-
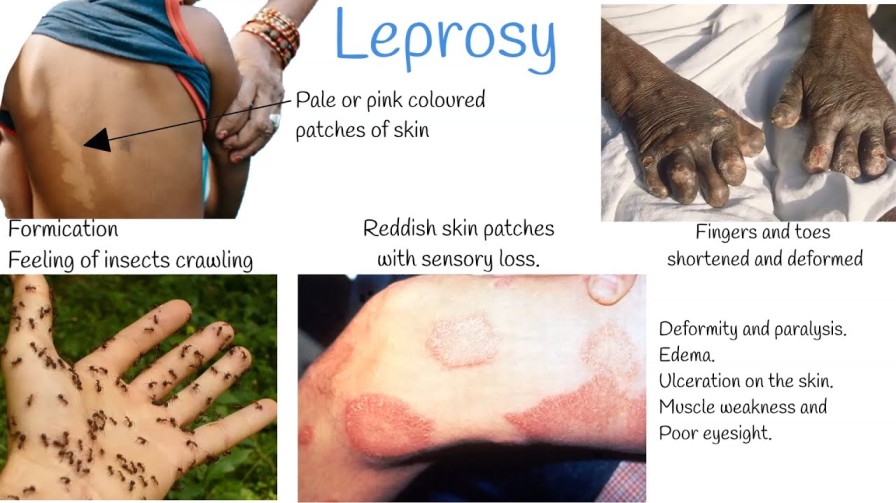
Leprosy
Leprosy Leprosy, also known as Hansen\’s disease, is a chronic infection caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatosis. It primarily affects the skin and peripheral nerves. Cause of Leprosy Leprosy is caused by Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatosis. M. lepromatosis is a relatively newly identified mycobacterium isolated from a fatal case of diffuse…
-

Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis Tuberculosis, commonly known as TB (short for tubercle bacillus), is a widespread and often deadly infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria. While primarily affecting the lungs, it can also impact other parts of the body. Around one-third of the world\’s population (1 in 3 or 3 out of 10 people) is affected…
-
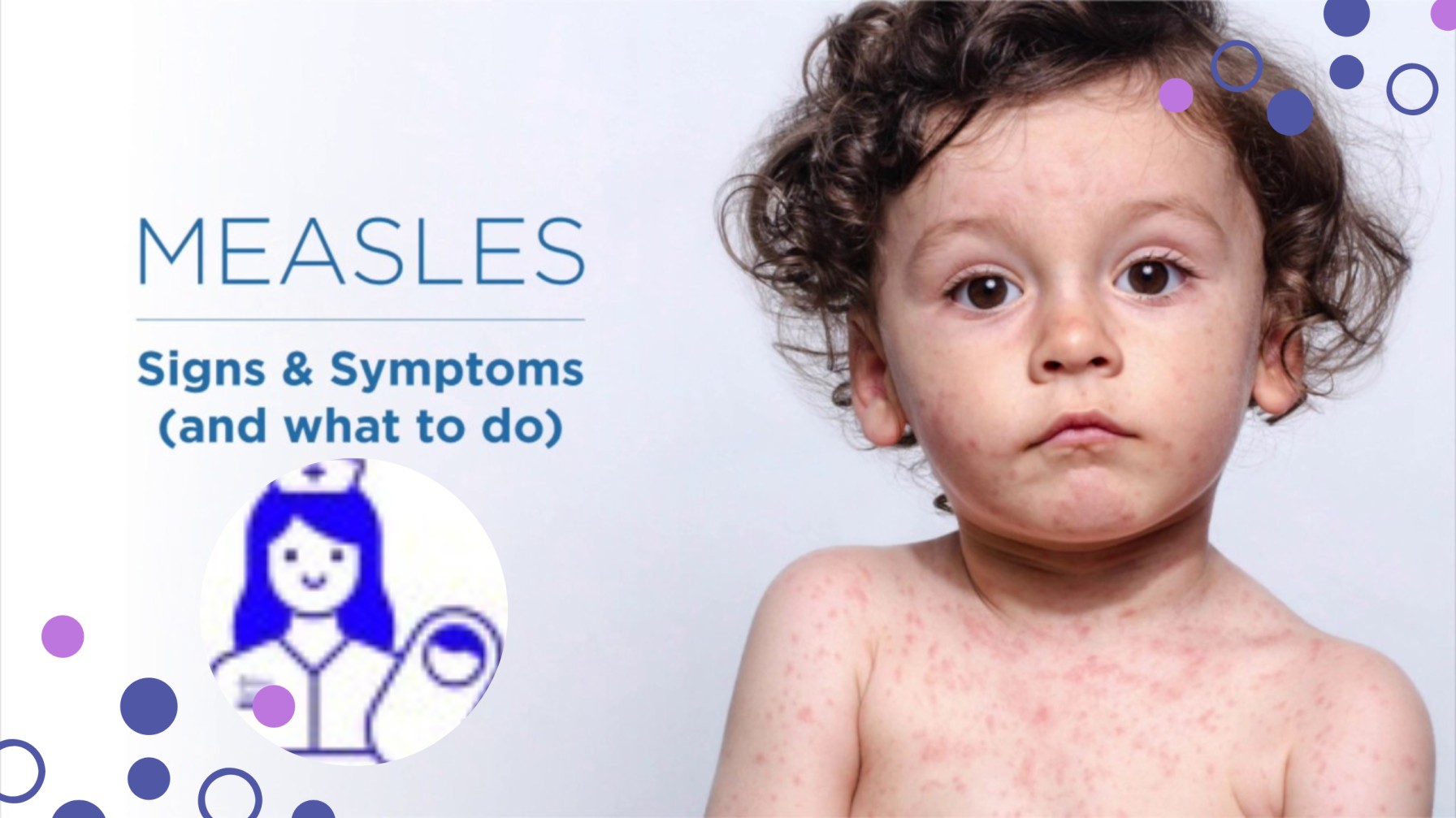
Measles
Measles Measles, also known as Morbilli, is a highly contagious acute infection of the respiratory system caused by the morbillivirus. It is characterized by a widespread skin rash, fever, and inflammation of the mucous membranes. The transmission of measles occurs through respiration, mainly by coming into contact with fluids from the nose and mouth of…
-
Malaria
Malaria Malaria is an infectious disease caused by a parasite belonging to the Plasmodium genus. It is primarily transmitted from one person to another through female mosquitoes of the Anopheles genus. The illness presents with acute febrile symptoms, including cycles of chills, fever, pain, and sweating. Historical records indicate that malaria has been afflicting humans…
-

Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever)
Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever) Typhoid fever is an acute bacterial infection characterized by fever and is primarily spread through contaminated food and water. Causes Typhoid fever is caused by Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi A and B. Transmission: Typhoid fever is contracted by the ingestion of the bacteria in contaminated food or water. Patients with…
-

Dysentery
Bacillary Dysentery (Shigellosis): Bacillary dysentery is an acute bacterial disease that primarily affects the large and small intestine, leading to symptoms such as bloody mucoid diarrhea. It is important not to confuse bacillary dysentery with diarrhea caused by other bacterial infections, as one of the distinguishing characteristics of bacillary dysentery is the presence of blood…
-

Cholera
Cholera Cholera is an infection of the small intestine caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. The infection is characterized by profuse watery stools, vomiting, dehydration, and collapse. Cause Cholera is specifically caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae. This bacterium is Gram stain negative and possesses a flagellum, a long projecting part that enables it to…
-

Gastroenteritis (GE)
Gastroenteritis (GE) Gastroenteritis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract that involves both the stomach (\”gastro\”-) and the small intestine (\”entero\”-), resulting in some combination of diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and cramping. The severity of infectious gastroenteritis depends on the immune system’s ability to resist the infection. Electrolytes (mainly sodium…
-

Introduction to communicable diseases
Introduction to communicable diseases Communicable diseases, also known as infectious diseases or transmissible diseases are diseases that spreads from one person or animal to another or from a surface to a person. Communicable diseases occur at all age groups outmost serious in childhood due to intensive exposure and poorly developed immunity. These diseases are to…
-

Psychosocial support to terminally ill patients
Psychosocial support to terminally ill patients Terminal illness refers to a condition that cannot be cured and is expected to result in the patient’s death within a certain timeframe. This devastating diagnosis not only affects the physical health of the individual but also has profound emotional and psychological implications. The knowledge that one’s life will…
