-

Infertility
INFERTILITY Infertility is the inability of a couple to conceive or to get a child after one year of regular coitus without having used any form of contraception. Infertility refers to failure to conceive in spite of regular unprotected sex during the child bearing age that is 15-49 years without any contraception for at…
-
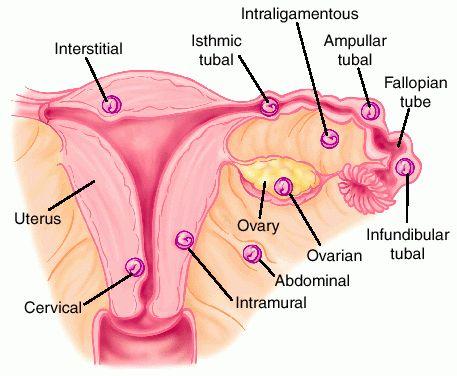
Ectopic Pregnancy
ECTOPIC PREGNANCY Ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterus. Instead of the fertilized egg traveling to and implanting in the uterus as it should during a normal pregnancy, it implants in a location where it cannot develop properly. Ectopic pregnancy is when the fertilized ovum embeds…
-

Under water seal drainage
UNDER WATER SEAL DRAINAGE Under water seal drainage is a system that allows drainage of the pleural space using an airtight system to maintain sub-atmospheric intrapleural pressure. It’s used when air or fluid gets trapped in the pleural space. Pleural Space: This is the space between the two layers of pleura, which are thin membranes…
-

MENSTRUAL DISORDERS
Menstrual Disorders Menstrual disorders are abnormalities in menstruation during reproductive life. Common disorders associated with menstruation are as follows; Amenorrhoea Dysmenorrhoea Menorrhagia Metrorrhagia Polymenorrhoea (epimenorrhoea) Dysfunctional uterine bleeding Endometriosis AMENORRHOEA Amenorrhoea refers to absence of menstruation which occurs in female during their reproductive age. Types of Amenorrhoea Primary amenorrhoea. This is the failure of menses…
-

Introduction To Gynaecology
INTRODUCTION TO GYNAECOLOGY Gynaecology is a branch of medicine which deals with diseases of the female reproductive systems. OVERVIEW OF ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The female reproductive system is composed of the external genitalia, internal genitalia and the mammary glands. EXTERNAL GENITALIA The female external genitalia, also known as the…
-

Nursing Management Question Approach
Nursing Care Management: Answering Questions with Confidence As nurses prepare for nursing exams, it is important to develop effective strategies for answering questions related to nursing care management. Nursing exams often include questions that require nurses to demonstrate their knowledge of nursing considerations, Nursing concerns, Nursing issues, and Nursing interventions. In this post, we…
-

Nursing Exam Question Approach
Click Here for Question Approach for Nursing Concerns, Interventions, Considerations, e.t.c Nursing Exam Question Approach. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore and provide examples of the Question Approach for nurses preparing for their nursing exams. We will cover question types such as EXPLAIN, OUTLINE, DESCRIBE, MENTION, IDENTIFY, STATE, LIST, WHAT, and GIVE. Also, we…
-
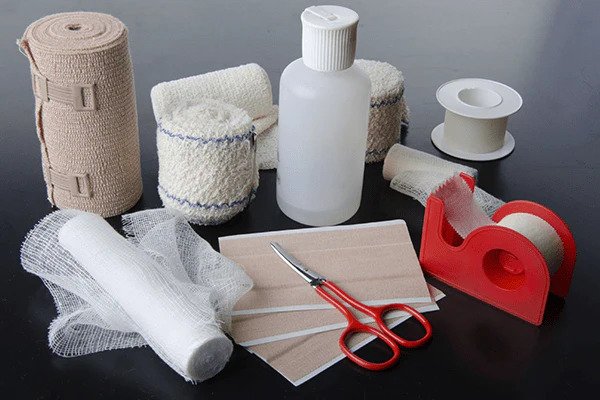

Dressings
DRESSINGS Addressing is any protective cover for the wound. It is usually a cotton material. Uses of dressings It helps to control bleeding. To prevent infections. To absorb any discharge. Prevents further injury to the wound. Points to note: All dressings should be at least 2.5cm (inch) bigger than the wound. Dressings should, if possible…
-

Injuries And Trauma
Injuries and Trauma FRACTURE A fracture is a break in the continuity of a bone. Any injury involving a bone should be considered a fracture until proved otherwise. CAUSES OF FRACTURE A fracture can be caused by direct force. This is when the injury occurs at the site where the forces have been applied e.g.…
-

First Aid Medical Emergencies
First Aid Medical Emergencies. First aid is a crucial skill that everyone should possess, as it enables individuals to provide immediate care and assistance to someone who has been injured or is experiencing a medical emergency. There are various medical emergencies that require prompt first aid intervention. Some of the most common ones include: DROWNING…
