-
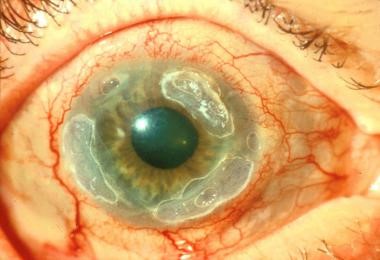
Corneal Ulcers
CORNEAL ULCERS Corneal ulcers are open sores or epithelial defects with underlying inflammation on the cornea, the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris and pupil. These ulcers are often visible as grey to white opaque or translucent areas on the normally clear cornea. In some cases, they may be too small…
-
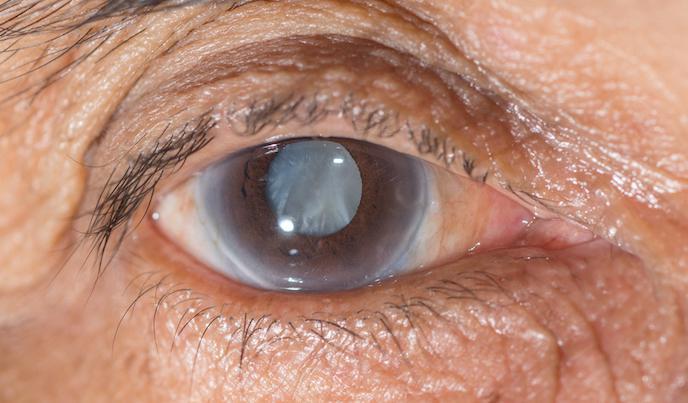
Glaucoma
GLAUCOMA Glaucoma is a group of disorder characterized by an abnormally high intraocular pressure , optic nerve dystrophy, and peripheral filed loss. (BRUNNER) Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases which result in damage to the optic nerve and vision loss due to IOP. It’s among the common causes of blindness. Glaucoma occurs as a…
-
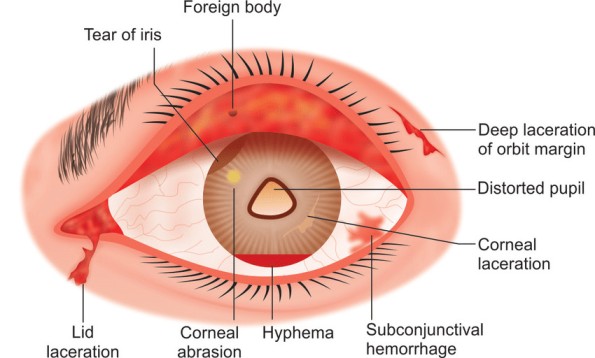
Eye Trauma
Eye Trauma (Ocular Trauma) Eye trauma is an injury to the eye that may result in visual impairment. Ocular trauma refers to any injury to the eye or its surrounding structures caused by physical, chemical, thermal, or radiation agents. It can range from minor irritations to severe injuries affecting vision or structural integrity. Commonly injured…
-

Foreign body in the Eye
FOREIGN BODY IN THE EYE Foreign object in the eye is something that enters the eye from outside the body. A foreign body in the eye refers to any external object or substance that enters and remains within the ocular structures, causing discomfort, irritation, or injury. It can be anything that does not naturally belong…
-

Stye (Hordeolum).
Stye Lecture Notes for Nurses Stye or Hordeolum A stye is a painful, red lump that forms on the edge of the eyelid. It is an acute infection of a small gland in the eyelid, most commonly caused by the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. The medical term is Hordeolum. A stye is a localized infection of…
-
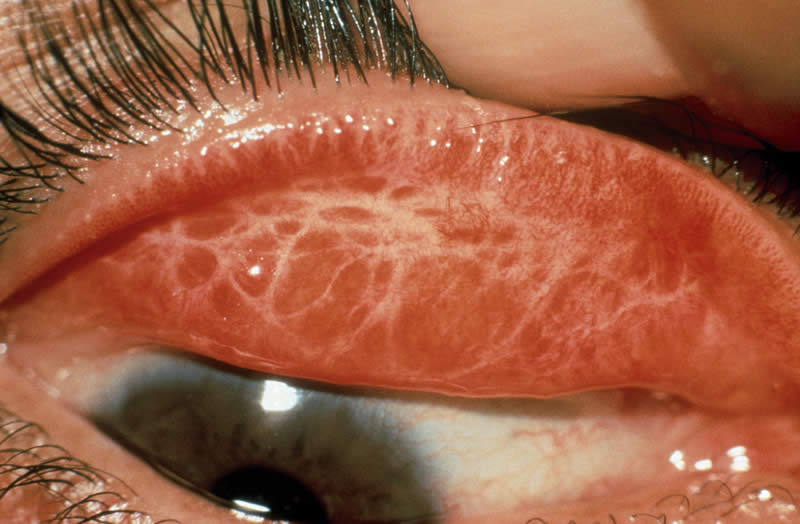
Trachoma
Trachoma Lecture Notes Trachoma Lecture Notes Trachoma is a contagious infection of the conjunctiva and cornea characterized by formation of granulation and scarring. – Is a Greek word meaning “Roughness” Trachoma is a chronic, infectious keratoconjunctivitis caused by repeated infection with specific serovars of Chlamydia trachomatis. It is the leading infectious cause of blindness worldwide.…
-

Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy
Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Lecture Notes Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) refers to a type of brain injury that occurs when the brain is deprived of adequate oxygen (hypoxia) and blood flow (ischemia) for a period of time. This deprivation leads to damage or destruction of brain cells. Hypoxia: A condition in which the body…
-

Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis Lecture Notes Conjunctivitis is medically defined as the inflammation of the conjunctiva. It is commonly known as “pink eye” or “red eye” due to the characteristic redness that often accompanies the condition. Inflammation: This refers to the body’s protective response to injury or irritation, involving increased blood flow, swelling, and often pain and redness.…
-

Eye Anatomy and Physiology
Eye Anatomy. Eye is the organ for sight. The globe-shaped eyeball occupies the anterior part of the orbit/eye socket. The eyeball is embedded in the orbital cavity. The eye contains the receptors for vision and a refracting system that focuses light rays on the receptors in the retina. Diagram Showing the structure of the Eye.…
-

Intracranial Hemorrhage
INTRACRANIAL HEMORRHAGE An intracranial hemorrhage is a type of bleeding that occurs inside the skull (cranium). Bleeding around or within the brain itself is known as a cerebral hemorrhage (or intracerebral hemorrhage). Bleeding caused by a blood vessel in the brain that has leaked or ruptured is called a hemorrhagic stroke. All bleeding within the…
