-
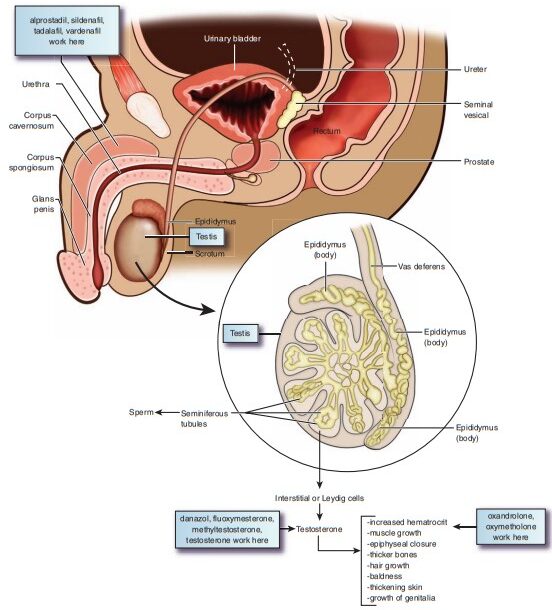
Androgens
Androgens Androgens are male sex hormones Androgens include Testosterone, which is produced in the testes, and the Androgens, which are produced in the Adrenal glands. Androgens are chiefly produced in the testes and small amounts in adrenal cortex. In female, small amounts are produced in the ovary and adrenal cortex. Testosterone is the most…
-

Uterine Relaxants
Uterine Relaxants Uterine Relaxants are drugs which inhibit uterine motility by decreasing the frequency and strength of contractions. Uterine Relaxants are drugs that inhibit uterine contractions and prolong pregnancy to allow the fetus develop more fully, thereby increasing the chances of neonatal survival. These drugs prevent premature labor. It can succeed if only the cervical…
-

Drugs used in Labor
Drugs used in Labour Drugs used in labour can be grouped according to the effect they have on the uterus. Uterine Stimulants/Uterine Mortility drugs. (Oxytocics) Uterine relaxants (Tocolytics) Uterine Stimulants/Uterine Motility Drugs(Oxytocics) Uterine motility drugs stimulate uterine contractions to assist labor (oxytocics) or induce abortion (abortifacients). Oxytocics Oxytocics stimulate contraction of the uterus, much like…
-
Fertility Drugs/Gonadotropin Drugs
Fertility Drugs Fertility drugs are drugs that stimulate the female reproductive system. Examples of Fertility drugs; Cetrorelix (Cetrotide) Chorionic gonadotropin (Chorex, Profasi, Pregnyl). Chorionic gonadotropin alpha (Ovidrel). Clomiphene (Clomid) Menotropins(Pergonal, Humegon). Therapeutic Actions and Indications. Women without primary ovarian failure who cannot get pregnant after 1 year of trying may be candidates for the use…
-
Estrogen Receptor Modulators
Estrogen Receptor Modulators Estrogen Receptor Modulators are agents that either stimulate or block specific estrogen receptor sites. They are used to stimulate specific estrogen receptors to achieve therapeutic effects of increased bone mass without stimulating the endometrium and causing other less desirable effects i.e. these drugs stimulate the estrogen receptors in the body so as to…
-

Gonadotropin drugs
GONADOTROPINS Gonadotropins are fertility medications given by injection that contain follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) alone or combined with luteinizing hormone (LH). Gonadotropins are hormones that stimulate the gonads, which are the sex organs in the body. Gonadotropins are produced by the pituitary gland, which is a small gland located at the base of the brain. The release of…
-

Pneumonia in Children
Pediatric Pneumonia Lecture Notes Pediatric Pneumonia Pneumonia remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in children worldwide, especially in developing countries. Its epidemiology and etiology differ significantly from adults, largely due to variations in immune system maturity, exposure patterns, and anatomical differences. Pneumonia is an acute inflammatory condition of the lung parenchyma caused by…
-

Asthma in Children
Paediatric Asthma Lecture Notes Paediatric Asthma Asthma is a chronic reversible inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by an obstruction of airflow. Asthma can be defined as: A chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Characterized by airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), leading to recurrent episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness, and coughing. These episodes are associated with…
-

Pericarditis
Pericarditis Lecture Notes PERICARDITIS Introduction Pericarditis is the inflammation of the pericardium, a double-layered sac that encloses the heart and the roots of the great vessels (aorta, pulmonary artery, vena cavae). This sac provides protection, lubrication, and helps to anchor the heart within the chest cavity. When inflamed, the layers of the pericardium can rub…
-

Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease To understand Rheumatic Heart Disease (RHD), we must first understand its precursor: Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF). These two conditions are intimately linked in a cause-and-effect relationship. Acute Rheumatic Fever (ARF) Acute Rheumatic Fever is a post-streptococcal, systemic inflammatory disease that can affect the…
