-
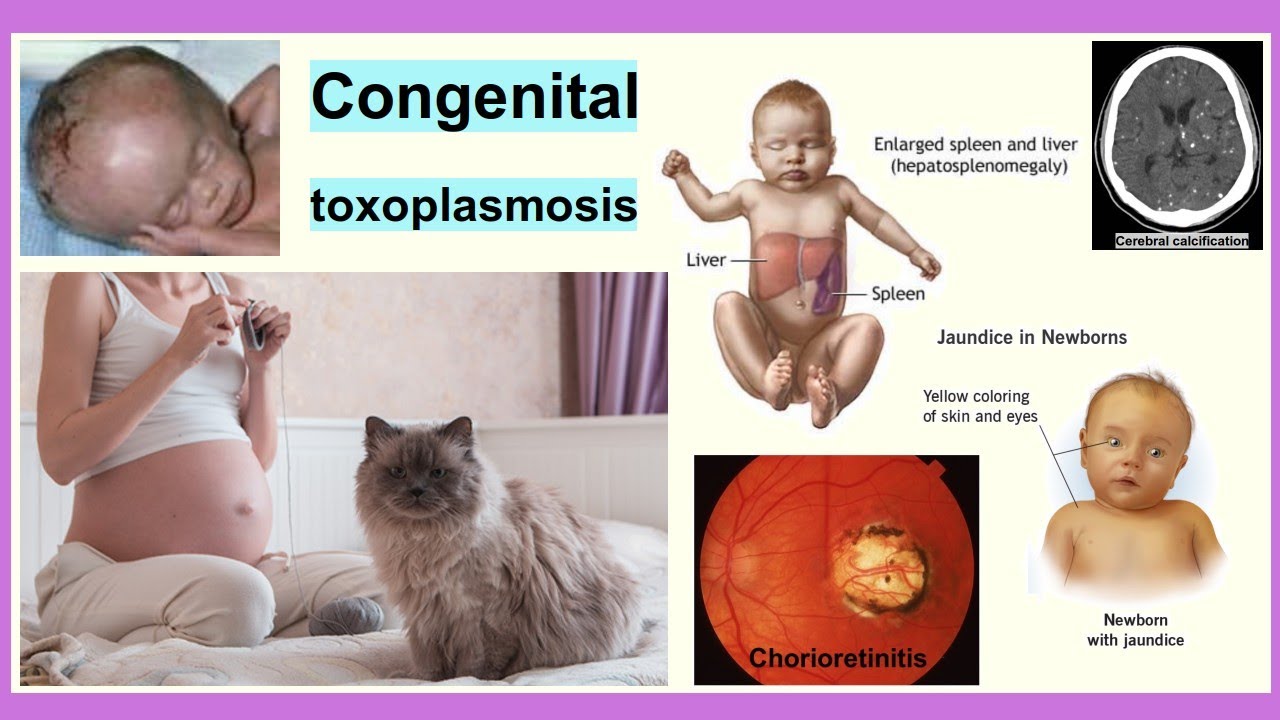
Congenital Toxoplasmosis
Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lecture Notes Congenital Toxoplasmosis Congenital toxoplasmosis is a disease that occurs in fetuses or new-borns infected with Toxoplasma gondii, a protozoan parasite, which is transmitted from mother to fetus. Congenital Toxoplasmosis is an infection of a fetus or newborn baby with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii, acquired in utero from an infected mother. Etiological…
-

Assessment of the Mentally Ill
Mental Health Assessment The psychiatric interview is the most important tool in psychiatry. It is the primary tool used to understand a patient’s problems, elicit signs and symptoms, uncover etiologies, and identify complications. This process is essential to making an accurate diagnosis, initiating treatment, and predicting outcomes. A mental health assessment is a comprehensive evaluation…
-

Mental Health
MENTAL HEALTH Mental health is a state of balance between the individual and the surrounding world. Mental health is a state of harmony between oneself and others. Mental health is a co-existence between the realities of the self and that of other people and that of the environment. HEALTH; it is a state of well…
-
Normal Midwifery Questions and answers
Vital observations. Vital observations like blood pressure is taken to rule out conditions like pre-eclampsia that will necessitate referral. Physical examination. This is done to exclude conditions like anaemia, jundice, dehydration, oedema, malnutrition. External pelvic assessment. This is done especially from 36 weeks of gestation those mothers who have not delivered vaginally and prime gravidas…
-
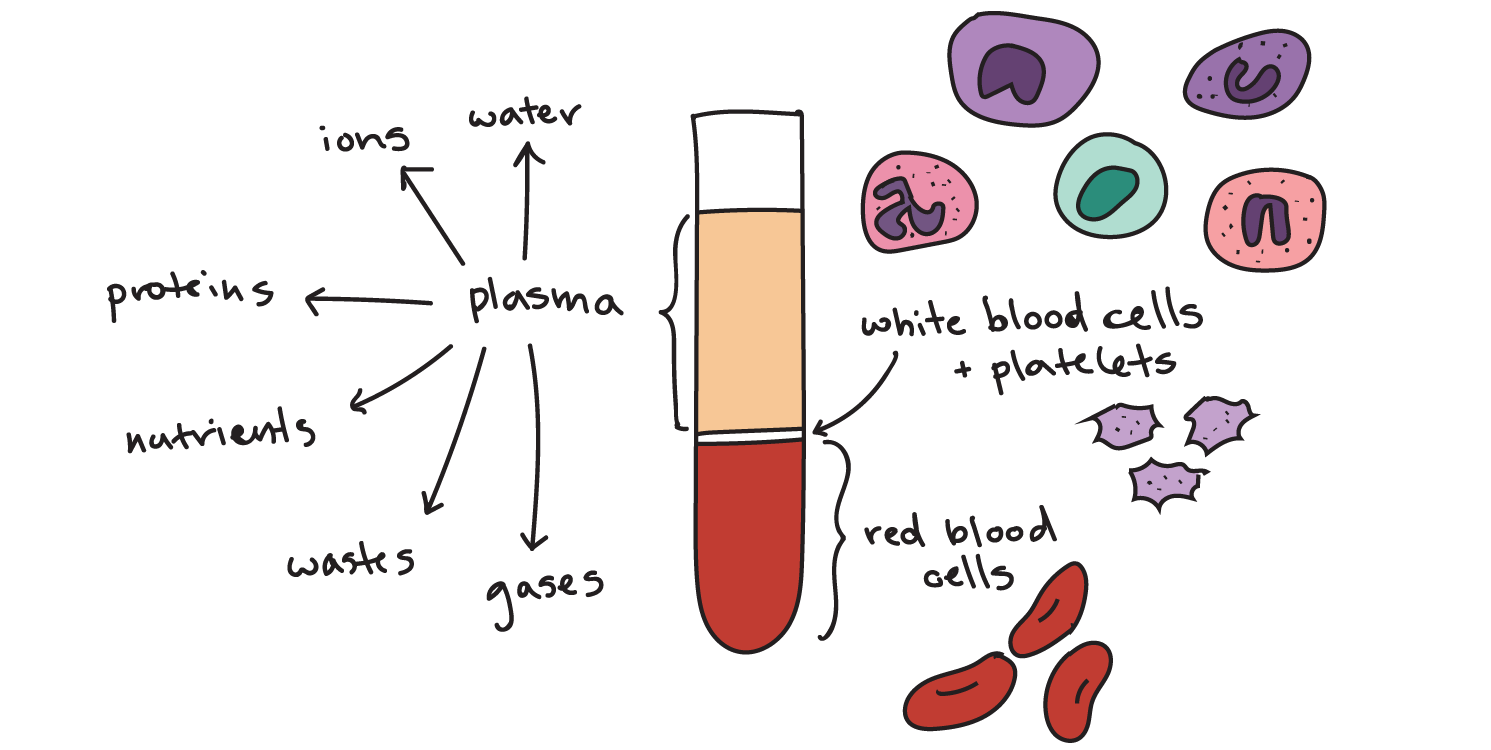
Blood and its composition
Module Unit CN-111: Anatomy and Physiology (I) Contact Hours: 60 Module Unit Description: Introduces students to the anatomy and physiology of the human body, covering the structure and function of different body parts and systems, specifically skeletal, muscular, circulatory, and digestive systems. Learning Outcomes for this Unit: By the end of this unit, the student…
-

Hodgkin’s Disease
Hodgkin’s Disease and Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Hodgkin’s Disease and Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma To understand Hodgkin’s disease and Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, we must first define what lymphomas are as a group of diseases. Lymphomas are a diverse group of cancers that originate in the lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell crucial for the immune system. These malignant lymphocytes…
-

DISEASE OF LYMPH VESSELS
Lymphedema Lecture Notes Lymphedema (pronounced lim-fa-DEE-ma) is a chronic, progressive, and often debilitating condition characterized by localized tissue swelling and fluid retention, which occurs when the lymphatic system is impaired or damaged. Breakdown of the key elements of this definition: Chronic and Progressive: Chronic: It is a long-term condition that typically does not resolve on…
-
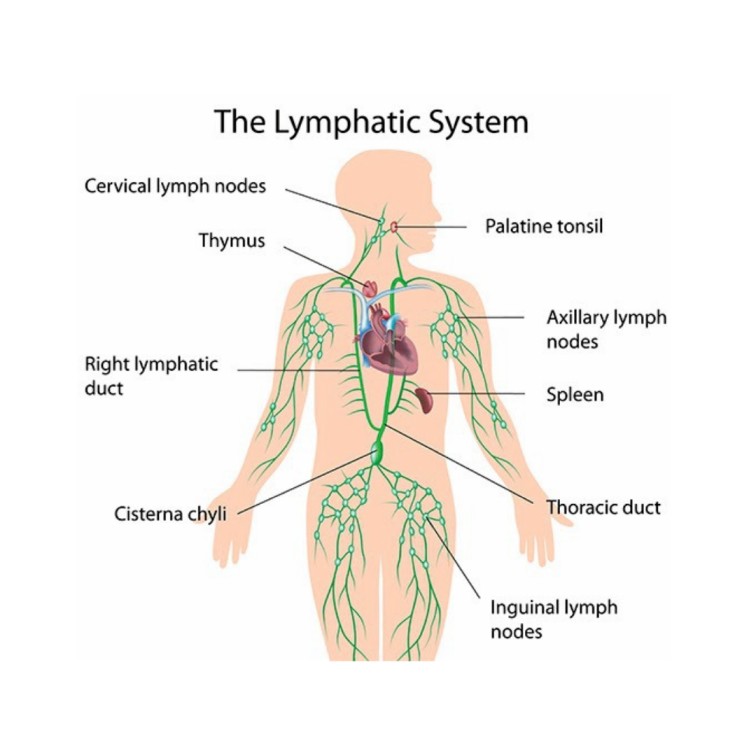
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lymphatic System
Anatomy and Physiology of Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is part of the circulatory system which begins with very small close ended vessels called lymphatic capillaries which is in contact with the surrounding tissues and interstitial fluid. The lymphatic system is almost a parallel system to the blood circulatory system. It consists of: Lymph Lymph…
-

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
BPH BPH-Benign prostatic hyperplasia is the enlargement, or hypertrophy, of the prostate gland. BPH is common in elderly men over 60 years and above Common causes of BPH and Pathophysiology The outcome of BPH depends on two major factors i.e. Anatomical factors: These involve enlargement of the Prostate gland which produces a physical blockage at…
-
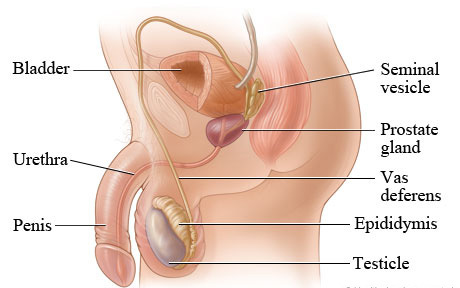
Erectile Dysfunction Medications
Erectile Dysfunction Erectile dysfunction, ED is the inability of the male to attain and maintain an erection sufficient to permit satisfactory sexual intercourse. Penile erectile dysfunction is a condition in which the corpus cavernosum does not fill with blood to allow for penile erection. This can result from the aging process and in vascular and…
