-

Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis Lecture Notes Onychomycosis Onychomycosis is a common infectious disease affecting the nail unit, specifically a fungal infection of the nail plate, nail bed, or both. The term “onychomycosis” is derived from Greek: onyx (nail) and mykes (fungus). It is a persistent and often progressive condition that, if left untreated, can lead to significant nail…
-

Herpes zoster
Herpes Zoster (Shingles) Lecture Notes Herpes Zoster (Shingles) Herpes Zoster, commonly known as shingles, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area on the body. It is caused by the reactivation of the Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV), the same virus that causes varicella (chickenpox). The incubation period ranges…
-
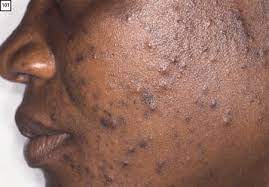
Acne Vulgaris
Acne Vulgaris Lecture Notes Acne Vulgaris Acne Vulgaris is an inflammatory skin disease caused by changes in the pilosebaceous units (skin structures comprising a hair follicle and its related sebaceous gland) of the skin. The term acne comes from a Greek word acme meaning a skin eruption. Acne vulgaris is the most common cutaneous disorder…
-

Dermatitis
Dermatitis Lecture Notes Dermatitis Lecture Notes “Dermatitis” is a broad, umbrella term derived from Greek, where “derma” means skin and “-itis” signifies inflammation. Therefore, dermatitis fundamentally refers to inflammation of the skin. It is characterized by a reaction pattern of the skin to various internal or external factors, leading to a range of symptoms. While…
-
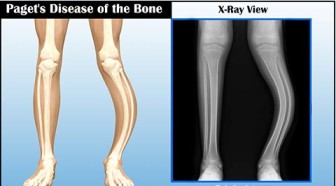
Paget’s disease
Paget’s Disease of Bone Lecture Notes Paget’s Disease of Bone Paget’s disease of bone is a disorder in which there’s a lot of bone remodeling that happens in some regions of the bone. There’s excessive bone resorption followed by excessive bone growth, and that leads to skeletal deformities and potential fractures. Paget’s disease of bone,…
-

Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis Lecture Notes Osteoporosis Lecture Notes Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to increased bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture. Osteoporosis is a musculoskeletal disorder in which bones deteriorate or become brittle and fragile due to low bone mass as a result of…
-
Antidepressants
Antidepressants Antidepressants are a type of medicine used to treat clinical depression. Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat majordepressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction. They are known as mood elevators. The first antidepressant drug to be discovered was a monoamine oxidase inhibitor by Crane (1957) and Kline (1958). Depression, or…
-

Medical Instruments For Nurses
MEDICAL INSTRUMENTS AND OTHER EQUIPMENTS Instrument/ Appliance Functions Sand bags It prevents movement of a limb in the treatment of special conditions. Bed block To elevate the bed Mouth gag To open the mouth of unconscious patient Air ring and its pump To prevent friction on the bed. Cardiac table Used by cardiac patients to…
-

Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Lecture Notes Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), often simply called lupus, is a chronic, autoimmune disease characterized by systemic inflammation that can affect virtually any organ system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues, causing…
-

Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic, systemic, inflammatory rheumatic disease that primarily affects the axial skeleton, particularly the sacroiliac joints and the spine. Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a medical condition that involves the inflammation (spondylitis) and fusion/stiffening (ankylosis) of the vertebrae or small bones in the spine. Ankylosing spondylitis…
