-

SKIN ALLERGIES
SKIN ALLERGIES Skin allergy, also known as allergic dermatitis, is a condition in which the immune system has an abnormal reaction to a harmless substance, known as an allergen, that comes into contact with the skin. Skin allergy is an abnormal reaction of the skin following an irritant that continues as long as there is…
-

ECZEMA
ECZEMA Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, or atopic eczema, is a dermatologic problem where patches of skin become inflamed, itchy, red, cracked, and rough. Blisters may sometimes occur. It is commonly seen in children. It is a relapsing skin problem that is manifested as pruritus, accompanied with swelling, redness, and dryness of the skin.…
-
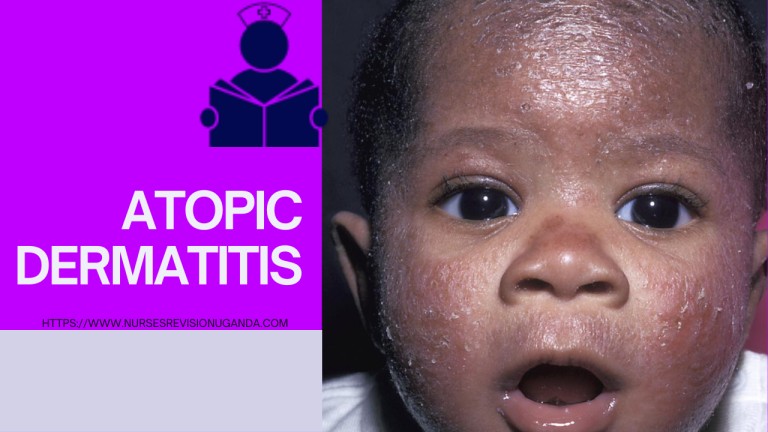
ATOPIC DERMATITIS
ATOPIC DERMATITIS. Atopic dermatitis (AD) also known as atopic eczema is a common type of eczema that causes the skin to become itchy, dry, and cracked. It results in itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which often thicken over time. Other names include “infantile eczema”, “flexural eczema”,…
-

Inguinal Buboes Syndrome
Inguinal Buboes Syndrome Inguinal buboes refer to localized swellings or enlarged lymph glands in the groin and femoral area. They are often locally described as “grenades.” Case Definition: Inguinal Buboes Syndrome is characterized by the clinical manifestation of localized swellings or enlarged lymph glands in the groin and femoral area. Aetiology It is crucial to…
-
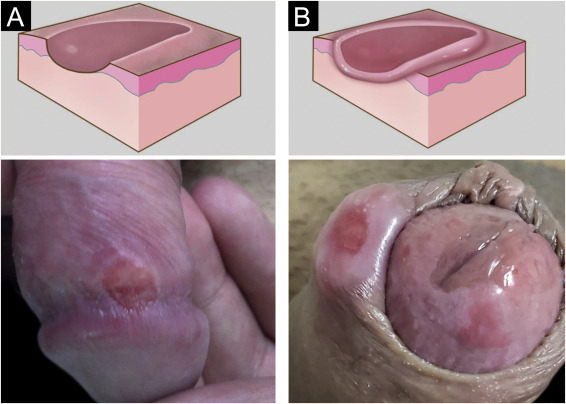
Genital Ulcer Syndrome
Genital Ulcer Syndrome Genital ulcer disease is a common syndrome affecting both men and women, characterized by single or multiple ulcers with different clinical manifestations. Genital ulcer disease refers to breaks in the skin or mucosa and may present as ulcers, sores or vesicles. Case Definition: Non-vesicular Genital Ulcer: Ulcer on the penis, scrotum,…
-
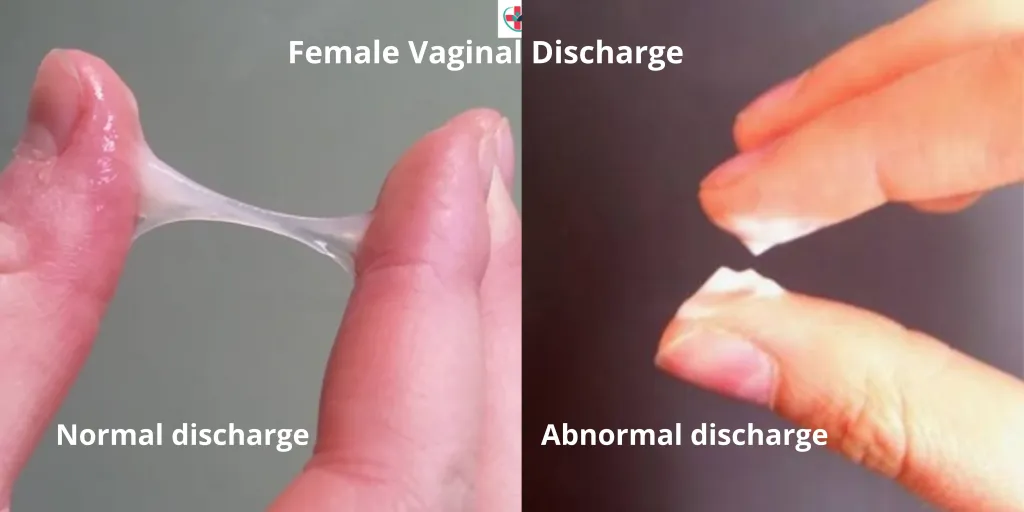
Abnormal Vaginal Discharge Syndrome
Abnormal Vaginal Discharge Syndrome Abnormal vaginal discharge is defined as discharge that is different from usual with respect to colour/odour/consistency (e.g. discoloured or purulent or malodorous). While all women experience physiological vaginal discharge, concerns arise when it is perceived as abnormal. This syndrome is primarily attributed to endogenous vaginal infections, such as bacterial vaginosis and…
-
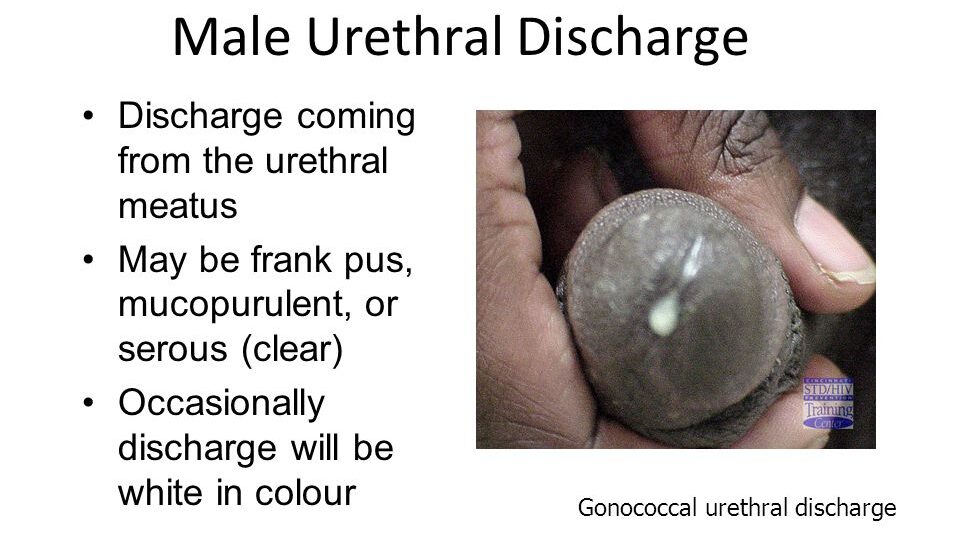
Urethral Discharge Syndrome
Urethral Discharge Syndrome Urethral discharge syndrome is a prevalent sexually transmitted infection (STI) among men, marked by purulent urethral discharge, with or without dysuria. The amount of discharge varies depending on the causative pathogens as well as prior antibiotic treatment. Clinical Presentation: Chief Complaint: Patients with this syndrome often complain of a discharge from…
-
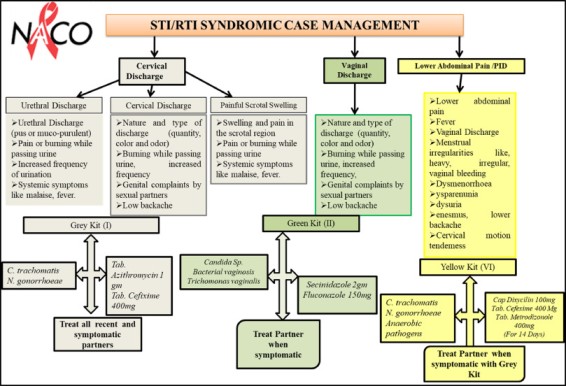
Syndromic management of STI
Syndromic Approach Syndromic approach to STI management is a method of diagnosing and treating sexually transmitted infections (STIs) based on the patient’s clinical signs and symptoms, rather than laboratory confirmation. Instead of targeting a specific pathogen, healthcare providers address the symptoms and syndromes associated with various STIs. It is very useful in settings where…
-
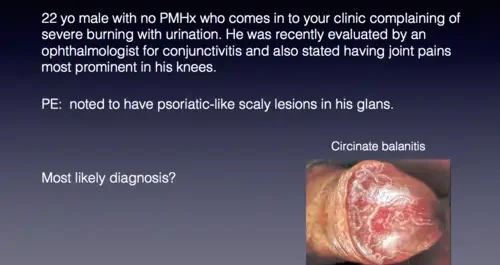
CHANCROID, BALANITIS & SYPHILIS
Chancroid(Soft Chancre) Chancroid is a sexually transmitted infection that causes painful open sores, or chancroids, to develop in the genital area. It can also often cause the lymph nodes in the groin to swell and become painful. Incubation period: 2-5 days. Cause Chancroid is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacteria Haemophilus ducreyi.…
