-
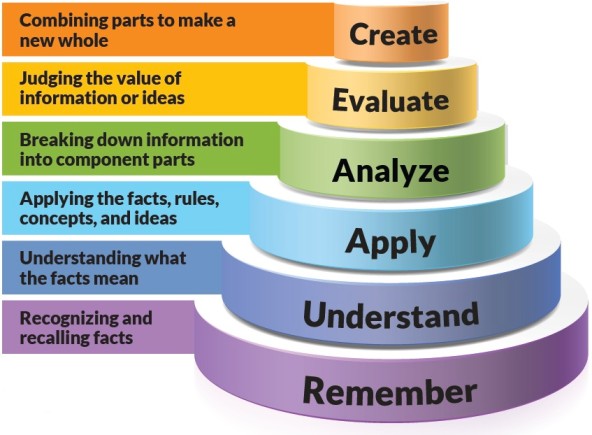
TEACHING-LEARNING (EDUCATIONAL) OBJECTIVES
TEACHING-LEARNING (EDUCATIONAL) OBJECTIVES Teaching-learning(Educational) objectives are statements describing desired changes in behavior as a result of specific teaching-learning activity. Behavior is what the student should know or be able to do after teaching-learning activity, i.e. Therefore in education: the objective describes students’ performance, not teacher performance. Or Educational objectives refer to what the student should…
-

ANDRAGOGY
ANDRAGOGY. Andragogy, often referred to as adult education, encompasses both the art and science of facilitating adult learning. Andragogy is the art and science of helping adults learn.It also refers to a method and practice of teaching adult learners. Reasons Behind Adult Learning Adults engage in learning for a variety of reasons, driven by their unique…
-

INTEGRATED DISEASE SURVEILLANCE
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo. INTEGRATED DISEASE SURVEILLANCE AND RESPONSE-IDSR IDSR – Is a strategy for a multi-disease surveillance of selected priority diseases or conditions which links the community, health facility, district and national levels allowing the rational use of resources for…
-
SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAM
SCHOOL HEALTH PROGRAM School Health Program is a strategic endeavor designed to elevate the quality of life for students while fostering a culture of proactive health awareness. Its fundamental purpose is to instill a sense of responsibility towards one’s well-being among students, their families, and school staff. The School Health Program is like a special…
-

CONSTRUCTIVISM
CONSTRUCTIVISM Constructivism is a type of learning theory that explains human learning as an active attempt to construct meaning in the world around us Constructivism divides learning into two types: Accommodation. Assimilation. The focus is on the individual’s desire and ability to learn, and the teacher is merely there to help guide self directed learning. …
-

Behaviorism
Behaviorism Behaviorism , also known as behavioral psychology, is a theory of learning based upon the idea that all behavior’s are acquired through conditioning. Conditioning occurs through interaction with the environment. According to behaviourism, behaviour can be studied in a systematic and observable manner with no consideration of internal mental states. There are two major…
-

METHODOLOGY
CHAPTER THREE: METHODOLOGY Methodology is the longest and most examinable, take note. 3.1 Introduction 3.2 Study Design and rationale 3.3 Study setting and rationale 3.4 Study Population 3.4.1 Sample Size Determination 3.4.2 Sampling Procedure 3.4.3 Inclusion Criteria 3.5 Definition of Variables 3.6 Research Instruments 3.7 Data collection Procedure 3.7.1 Data management 3.7.2 Data analysis 3.8 Ethical Consideration 3.9 Limitations of…
-

LITERATURE REVIEW
CHAPTER TWO: LITERATURE REVIEW Literature review refers to the collection of scholarly information about any research problem/topic It is a systematic gathering of information, analysing and reviewing documents from written or done by other scholars that have a relation to your problem being investigated It is a requirement for ay researcher to do a preliminary…
-
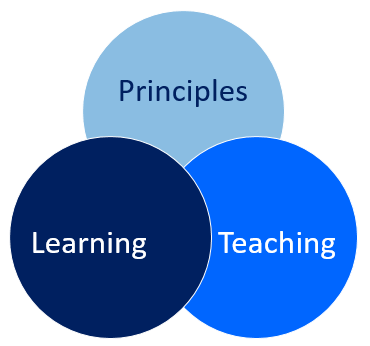
PRINCIPLES OF TEACHING AND LEARNING
PRINCIPLES OF TEACHING AND LEARNING The principles of teaching and learning will assist the teacher to achieve purpose of teaching. It guides the teacher on the elements pertaining teaching such as whom to teach, why teach, where to teach, what to teach, how to teach and when to teach. Principle of motivation: The best teacher…
-

PHILOSOPHIES OF EDUCATION
PHILOSOPHIES OF EDUCATION Philosophy refers to search for wisdom and truth or the study of the principles of human behavior and reasoning Education is the process of facilitating learning, or the acquisition of knowledge, skills, values, beliefs, and habits.There are various ways how learners can use to search for the truth of what has been taught.These philosophies…
