Table of Contents
ToggleUrethral Discharge Syndrome
Urethral discharge syndrome is a prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) among men, marked by purulent urethral discharge, with or without dysuria.
The amount of discharge varies depending on the causative pathogens as well as prior antibiotic treatment.
Clinical Presentation:
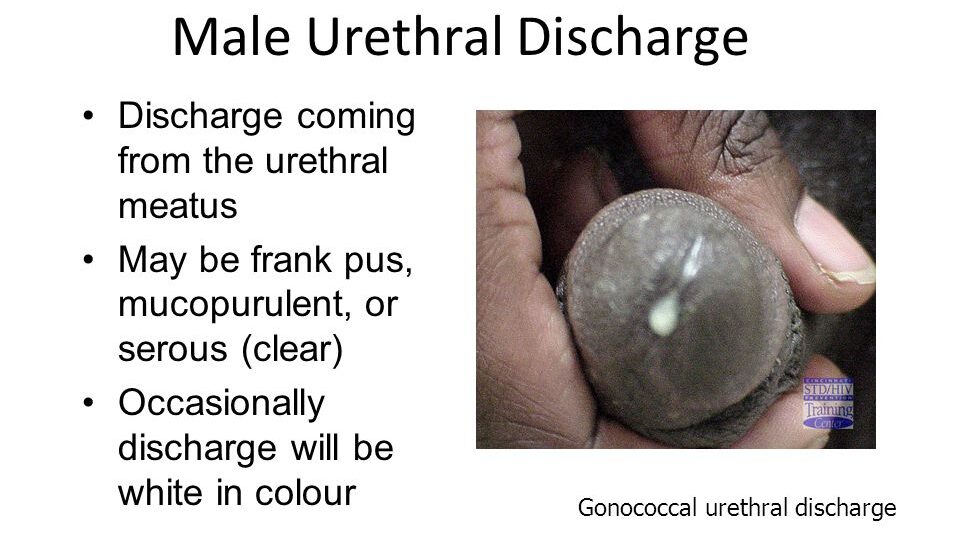
- Chief Complaint: Patients with this syndrome often complain of a discharge from the urethra. Mucus or pus at the tip of the penis; staining underwear
- Symptoms: They may have symptoms of burning sensation while passing urine and frequency of micturition.
Physical Examination:
- Visual Inspection: Examination might reveal a purulent discharge from the urethra. If the discharge is not readily seen, it may be necessary to milk the penis and massage it forwards before the discharge becomes visible. If the discharge is copious, do not milk or squeeze the penis.
- Prepuce Examination: If the patient is not circumcised, you should examine with the foreskin retracted so that you ascertain whether the discharge is from the urethra or from beneath the prepuce.
- Discharge Characteristics: The discharge may range from frank pus to mucopurulent.
Case Definition: Urethral discharge in men with or without dysuria.
Causes (Common and Uncommon):
- Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia Trachomatis: This syndrome is commonly caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis in over 98% of cases.
- Other Infectious Agents: Trichomonas vaginalis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, and Mycoplasma spp.
- Mixed Infections: Mixed infections especially of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis occur
Management:
All male patients with urethral discharge should be managed according to the syndromic chart.
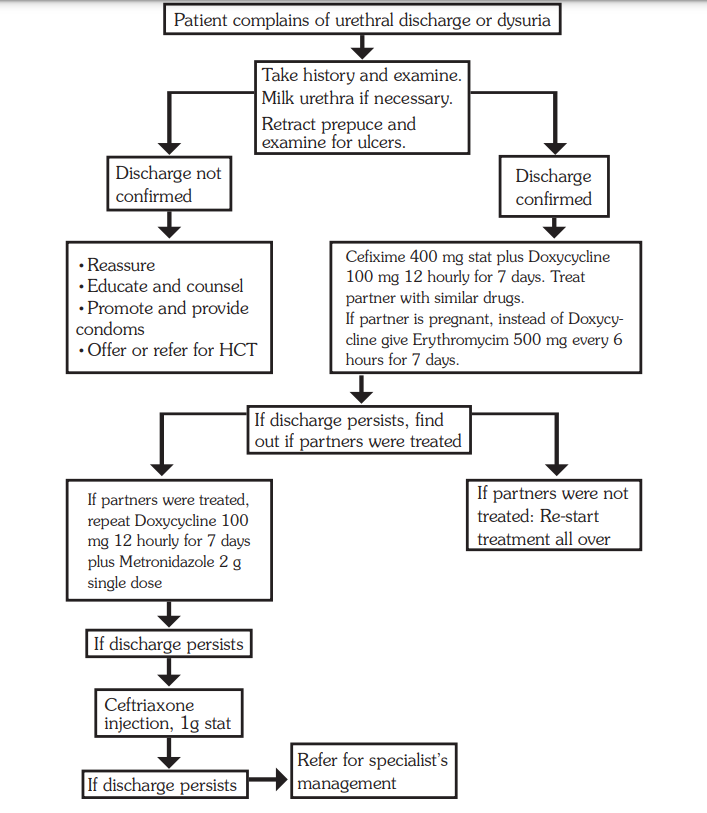
Medicines
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM or Cefixime 400 mg single dose plus Doxycycline 100 mg every 12 hours for 7 days
If partner is pregnant
- Substitute doxycycline with erythromycin 500 mg every 6 hours for 7 days or Azithromycin 1 g stat if available
Treatment Procedure:
Clinical Assessment:
- Obtain a comprehensive medical history and conduct a thorough examination of the client.
- If urethral discharge is not evident, perform urethral milking.
- Retract the prepuce (if applicable) and examine for ulcers.
Comprehensive Treatment:
- Treat both the patient and their sexual partners simultaneously.
- Provide counselling on abstinence or emphasize condom use to prevent further transmission.
Medication:
- Administer Ceftriaxone 250 mg intramuscularly (IM) or Cefixime 400 mg as a single dose.
- Prescribe Doxycycline 100 mg every 12 hours for a duration of 7 days.
For Pregnant Partners:
- If the partner is pregnant, substitute Doxycycline with Erythromycin 500 mg every 6 hours for 7 days.
- Alternatively, administer Azithromycin 1 g as a single stat dose if available.
Persistent Symptoms Despite Partner Treatment:
- Investigate for the presence of ulcers under the prepuce.
- If discharge or dysuria persists, repeat Doxycycline 100 mg every 12 hours for 7 days.
- Administer Metronidazole 2 g as a single dose.
If Partners Were Not Treated Initially:
- Restart the initial treatment regimen and ensure partners are treated simultaneously.
Comprehensive STD Case Management Package:
- Education: Emphasis on treatment compliance.
- Condom Promotion: Provision and demonstration of correct usage.
- Partner Notification: Treatment for partners, whether symptomatic or not.
- HIV VCT Services: Offer or refer when necessary.
Continued Persistence of Discharge:
- Administer Ceftriaxone 1 g IM.
- If symptoms persist, consider referral for specialist management.
Counsel and educate all clients on:
- Treatment compliance.
- Condom use and provide condoms.
- Partner management.
- Offer or refer for HIV VCT services if necessary.
- Schedule a return visit.
- Abstinence from sex till all symptoms have resolved.

What is the price range of the medicine in Kampala and pharmacies where they could be gotten.