormone production and menstrual regularity.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): This condition is characterized by hormonal imbalances, enlarged ovaries with cysts, and irregular menstrual cycles.
- Uterine abnormalities: Conditions such as uterine fibroids, polyps, or adenomyosis can cause abnormal bleeding and frequent periods.
- Stress and lifestyle factors: Chronic stress, excessive exercise, drastic weight changes, and poor nutrition can disrupt the hormonal balance and contribute to polymenorrhea.
Signs and Symptoms of Polymenorrhea/Epimenorrhoea:
- Menstrual Cycles Shorter than 21 Days: Defined by the duration between the onset of one period and the beginning of the next, with cycles constantly falling below the normal 21-days.
- Frequent Menstrual Periods: Menstrual bleeding occurring every two weeks or at intervals of less than 14 days, indicating increased frequency compared to the standard monthly cycle.
- Altered Bleeding Patterns: Variations in blood flow, with episodes of lighter or heavier bleeding than what is considered for the individual.
- Increased Menstrual Discomfort: Discomfort or pain associated with menstruation, more than the discomfort experienced during a regular menstrual cycle.
- Fatigue or Tiredness: Resulting from more frequent blood loss due to polymenorrhea, leading to a decrease in energy levels and an increased sense of tiredness.
- Emotional and Psychological Impact: Potential emotional consequences, including anxiety or mood swings, from the physical and hormonal changes associated with more frequent menstrual cycles.
Investigations for Polymenorrhea/Epimenorrhoea:
- Medical history and physical examination: A thorough evaluation of the menstrual patterns, symptoms, and any underlying medical conditions is conducted. A pelvic examination may be performed to assess the reproductive organs.
- Hormone level assessment: Blood tests may be done to measure hormone levels, including oestrogen, progesterone, thyroid hormones, and other relevant hormones.
- Pelvic ultrasound: This imaging test can provide visual information about the ovaries, uterus, and any structural abnormalities.
- Endometrial biopsy: A sample of the uterine lining may be obtained and examined to rule out any abnormalities or cancer.
Medical and Nursing Management of Polymenorrhea/Epimenorrhoea:
- Hormonal therapy: Depending on the underlying cause, hormonal medications, such as oral contraceptives or hormone-regulating medications, may be prescribed to regulate the menstrual cycle and reduce the frequency of periods.
- Treatment of underlying conditions: If polymenorrhea is caused by conditions such as PCOS or uterine abnormalities, appropriate treatment strategies will be implemented to address the specific cause. Carry out dilatation and curettage (D&C) to remove retained products if its the cause.
- Lifestyle modifications: Stress reduction techniques, maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate sleep can help regulate hormonal balance and promote overall well-being.
- Supportive care: Nursing management focuses on providing emotional support, educating patients about menstrual hygiene, symptom management, and lifestyle modifications.
- Monitoring and follow-up: Monitoring patients’ response to treatment, assessing the effectiveness of interventions, and ensuring appropriate follow-up care should be put into considerations.

