-

Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle Cell Disease/Sickle Cell Anaemia Sickle cell disease is an inherited red-blood cell disorder which causes the body to produce abnormally shaped red blood cells. Sickle cell disease is inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. Normal Hb A gets replaced with Abnormal Hb S. Children with this disorder have atypical haemoglobin molecules called haemoglobin S…
-

Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents
EATING DISORDERS Eating disorders are conditions characterized by an extreme disturbance in eating related behaviour. OR Eating disorders are moderate to severe illnesses that are characterized by disturbances in thinking and behaviour around food, eating and body weight or shape. The DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, American Psychiatric Association,2013) outlines six types…
-

Disaster Preparedness and Management
DISASTER Disaster is an occurrence disrupting the normal conditions of existence and causing a level of suffering that exceeds the capacity of adjustment of the affected community, WHO Disaster is also defined as a sudden/unexpected catastrophic event causing serious disruption of the functioning of a community or society that exceed the ability of the affected…
-

Introduction To Palliative Care
Palliative Care Palliative care is an approach that improves the quality of life of patients and families facing the problem associated with life threating illness through the prevention and relief of suffering by means of early identification and assessment and treatment of pain and other problems which are physical , psychological and spiritual. WHO definition…
-
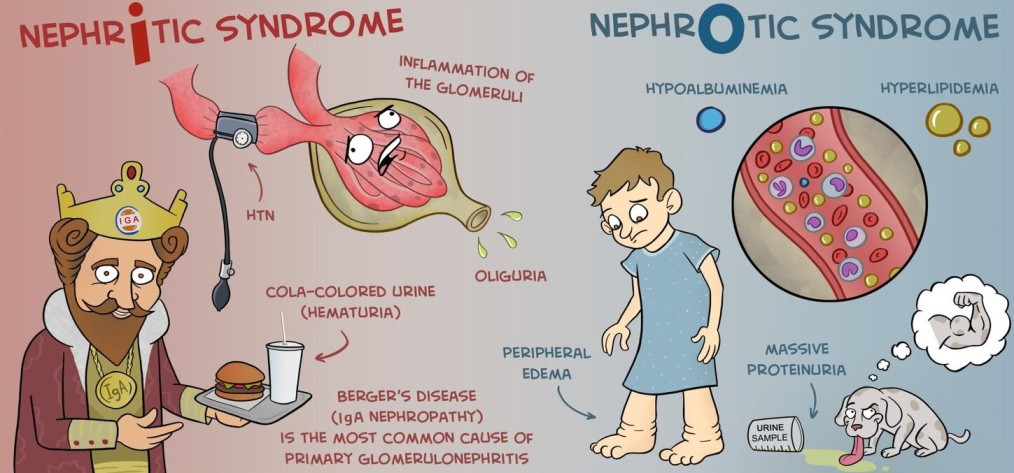
Nephrotic and Nephritic syndromes
NEPHROTIC SYNDROME. Nephrotic syndrome, or nephrosis, is a constellation of symptoms characterized by nephrotic range, massive proteinuria, edema, and hypoalbuminemia with or without hyperlipidemia. MASSIVE Proteinuria >3.5g/24 hours Or spot urine protein: creatinine ratio >300 – 350 mg/mmol Hypoalbuminemia <25g/L, Edema,(Generalized edema is called Anasarca) And often: Hyperlipidemia/dyslipidemia (total cholesterol >10 mmol/L) Additionally, the…
-
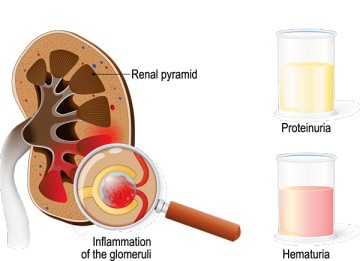
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis (GN) Glomerulonephritis (GN) refers to a group of kidney diseases characterized primarily by inflammation and damage to the glomeruli, the tiny filtering units within the kidneys. Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory condition of the kidneys characterized by increased permeability of the glomerular filtration barrier causing filtration of RBCs and proteins. While the primary site of…
-
Renal Failure
RENAL FAILURE (Acute and Chronic) Renal failure refers to reduction in renal/kidney function. Renal failure, also known as kidney failure, describes a situation where the kidneys lose their ability to function adequately. This means they cannot effectively filter waste products from the blood, regulate electrolytes and fluids, or perform their essential endocrine functions. The term…
-

Kidney Stones / Renal Calculi
Kidney Stones/Renal Calculi Lecture Notes Kidney Stones, also known as renal calculi, renal lithiasis, or nephrolithiasis, are small, hard deposits formed from mineral and acid salts that crystallize within the urinary tract. These deposits can form on the inner surfaces of the kidneys, but can also occur in the ureters or bladder. They can be…
-

Cystitis
Cystitis Lecture Notes Cystitis literally means “inflammation of the bladder.” In clinical practice, it almost invariably refers to inflammation of the bladder lining, most commonly caused by a bacterial infection of the lower urinary tract. This makes it a subset of what is broadly termed a “Urinary Tract Infection” (UTI). Key Characteristics: Infection: Predominantly bacterial,…
-

Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are bacterial infections that can occur in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. The most common cause of UTIs is the colonization of bacteria from the gastrointestinal tract, with Escherichia coli (E. coli) being the most frequently implicated pathogen. Other…
